
Hello! I wanted to talk to my good friend yesterday. Long time no see and did not communicate with her.
I called her on the phone. I was immediately alerted by her weakened voice. It turned out that she was bitten by a tick, and there are suspicions of infection with encephalitis.
They were just waiting for the ambulance to inspect. She wished her a speedy recovery, for jokes are bad with ticks. Do you want to know what symptoms a person gets from a tick bite? Now I will tell you in detail about them so that you are informed.
The content of the article:
Encephalitis tick - signs, diagnosis, treatment, consequences and prevention of the virus
When spring is in the yard, urban residents seek nature, summer residents cultivate beds, tourists rush to open the hiking season, parents take a walk with their children, and some just relax in nature and eat barbecue.
In all this fuss, we forget about the dangers lurking in the grass and on the trees. After all, spring and summer is the peak of tick activity, and they can lie in wait not only in nature, but also in the playground.
Tick-borne encephalitis is a dangerous viral disease that can have serious consequences - from persistent neurological or mental disorders to the death of the patient. The carriers of the virus are ixodid ticks and rodents.
Infection pathways
There are two ways of infection with the virus:
- Transmissible. Through the bite of an infected tick-transmitting disease. This is the most common method of infection when non-compliance with safety rules in nature.
- Alimentary. In this case, infection occurs through the use of fresh milk of goats, sheep and cows. Rare cases of the defeat of entire families with this method of infection are noted. Knowing that the virus is not resistant to high temperatures, simply boiling milk will help to avoid this method of infection.
Infection can occur even if the tick just digged in and was immediately removed.
Forms of Encephalitis:
- Febrile;
- Meningeal
- Meningoencephalitic;
- Polio;
- Polyradiculoneuritis.
The course of each form has its own specific symptoms. Despite the fact that not every tick can be a carrier of the disease, when sucking an insect, you urgently need to contact a medical institution for help, because the insect can also carry other dangerous diseases.
Encephalitis Tick Habitats
The spread of the disease is of a natural focal nature. Tick-borne encephalitis in Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Kazakhstan is most often found in the middle lane, where the conditions for life and reproduction are the best.Dense wooded thickets, marshland, taiga are ideal places for parasites to hunt for people and animals.
Transcarpathian region of Ukraine, almost the entire territory of Belarus - areas of encephalitis ticks, where the risk of infection is most likely. Annually, a letter (.pdf) is published on the Rospotrebnadzor website on areas endemic for tick-borne encephalitis last year.
Living in high-risk areas is not always an alarm. Often the cause of the spread of tick-borne encephalitis is non-compliance with safety precautions when camping. Many people blithely behave in the focus of tick activity, without resorting to basic methods of protection.
Signs and symptoms of the disease
Signs and symptoms of the development of the disease vary depending on the degree of the body's defenses, the amount of virus (depends on the number of sucking ticks and the amount of virus injected into the blood). People and animals have different types of manifestations of infection.
When bitten by an infected insect, the virus begins to multiply in the wound and does not cause any obvious discomfort. The first signs of encephalitis after a tick bite appear only after 7-10 days, but in a weakened body the symptoms appear already on 2-4 days.
All forms of the disease begin acutely with flu-like symptoms:
- fever and fever up to 39-39.8 degrees;
- malaise, body aches;
- weakness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- headache.
In this case, the fever coincides with the active reproduction of the virus in the blood and can last from 5 to 10 days. If the development of the disease stops at this, then this is a mild febrile form of the course of the disease.
A person is easily restored and receives a stable immunity to the virus. In rare cases, the febrile form becomes chronic.
If the disease proceeds to the next stage, then after a fever a 7-10-day remission occurs, it seems to a person that the disease has receded. But after resting, the fever repeats, the virus penetrates the blood-brain barrier, the nervous system is affected, and encephalitis passes into the meningeal form.
With this lesion, internal organs suffer, where at this moment the virus is actively multiplying. After a tick bite, the symptoms of encephalitis of the meningial form are manifested as follows:
- fever;
- severe headaches;
- photophobia;
- stiff neck (the patient cannot tilt his head to the chest due to tension and stiffness of the neck muscles).
Meningoencephalitic and poliomyelitis forms of encephalitis are a type of focal infection, in this case brain tissue is affected and often the consequences of the disease are irreversible, and often fatal.
The following symptoms are distinguished depending on the location of the affected tissue:
- When the meningoencephalitic form is characterized by hallucinations, mental disorders, impaired consciousness, paralysis and paresis, epilepsy attacks.
- With the polio form, the symptoms are similar to poliomyelitis - persistent paralysis of the muscles of the hands, neck, leading to disability.
- With a polyradiculoneurotic form, peripheral nerves are affected, pain, limp limb, goosebumps, impaired sensation and the development of flaccid paralysis starting from the lower extremities, severe pain in the groin and front of the thighs are noted.
Diagnostic Methods
A comprehensive approach is needed to diagnose tick-borne encephalitis, because the symptoms are often similar to symptoms of other diseases, such as central nervous system tumors, flu, typhus, Lyme disease, and other types of encephalitis. Therefore, for the formulation of the analysis using:
- Collection of endemic and clinical data. At the beginning of the detection of tick-borne encephalitis, the diagnosis is reduced to collecting data on visits to forests of patients endemic for infection, an analysis of clinical symptoms and signs of the disease.
- Spinal puncture and cerebrospinal fluid analysis. The patient undergoes a puncture of the spine in the region of the lumbar region, and cerebrospinal fluid is taken for analysis. It is difficult to make a diagnosis on the basis of this study, but it is possible to detect the presence of bleeding, purulent inflammation and other CNS lesions.
- Serological method. Laboratory diagnosis of encephalitis is based on taking paired blood serum and comparing them to increase immunoglobulins of group G and M. IgM indicates recent contact with the infection, and IgG indicates formed immunity against the virus, the presence of titers of both antibodies indicates the active phase of the disease. This method cannot be decisive in the diagnosis, since the presence of these proteins may indicate another cross infection.
- Molecular biological method. If the tick bit you, and you were able to remove it without complications, then in no case do not throw out the insect. Place the animal in a glass container with air access to conduct a tick test for encephalitis. With the development of the disease - this can be a decisive factor in the diagnosis. Tick tests for encephalitis are carried out in SES, infectious diseases hospitals and specialized clinics.
- Virological method. The most accurate, as it detects the presence of the virus in the blood (PCR reaction) and cerebrospinal fluid (PCR reaction and the introduction of cerebrospinal fluid into the brain of newborn mice).
The diagnosis of tick-borne encephalitis is made only after a comprehensive examination of the patient.
Encephalitis Treatment
Treatment of tick-borne encephalitis virus-infected should be carried out in a hospital under the supervision of an infectious disease doctor. But the methods of managing sick people and animals are different.
Treatment of tick-borne encephalitis in humans should consist of the following measures:
- Strict bed rest. Hospitalization of a patient with strict bed rest for the entire treatment period is organized.
- Antiviral therapy. In the first three days of the disease, an anti-encephalitic tick-borne gamma globulin is administered in a dose of 3-6 ml. intramuscularly. This treatment is justified only in the early stages of the disease, since in severe cases, specific gamma globulin begins to be produced as a protective function of the body.
- Symptomatic Therapy It is aimed at reducing the symptoms of intoxication of the body, reducing the severity of specific neurological signs.
- There is a theory that bees can treat encephalitis. But this method is not scientifically proven and does not have a proven effective base.
The treatment of tick-borne encephalitis in children is carried out according to the same scheme, only detoxification therapy with infusion solutions and dehydration are added to reduce tissue swelling. Treatment of children should be carried out necessarily in an infectious diseases hospital, since reduced body reserves can lead to death.
Consequences of a bite
Complications of tick-borne encephalitis are serious and in most cases can only be partially restored. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment of the disease is extremely important.
Adult Complications. With a febrile and meningeal form of encephalitis, the consequences in adults are minimal. After the course of treatment, a full recovery occurs.
Complications in children. The effects of encephalitis in children are irreversible. 10% of children die within a week, many still have muscle twitches, flaccid paralysis of the hands, atrophy of the shoulder girdle, carriage of the virus.
Prevention
Prevention of tick-borne encephalitis in areas endemic for the disease should be regular and thorough.
Adult Prevention. Measures for the prevention of encephalitis are specific and non-specific. Specific measures include vaccination of the population in areas unfavorable for tick-borne encephalitis. Vaccination promotes the development of persistent immunity to the disease.
With standard vaccination, the first dose of the vaccine is administered in the fall, revaccination is repeated after 1-3 months and after 12 months. Then re-vaccination is carried out every 2 years.
Vaccination according to the accelerated schedule is carried out in the spring, when ticks have already become active. After the first dose, the second is administered after 14 days. During the development of immunity, it is recommended to avoid contact with insects.
Contraindications to vaccination are almost the same everywhere:
- chronic non-infectious diseases in the acute stage (diabetes mellitus, stroke hypertension 2 and 3 tbsp., tuberculosis and others);
- allergic reactions during exacerbation;
- acute reaction to the introduction of the vaccine earlier;
- infectious diseases;
- pregnancy;
- intolerance to the components of the vaccine.
Prevention of encephalitis in humans can be nonspecific in nature - this is the use of special anti-mite clothing, repellents in nature, a mandatory examination after visiting forest park areas.
The drug is administered only in a hospital setting. Iodantipyrine and rimantadine are also used to increase the effectiveness of emergency immunization.
Prevention in children. Tick-borne encephalitis prevention in children has the same principles as in adults.
Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis is given to children after examination by a pediatrician from 12 months in endemic areas. Vaccination is carried out only in a hospital and a doctor’s opinion on the absence of contraindications.
Contraindications include infectious and non-infectious diseases in the acute phase, intolerance to the components of the vaccine, an acute reaction to previously introduced vaccines, children under 1 year old.
The correct behavior in nature is the use of protective clothing, regular inspection, the use of children's repellents. As an emergency prevention, children under 14 years of age are put 1.5-2 ml. tick-borne immunoglobulin and Anaferon is prescribed as an antiviral drug.
Be careful in nature, use available remedies and remember that an encephalitis tick bite can have disastrous consequences.
Tick bites: signs, consequences and prevention
In nature, there are more than 40,000 species of ticks. Among them, the most dangerous for humans are blood-sucking ixodid ticks. They resemble small brown bugs with four pairs of paws and a proboscis (the size of a hungry individual is about 5 mm, a saturated tick usually increases significantly).
However, not all ticks are universal carriers of infections.Many of them are sterile, that is, they do not contain viruses and bacteria harmful to humans (the number of infectious and non-infectious ticks varies depending on the region). But since it is impossible to determine by the appearance of a tick whether it is infected or not, it is always necessary to remain alert.
Biting people, both females and males of arthropods. Usually this happens after the end of a long autumn-winter hibernation - ticks wake up and need blood. The source of nutrition for them can be both an animal and a person.
Potential food is hunted as follows: a tick with hooks on its legs climbs up grass blades or sticks sticking up and waits for a victim, if any, an arthropod grabs it with its front legs and starts looking for a place suitable for a bite.
They can be found on the neck and on the head only because they, once on the human body, always move upward in search of an open and “juicy” skin area. The favorite habitats of ixodid ticks in nature are wet and shaded areas:
- ravines;
- bottom of meadows;
- forest edges;
- thickets of willow along the banks of forest ponds;
- roadsides of forest paths.
First signs of a bite
As a rule, people do not feel the very moment of a bite, but detect a tick when it is already firmly stuck to the body. The explanation is simple: during the puncture of the victim’s skin, the arthropod, together with saliva, releases active substances into the wound that have some analgesic effect.
Allergy-prone people at the site of the bite may develop a severe allergic reaction with itching and redness of the skin. In rare cases, a tick bite can lead to Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock.
Symptoms of these conditions are as follows: swelling of the face, difficulty breathing, a sharp deterioration in well-being, loss of consciousness, etc. In addition, due to a tick bite, a person's body temperature may increase, aches in the muscles and joints, chills, severe drowsiness may appear.
In general, the severity of the body's response to an arthropod bite depends on the state of health. In allergy sufferers, young children, the elderly, the reaction can be very violent. In healthy adults, contact with a tick may not affect their well-being, and they will learn about the fact of a bite only after seeing an incomprehensible formation on their body.
What should I do if bitten by a tick?
Since the probability of infection with dangerous infections increases significantly with prolonged contact of the human body with a tick, the main thing to do is to remove the arthropod.
Therefore, if there are no tick removal skills, but there is a possibility, it is better to contact the nearest medical institution, where they will expertly carry out the extraction of the arthropod and give recommendations for further actions.
In addition, you can ask all questions of interest regarding tactics of behavior in the presence of a tick on the body by phone 103 (by calling an ambulance).
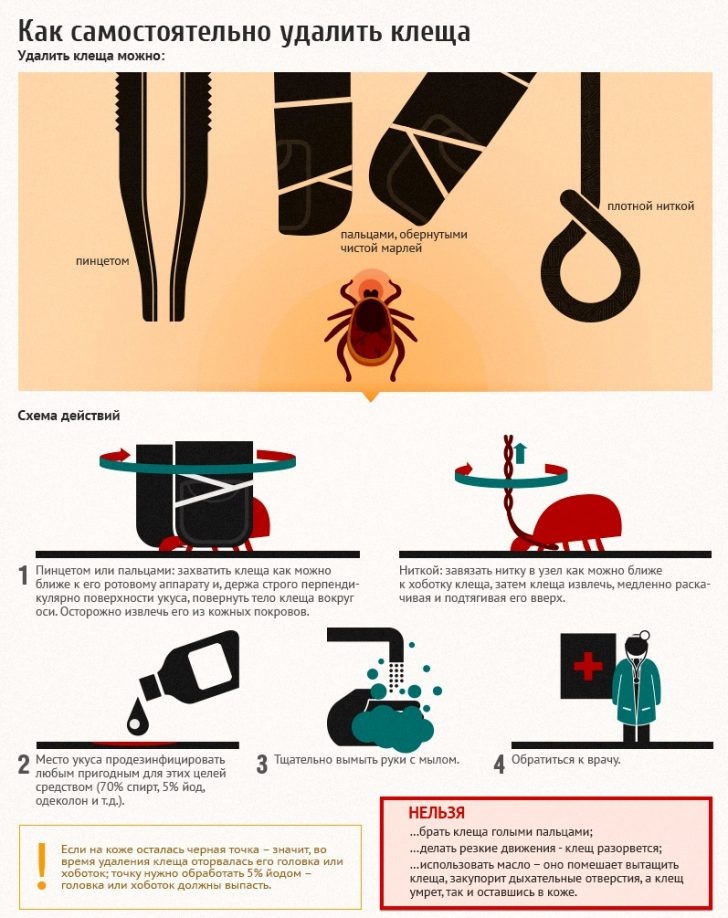
Removal Recommendations
It is best to remove the tick with a special device that is sold in pharmacies. This can be a pen-lasso, UNIKLIN TIK TWISTER, etc. If there is no pharmacy nearby, you can use ordinary cosmetic tweezers or sewing thread.
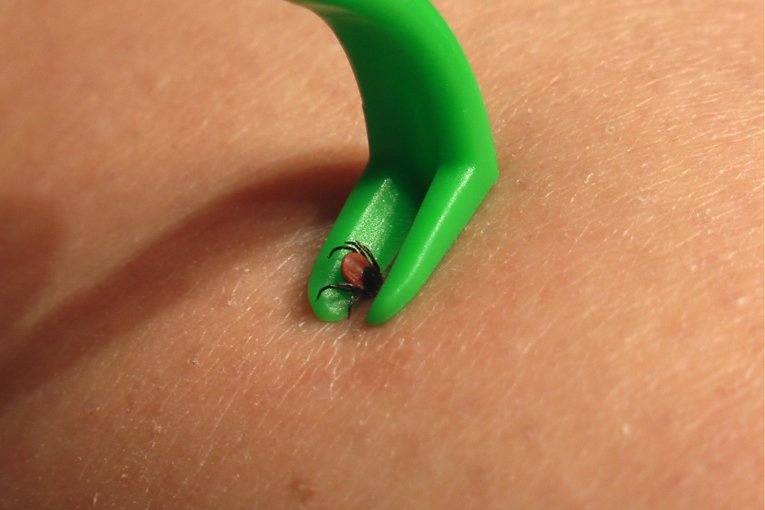
The person who will remove the tick must take care of his safety - wear rubber gloves or wrap your fingers in a bandage. It is also advisable to prepare in advance a plastic container with a lid or a plastic bag for a tick (so that it can be safely delivered to the laboratory).
The removal procedure itself must be carried out as follows:
- Grab an arthropod with tweezers or a special device as close to the proboscis as possible (this is the part of the animal’s body that is in the skin). If a thread is used, a loop should be made from it, which must be carefully tightened over the tick head embedded in the skin.
- Gently pull up. At the same time, great efforts cannot be applied, a mite can simply burst from them, and all its contents will fall on the skin and in the wound. In addition, the trunk of the arthropod with a sharp jerk remains in the wound, because of this inflammation and even suppuration can occur.
- After removing the tick, wash the skin with soapy water and treat with any product containing alcohol. There is no need to apply a bandage. If the head of the arthropod remains in the skin, you should try to remove it from the body with a sterile needle as a splinter.
Sunflower oil, oily ointments, airtight dressings and other folk remedies for tick control are not effective, their use only takes precious time.
After removing the tick, it is advisable to do the following:
- Mark the date on the calendar when everything happened.
- Call your therapist or family doctor, explain the situation and ask about the timing and timing of blood tests and some preventive measures (in some cases, immunoglobulins are administered to the tick-borne encephalitis affected by tick bites, antiviral drugs are prescribed, etc.) .
- Take the tick to the laboratory. Information about the laboratories can be found on the website of the Rospotrebnadzor in their region.
Be sure to visit a doctor in the following cases:
- If there are signs of inflammation in the bite area (swelling, redness, etc.).
- If in the interval from 3 to 30 days after the bite, red spots appeared on the skin.
- If the body temperature rises, muscle pain, unmotivated weakness and other unpleasant symptoms appear (these signs are especially important to monitor during the first 2 months after a bite).
h3> Consequences
Ixodid ticks are carriers of the following infectious diseases:
- Tick-borne encephalitis, in which the patient due to damage to the gray matter of the brain there are various neurological disorders, mental disorders, even a fatal outcome is possible.
- Tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme disease) is a polymorphic disease in which the skin, lymphatic system, joints, heart and other internal organs are affected. Borrelia, the causative agents of borreliosis, in the study of ixodid ticks are found most often.
- Monocytic ehrlichiosis, which is characterized by neurological disorders, general intoxication syndrome, airway inflammation and other pathological manifestations.
- Granulocytic anaplasmosis. This disease resembles ARI or intestinal infection and is quite easy. Persons with weakened immune systems may develop complications from the nervous system and kidneys.
How to protect yourself from bites?
In order not to become a victim of ticks, when visiting potentially dangerous places (park, forest, etc.), you must adhere to a number of rules:
- Wear the right clothes. It should be light so that ticks are visible, and maximally covering and protecting the body from arthropods getting behind the collar, under the leg, under the sleeve.
- Since ticks attack from below, trousers should be tucked into socks and boots.
- Always use repellents.Today, manufacturers offer a large number of protective agents against ticks, among them you can choose safe ones even for small children. There are also special suits soaked in acaricidal substances. Upon contact with acaricides, ticks die and fall away from clothing.
- Move along the widest paths, minimizing foot contact with grass and shrubs.
- Inspect clothing periodically.
- After returning home, to inspect both clothing and the body, paying special attention to the following places: ears, hairline, interdigital folds, popliteal areas, inguinal region, perineum, navel.
In regions with a high incidence of tick-borne encephalitis, residents are advised to get vaccinated. Today it is the best way to protect against a dangerous disease.
The consequences and symptoms of a tick bite
The tick is a small arthropod animal from the order of arachnids, reaches up to 3 mm in length and lives in different places of our Earth. There are many types of ticks. Among them, a special danger in the spread of certain infectious diseases: borreliosis, hemorrhagic fever and tick-borne encephalitis - is a forest tick.
Ticks are located in places not higher than undersized shrubs. Favorable living conditions are moist, dark places of forests, parks. It is important to remember that not with every bite a person can become infected with dangerous diseases. According to statistics, only a few of the tens of thousands of tick-bitten patients fall ill.
Unfortunately, there are no special signs by which a tick can be distinguished with pathogens. To know about this is possible only in laboratory conditions, as well as the clinical signs of the disease after a bite. Bacteria and viruses are carried by females, males, nymphs and larvae.
Symptoms
The peak of the highest activity of ticks appears from the beginning of April and decreases at the end of June. Their maximum number is recorded in the month of May. In early July, many ticks die out. Insects are inactive, cannot fly and move quickly. They expect their victim (human or animal) sitting motionless on the grass, squat branches.
The approach of a person changes the behavior of the tick: it spreads its legs and tries to catch. Favorite warm, soft areas of the body are: axillary hollows, neck, shoulders, to which he slowly creeps. When a person is bitten by a tick, no painful symptoms are felt, since the bite is completely painless.
The brightness of the symptoms will be directly affected by the number of ticks sucked to the person, as well as his size and state of health. A strong manifestation of signs of a bite should be expected in the elderly or children, people with a history of chronic diseases, allergies, immunodeficiency states.
“Favorite” places of the tick: the scalp, ears, armpits, inguinal region, the inside of the elbow bends and knees - where the skin is thinner and closer to the vessels. The first signs of a tick bite can manifest in a person 2-3 hours after a bite:
- weakness, drowsiness;
- chills;
- joint aches;
- photophobia.
Then other symptoms of a tick bite appear:
- hyperthermia up to 37-38 degrees against the background of lowering pressure and tachycardia;
- tachycardia (more than 60 beats per minute);
- itching and rashes;
- lymphadenopathy (an increase in regional lymph nodes).
Strong responses of the human body to a tick bite are manifested in the form of: headache; nausea and vomiting labored, hoarse breathing; nerve manifestations in the form of hallucinations and more.
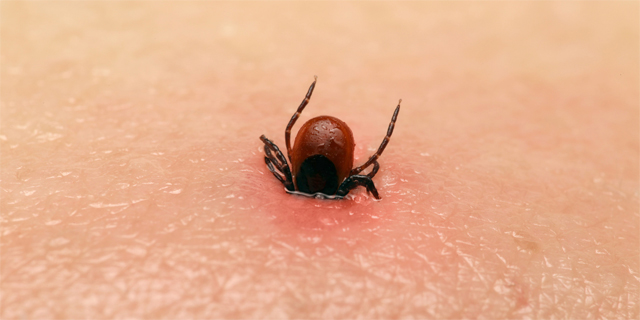
The tick is clearly visible on the body. In appearance, it resembles a mole.Tick paws are similar to hair outgrowths. In a sucked state, it can be for a long time.
What should I do if bitten by a tick?
The main goal of all further manipulations with the tick is to remove it. It is necessary to seek first aid from a specialist. If not possible, then you should try to extract the insect yourself.
In some sources, it is recommended to lubricate the tick with oil, hydrogen peroxide, alcohol or cream. Then after a while he should crawl out by himself. Another method involves the use of a thread that captures an insect and gently retracts from the skin.
Almost always, as a result of such manipulations, the tick is able to be removed intact. A further tactic after its removal is the treatment of the wound with iodine solution and observation of the bite site. The appearance of a small pink spot, which should disappear after a few days, is considered a normal reaction.
The part of the tick that could not be removed in the coming days should be evacuated outside. The extracted tick can be returned to the laboratory for research for infectious diseases. The reason for contacting the infectious disease specialist is an increase in the spot at the site of the bite in diameter, the appearance of a rash, and a deterioration in overall well-being.
Effects
Not all ticks are contagious, and carry a threat of infection for humans. In any case, the earlier the tick was removed, the less likely it is to pick up any of these infections:
Tick-borne encephalitis - an infectious disease of a viral nature, the main symptoms of which are: intoxication, hyperthermia, damage to the central nervous system (encephalitis, meningitis).
Borreliosis (Lyme disease) - an infectious disease of a bacterial nature, which has a large polymorphism of clinical symptoms. In addition to general intoxication, accompanied by fever, headache, fatigue, a typical sign of the disease is a migratory rash.
Bacteria infect various organs and systems (nervous, musculoskeletal, cardiovascular), especially those with a genetic predisposition to damage. Lack of timely assistance and further treatment can lead to disability.
Hemorrhagic fever - an infectious disease caused by a virus. The main symptoms: intoxication with severe fever, a change in blood composition, as well as parenchymal and subcutaneous hemorrhages. Distinguish Omsk, Crimean fever.
Etiotropic treatment consists in the appointment of antiviral drugs, as well as a solution of glucose, vitamins (K, P), which strengthen the vessel wall. With timely contact with a specialist, the prognosis of treatment is favorable.
Prevention: how to prevent?
Observing simple recommendations, you can protect yourself from an insect bite:
- Ticks are not able to bite through clothing. They need an open area of skin. That is why clothing is a reliable means of protection against ticks;
- Heading into the forest, care should be taken to protect exposed parts of the body, especially the skin of the legs. Socks should be worn over the pants, the sleeves of the sweater should fit snugly against the wrist. It is advisable to wear light-colored clothing. It is on it that ticks are more noticeable. Effective tick repellents are effective.They are recommended to be applied to places where the tick can penetrate: collar, shirt sleeves, belt, socks, etc .;
- It is important to regularly inspect body areas after visiting a park or forest. The tick moves slowly to the surface of the body it needs, therefore, before the bite it can be found and removed;
- If a tick is found on the body, it is necessary to consult an infectious disease specialist.
Tick bite - what to do?
The tick refers to small arachnid insects that feed mainly on the blood of animals. Not all types of ticks are dangerous to humans - forest ticks are the most dangerous.
The tick is the main carrier of many infectious diseases. In our country, only two of them are registered - tick-borne encephalitis and tick-borne borreliosis, or Lyme disease. Human infection occurs mainly through the blood when a tick bites. But infection is also possible when eating raw goat milk.
The insect lives mainly in the grass, less often in low shrubs. It is usually inactive and moves very slowly. Usually ticks climb onto thin stems of plants and blades of grass and spend most of their lives in this state, waiting for the approach of the victim - a person or an animal.
The paws of the insect are equipped with special microscopic claws, allowing it to firmly fix on clothes.
Once on the human body, the tick does not immediately bite into the skin. The blood-sucking parasite tries to climb as high as possible, so the main places of bites are often the shoulders, axillary region, back and neck. The tick bite is completely painless, because its saliva contains a powerful analgesic substance.
The blood-soaked tick increases in size and can reach 10 mm in length. But usually it is possible to see the blood-sucking parasite much earlier.
How to detect a tick
To do this, you must carefully examine your body in front of the mirror after visiting potentially dangerous places (forest-park areas). Even if the tick is very small, you will most likely notice a dangerous tubercle.
“Favorite” places of the tick: the scalp, ears, armpits, inguinal region, the inside of the elbow bends and knees - where the skin is thinner and closer to the vessels.
The extracted insect must be directed to the study. Not every tick is a carrier of dangerous infectious diseases, laboratory analysis allows you to determine the infection of the tick.
Tick-borne encephalitis
The first signs of tick-borne encephalitis appear, as a rule, after 10 days or more from the moment the infection enters the bloodstream. It:
- general and muscle weakness in the neck, arms and legs
- numbness in the neck and face
- chills, fever
- nausea, vomiting
- severe headache
- staining of the skin of the face, neck, mucous membrane of the oral cavity and eyes in red
If these signs appear, you need to urgently consult an infectious disease specialist or therapist of the polyclinic, the emergency department of the infectious diseases hospital, and if you are in serious condition, seek emergency medical attention.
The primary measures for a tick bite are aimed precisely at preventing the development of this disease, since in some cases it leads to disability or death.
Emergency prevention of tick-borne encephalitis involves the introduction of antiviral drugs and immunoglobulin into the body of the affected person.Such measures are effective only in the first 3 days from the moment the infection enters the human blood.
Borreliosis
Forest tick is the main carrier of another serious disease - Lyme disease, or borreliosis, which affects cells of the central nervous system, musculoskeletal system, skin, heart. The first signs of the disease are usually:
- redness of the skin in the area of the parasite's bite
- gradual increase in the size of the red spot
- transformation of redness from a rounded spot into a ring with a pale bluish center
If such manifestations are found in oneself, an infectious disease specialist should be consulted immediately, and in the absence of it, a physician.
The presence of a dangerous infection in human blood is detected only three weeks after a tick bite. Emergency treatment of tick-borne borreliosis includes taking special medications prescribed by your doctor. In the absence of adequate therapy, the disease becomes chronic and can lead to disability.
The tick poses a great danger to human health and life. If a blood-sucking parasite is found on its body, it is imperative to seek medical help. The likelihood of adverse effects on the human body with timely treatment is extremely low.
Symptoms and consequences of a tick bite in humans
A tick is a small insect that feeds on the blood of animals and people. Like mosquitoes, ticks get drunk on blood and fall off. But if mosquitoes do this quickly, then the tick can suck the victim’s blood for up to 4 days.
Ticks are in the grass and shrubs, waiting for their prey, and first fall on the lower part of the human body, so a tick bite in the leg is often found. Insects move pretty quickly through the body in search of an attractive place, and often a person discovers that a tick has bitten on its neck, head, and upper back.
Signs of a tick bite do not appear immediately. By itself, a tick bite is not dangerous, it only causes itching and redness of the skin. But these insects are carriers of about 30 dangerous diseases, microbes.
Therefore, you need to know what a tick bite looks like on a person’s body, how to properly remove an insect from the skin, in which cases you need to urgently see a doctor, what symptoms can occur after a tick bite, what are the consequences and how to avoid them.
What does it look like
Favorite places for ticks on the human body are the head, skin behind the ears, bends of the elbows, knees, inguinal region, armpits, back, stomach, neck. Returning from the forest, from outdoor recreation, these places need to be checked first.
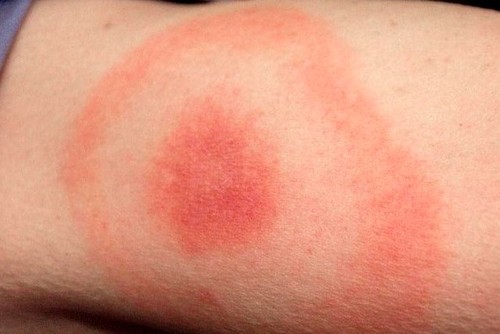
When a bite occurs, the skin is injured, inflammation develops under the influence of insect saliva, an allergic reaction often occurs, the skin turns red at the site of the bite, and itching appears over time. It looks like a tick bite as follows:
If a tick is infected with an infectious disease, the bite site may look specific. For example, in the photo below, the bite of a tick infected with borreliosis - the spot is large (up to 20, and sometimes 60 cm in diameter), intense red at the edges, the center of the spot is blue or white.
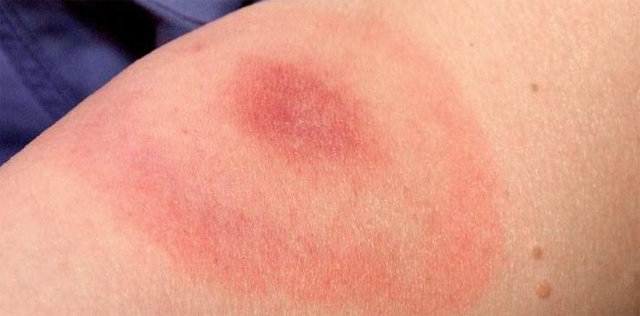
Symptoms and signs
A tick attached to the body is clearly visible. Due to the anesthetic substance in the saliva, the insect bite is not felt, but when examining the body, it is not difficult to see. If a tick is found, it must be removed by swaying from side to side, and then pulling it counterclockwise.
The severity of symptoms may vary. How tick bites appear depends on the age, individual characteristics, general condition of the person, on the number of sucking insects.
The symptoms of a tick bite are more severe in children, the elderly, allergy sufferers, people suffering from chronic diseases, and people with weakened immune systems.
If the tick was not infected, then redness and itching pass quickly enough without a trace, no other symptoms appear. If the insect was infected, then after a tick has bitten, signs such as general weakness, chills, drowsiness, body aches, joints, photophobia, numbness of the neck appear.
In severe cases, attacks of nausea, vomiting, headache, nerve manifestations (for example, hallucinations, delusions, convulsions, loss of consciousness), difficulty breathing may occur.
One of the most common symptoms if a tick is bitten is an increase in body temperature. This occurs during the first hours after a bite and is an allergic reaction to insect saliva entering the body.
The temperature after a tick bite can rise within 10 days. If a high temperature is recorded during this period, this is a sign of the development of an infectious process.
For example, tick-borne encephalitis is characterized by fever (increase in body temperature up to 38-40 degrees) for 2-4 days, which lasts about two days, then the temperature drops. At 8-10 days, the temperature may rise again.
With borreliosis, at the first stage (first week), the temperature rises to 40 degrees, being one of the signs of acute intoxication syndrome. An increase in temperature after a tick bite is characteristic of all types of infections that are transmitted by ticks.
Possible consequences
What could be the consequences of a tick bite? If the tick was not infected, then after a bite, itching may disturb for some time, a local allergic reaction - redness of the skin, fever. All symptoms pass quickly enough.
The consequences of a tick bite infected with an infection can be very serious. Infections can affect various organs and systems: skin, nervous system, joints, bones, muscles, cardiovascular system, lungs, kidneys, liver.
With an unfavorable development of events, the consequences of an encephalitis tick bite in a person become a deterioration in the quality of life on an ongoing basis, for example, impaired motor functions, epilepsy. Lethal outcome is possible.
In order to avoid serious complications after a tick bite in a person, when an insect is found, the occurrence of the symptoms described above, you must immediately consult a doctor, take a blood test. The sooner therapy is started, the less likely it is that negative consequences will occur if a tick is bitten.
In areas where the incidence of tick-borne infections is high, vaccination against encephalitis and other infections is widespread. Such a measure minimizes the symptoms and consequences of a tick bite.
leave a comment