
Hello! For most of my life I fought insects with improvised means and with the help of popular councils.
For the most part, this approach paid off. But last year I was subjected to such insect attacks that I decided to use insecticides.
The effect of chemicals in the fight against parasites was good. But is it safe for humans? Now I want to tell you as much as possible about cypermethrin and its effect on humans. Already on the basis of this information, let everyone decide for himself whether to use it.
The content of the article:
Are the pesticides currently in use safe?
The constant growing population of the planet needs to be fed with something. And, since every berry and every grain counts, farmers do not want to share their crops with insects and fungi. That is why pesticides that are highly toxic to humans are being replaced by new substances that are more toxic to insects and less dangerous to humans.
Neonicotinoids and Imidacloprid
One of the newest groups of pesticides is neonicotinoids. The name itself suggests that their "predecessor" was nicotine - a universal poison that many of us poison grass completely voluntarily. Tobacco infusions were used to spray pest-affected plants.
It should be noted that in Europe it has been banned since the end of 2013. This ban is due to the fact that a drug highly toxic to insects does not distinguish harmful Colorado beetles from healthy bees, and environmentalists have sounded the alarm.
The effect of imidacloprid on humans is still not fully understood. Previously, studies have not proven its ability to cause cancer, mutations or defects in the fetus. But prolonged exposure at low doses damages the liver and thyroid gland.
On average, 3 out of 4 bananas, cauliflower heads or spinach leaves that are available to us in the markets were processed with imidacloprid. Its residual amounts in products are usually less than permitted, and such products are considered to be in compliance with the standards. Maybe this is not a good comparison, but one cigarette has also not killed anyone.
Since imidacloprid is a systemic insecticide, thoroughly washing vegetables to get rid of it is not enough - it is spread throughout the plant.
Pyrethroids: Deltamethrin and Alpha Cypermethrin
Like many modern discoveries and inventions, the appearance of pyrethroids was not an accident. For decades, gardeners have used chamomile infusions, but, despite the effectiveness of such treatments, the duration of action of such a natural preparation was not pleasing.
Pyrethrins - natural insecticides found in chamomiles - decompose under the influence of light. Studying them in more detail, scientists synthesized substances with the same properties, but much more persistent. So, their half-life is about 20 days, in contrast to several hours for natural compounds.
But we do not receive such high doses of pyrethroids with food. For example, a bottle with 2 ml of the drug contains 200 mg of the active substance.
For spraying plants from insects on one hundred parts, the contents of the bottle are diluted in 4 liters of water. On average, 40-45 tomato bushes grow on such an area. Suppose, on average, 2 kg of fruit is harvested from one bush. It turns out that immediately after processing one tomato contains a maximum of 0.5 mg of substance.
Given that the harvest is carried out after meeting the waiting time (the drug decomposes over time), in order to get a dangerous dose of alpha-cypermethrin, you need to have access to the drug directly, and not to the plants treated by it.
Another popular drug from this group, deltamethrin, is dangerous for humans with allergies, and if it comes into contact with the skin, it can cause ulcers.
But this also concerns people who work directly with him, since he does not accumulate in the human body.
Copper-containing pesticides and synthetic fungicides
The rule “to warn is easier than to cure" also applies in agriculture. Fungal diseases of plants can cause huge losses to the farmer. Measures to protect crops from diseases often include treatment with copper-containing pesticides - this is a relatively cheap way of prevention.
All summer residents have heard about the "Bordeaux mixture" - this is one of the most popular drugs based on copper. Since the duration of the protective effect from such treatments is only 10-20 days, they are often repeated.
But copper is toxic to the plant’s body (agronomists call it “phytotoxicity”), both for animals and for humans.
Just 0.5 g of copper sulfate (which is part of the Bordeaux mixture) is enough for the appearance of symptoms of poisoning. Copper accumulates in the liver, kidneys, brain, plays a role in the destruction of red blood cells. Chronic copper poisoning leads to kidney and liver failure.
For each treatment with this popular fungicide per tomato plant, for example, 0.1 g of copper (0.38 g of copper sulphate) is ingested. Of course, we do not eat tomato leaves, and do not even eat the whole crop from the bush at a time, but copper accumulates in the plants. The vitriol washed off from the leaves enters the soil and can be absorbed by the roots.
Due to the high toxicity of copper, spraying is stopped 20-30 days before harvest. However, if this is not controlled, you cannot be sure that the tomato that fell into your hands does not contain copper sulfate on the surface - it is better to wash it thoroughly.
Before we get two from one cell, all the genetic information in the cell nucleus - all the instructions for the existence of the body, DNA - doubles. Then, in the process, each of the “portions” of DNA (exactly the same portions) goes to its cell pole.
This process is almost the same for all cellular organisms - fungi, and plants, and humans. Benomil and synthetic pesticides similar to it destroy protein “pathways” along which chromosomes (in which DNA is enclosed) must diverge after replication.
As a result, cell division ends abnormally, information in the nucleus of daughter cells is distorted, somewhere there are not enough chromosomes, and somewhere doubled. Since these same “paths” consist of the same proteins in both fungi and animals, benomyl, entering the human body, can have the same effect on dividing cells.
Therefore, it will be useful to remove the external leaves of the cabbage before eating it.
Glyphosate and its harm to humans
Cultivated agricultural plants require care - they are no longer able to survive and give birth without a human being. Wild plants - on the contrary, are just waiting for the opportunity to take a place on fertilized arable land.
In order not to share the nutrients with weeds, farmers use herbicides. The manual labor of weed removal is too expensive, so chemical plant protection products come to the rescue.
The harm of glyphosate to humans is still under discussion. Toxicological studies (when they try to give poison to rodents and observe them) show conflicting results. Epidemiological data (when they analyze information about people's health in regions where poison is used) also does not give a clear picture.
For example, in Argentina, in places of active use of glyphosate, a higher incidence of cancer (especially lymphomas) and more frequent cases of fetal malformations.
Cases of male infertility have become more frequent. Is glyphosate dangerous? It is still difficult to put a bullet in this discussion, since it is impossible to say for sure that all these problems are exclusively associated with glyphosate.
The good news is that if you bought vegetables, there is practically no glyphosate in them. Bad news - if your water intake (well, well) is treated with glyphosate fields, think about the constant purchase of drinking water.
Organophosphate Pesticides
Organochlorine compounds were replaced by organophosphorus pesticides. They are also effective against insects, but not so persistent and not so accumulate in the environment. They also have high toxicity to humans and warm-blooded animals, and can also lead to the appearance of invulnerable populations of harmful insects.
Nerve cells have many processes, and so-called synapses exist to transmit an impulse from one cell to another. Imagine a secretary who receives an email, prints, re-dials and sends an email to another addressee.
Despite the absurdity of such a comparison in real life, such “printed letters” are special substances - mediators, and the “AChE” enzyme is the “secretary”. By blocking it, we distort the signals of the nervous system.In insects in this way, organophosphorus pesticides cause seizures, tremors, paralysis and death.
It is important that pesticides of this group are still allowed and widely used, therefore, intoxication with organophosphorus pesticides is a very real threat.
The substance itself can accumulate (for example, chlorpyrifos), as well as the products of its processing by the body (fenthion), which can be as toxic as the original substance.
But what is dangerous, damaged AChE molecules can also accumulate. This is usually dangerous for those who deal directly with pesticide field treatment. But in case of violation of the rules for harvesting the processed crop, the residual amount of PO of pesticides can get to your table.
If you have doubts about the content of organophosphorus pesticides in products, give them heat treatment - these substances will not stand it. True, you also need to remember that they are not afraid of an acidic environment, so sauerkraut will contain these pesticides if it was processed by them.
What can we do against insects?
How to protect our children, and adults, from biting, stinging, sometimes endlessly annoying brothers of our lesser - arthropods? In the summertime, perhaps, only in the Arctic and Antarctica they do not ask this question.
They belong to the same detachment as mosquitoes - “two-winged”. Less often, we have to deal with representatives of the hymenoptera squad - bees, bumblebees, wasps, hornets. Contacts with them occur, although rarely, but, nevertheless, very painfully.
Even less often, we encounter such representatives of the “insect” class as fleas, bugs and lice, as well as representatives of the “arachnid” class (spiders are not insects!) - in fact, spiders and ticks.
I do not want to live side by side with them, but I have to. How to protect yourself and protect your children from the treacherous attack of the “biting brotherhood”?
Protecting ourselves!
First of all, you should limit access to open areas of the body as much as possible - put on clothes, preferably with cuffs, which will protect your body from bites. Open areas of the body can be sprayed or greased with repellents in strict accordance with the instructions contained in the annotations.
For people sleeping during the daytime, especially for sick and elderly people, mosquito nets treated with insecticide can be good protection, and for small children, canopies over the beds.
Repellents or insecticides?
Insecticides, repellents, fumigants are words that are widely heard in the summertime. But does everyone know what it is?
Insecticides (the word comes from the Latin insectum - insect and caedo - kill) - substances of chemical or biological origin for the destruction of harmful insects.
They have been used by mankind since time immemorial. Even Aristotle, at one time studying insects (by the way, he belongs to the oldest classification of insects that has survived to this day), described in his writings the action of sulfur to rid a person of lice.
The Chinese used arsenic and tobacco infusions to control insects. And during the time of Alexander the Great, his warriors used a powder of some types of mountain chamomile (pyrethrum) containing pyrethrins, substances that block the transmission of nerve impulses, in order to kill parasites and cause paralysis and quick death.
Currently, synthetic analogues of natural pyrethrins are used, which have high insecticidal activity and are more stable in the light (they oxidize much more slowly) than natural pyrethrins. For example, synthetic deltamethrin is more than 900 times more active than pyrethrin.
There are different types of insecticides: insectoacaricides - substances that kill insects and ticks, larvicides - substances that kill insect larvae, ovicides - substances that kill insect eggs, and acids - substances to fight aphids.
But in our time, insecticides are not always “killer” substances. The goal of insecticides is to protect against insects. And protection does not necessarily imply “total” extermination.
Taking into account the fact that representatives of the class "arthropods" occupy a certain place in the food chain of a huge number of animals, it would be extremely unwise to conduct a conversation about their complete extermination.
In this regard, there are insecticides, so to speak, gentle action:
- attractants - substances to attract insects into a trap;
- pheromones - substances of an extrahormonal type, released into the atmosphere by insects of the same species as signals of a “trace”, food, mating, etc., again, to lure insects into a trap;
- sterilizers - substances acting on the reproductive system of unwanted insects, thus preventing their development and reproduction;
- repellents - substances that repel unwanted arthropods;
- aphidants - substances that reduce the appetite of harmful insects or completely deterring food.
Repellents and aphids are considered the most “green” insecticides.
How do insecticides work?
First of all, they need to somehow be conveyed directly to an insect or arachnid. There are several methods of “application”: they spray, pollinate, use aerosols and fumigation with insecticides. More on this later.
Contact - when insect poisoning occurs in contact with any part of their body (used against pests with a piercing-sucking mouth apparatus).
Intestinal - cause poisoning in representatives of insects having a gnawing type of the oral apparatus, when an insecticide enters the intestine with food.
Systemic, when plants are used in transit to deliver a drug to an insect. Penetrating into a plant, moving along its vascular system, the insecticide infects insects living on this plant and feeding on its juice.
Finally, fumigants are drugs that poison insects through the respiratory tract.
Electric fumigators are widely used, using a plate or a bottle of liquid containing an insecticide, as well as smoke spirals. The active substances in the fumigators, as a rule, are synthetic pyrethroids with a long residual effect.
Being non-toxic to warm-blooded animals and humans, they are nonetheless a potent insecticide. Most often, pralletrin (aka Etok), a synthetic insecticide with a wide spectrum of activity and high selective biological activity, is used as an active substance in fumigators.
Highly toxic for dipterans. Along with pralletrin, the substance of the “previous generation” esbiotrin is used. The principle of its action is similar to pralletrin, but its concentration in the preparations is much higher.
How do repellents work?
Repellents (lat. Repellens - repulsive, repulsive) - a natural or chemical substance used to repel arthropods. Unlike insecticides that kill arthropods, repellents do not destroy them.
According to the method of action, they are divided into olfactory (acting on the nerve endings of the olfactory organs) and contact (acting on arthropods when they come in contact with the treated surface). Used in the form of creams, lotions, ointments, emulsions and aerosols.
The basis of the vast majority of repellents, the active substance is diethyltoluamide (DETA). A wonderful organic chemical compound with a repellent and insecticidal effect.
It was developed in 1946 to protect the personnel of the US Army units in regions with a large number of insects. Since 1965, it has been part of most individual repellents. In addition to diethyltoluamide, the active substance of repellents can be icaridin, IR3535, etc.
Note that the IR3535 repellent belongs to the fourth (low hazard) class according to the classification of hazardous substances and is the only substance allowed for children over one year old.
The main thing is safety for humans
Although the danger of using repellents and insecticides for humans is not acute (manufacturers assure us of the safety of the manufactured product), it nevertheless makes us be careful and handle such drugs very carefully.
Almost all repellents and insecticides have contraindications and side effects. Examine them carefully before use.
Try to avoid getting the drugs on the mucous membrane of the nose, mouth and eyes, avoid getting on scratches and open wounds.
Pay attention to the composition. The manufacturer must indicate the composition, including the percentage of active substance. Do not be lazy to study annotations.
Caution! Acaricidal agent - cypermethrin
Almost all acaricides (against ticks) are dangerous. Apply them only on clothes. Otherwise, poisoning cannot be avoided. The active substance they use is the insecto-acaricide alfamethrin (alpha-cypermethrin, MGK), which has a nerve-paralytic effect on ticks.
When poisoning with alpha-cypermethrin, there is a violation of coordination of movements, tremors, convulsions, salivation, lacrimation. If drugs get into the body, you should immediately consult a doctor.
It is necessary to drink plenty of water, activated carbon, saline laxative. If the product comes into contact with eyes, rinse thoroughly with running water, and if it comes into contact with the skin, wash with running water and soap.
Don’t be afraid of possible troubles while using insecticides and repellents. With proper use of drugs, taking into account the recommendations of the annotations, the side effect will be minimal. But the benefits of using insecticides are an indisputable fact.
Folk remedies
Those who are wary of chemical preparations, it remains to use folk remedies for repelling and destroying arthropods.
There is an opinion that arthropods do not tolerate some pungent odors. For example, using vegetable decoctions and various aromatic oils with a strong smell can protect yourself from their annoying attention.
It is believed that the smell of fresh leaves of bracken, bay oil, a strong infusion of bay leaves is unbearable for flies.
Mosquitoes dislike the smell of elderberry, tomato, a strong infusion of wheatgrass rhizomes.
To folk remedies that repel mosquitoes and midges, include tobacco, valerian, bird cherry, basil, cloves, eucalyptus.
Camphor, cedar oil, saturated broth of wormwood are considered good, effective means of repelling insects. Also, carbolic acid can come to the rescue.
An excellent folk remedy can be considered tea tree oil. It can be used not only as a repellent, but also as a tool that perfectly helps with bites, relieves inflammation and relieves itching.
Among fishermen, vanilla is considered an effective remedy. Any baby cream is mixed with vanilla or vanilla, applied to the skin, and after that you will not be afraid of mosquitoes or mosquitoes.
Perhaps it is worth noting that most folk remedies for combating arthropods are natural repellents. They only scare away, not kill. Therefore, using repellent, do not be too lazy to open a window and let them out of the room.
Insecticides. An old folk remedy destroying arthropods is Persian, Caucasian or Dalmatian chamomile, it is also a feverfew. Inflorescences, stems and leaves of a dried plant, powdered, affect the nerve cells of insects.
How to be, what to do if you have already been bitten?
With bites of mosquitoes and midges, soda-salt lotions are an effective way to relieve itching. For one glass of boiled cold water we take one teaspoon of drinking soda and half a teaspoon of salt. If you have been bitten for a long time and carefully, and “there is simply no living place” on you, in this case you can take a bath with sea salt by adding soda to this solution.
In folk medicine, insect bites are treated in a number of ways that can be described as "what turns up by the arm." The bite site is rubbed with elderberry leaves, ice is applied or just cold metal objects.
Mosquito bites, as a rule, do not cause serious complications, but bites of midges, horseflies, gadflies, bees, bumblebees and wasps can lead to serious consequences, especially in people prone to allergies. In such cases, it is very useful to have antihistamines (antiallergic) drugs with you.
If a bee stings you, you must take out the sting. Wipe the stung area with alcohol, cologne. It is useful to immediately drink a glass of water with a tablespoon of honey diluted in it. If the place where you were stung is reddened, itchy and swollen, you should take an antihistamine and immediately consult a doctor.
Wasps, bumblebees, hornets do not leave a sting in a wound, but their attack is no less painful than a bee, as they still inject poison into the wound. The larger the insect, the greater the amount of poison that enters the wound. Therefore, to a greater extent than bees, you should beware of the attacks of bumblebees and hornets.
We are not afraid of ticks!
Separately, it should be said about what needs to be done and how to behave when a tick attack. So, you found that you were bitten by a tick. Do not panic! Not necessarily headlong to run to a traumatologist or surgeon.
Also, for this purpose, you can use tweezers or a special device for removing mites, similar to a nail clipper and working on the same principle.If you can’t completely remove the tick by yourself, you need to see a doctor.
The decisive risk factor for infection is time. The less time the tick spends in the wound, the less chance of infection.
After the tick is removed, it should be placed in a hermetically sealed container and must be taken to the laboratory for research without fail. Information on where you can take the tick for analysis can be obtained by calling the emergency department.
By the way, the tick can be examined at any time, despite the statute of limitations. The laboratory accepts dead ticks for analysis, since the causative agent of the disease does not disappear from it anywhere. The laboratory reports the results of the research to the infectious disease specialist at the place of residence, and he, if necessary, should prescribe a course of treatment.
But nothing can be done after a tick bite. A disease can develop faster than the analysis is ready! It is important during the first three days after the bite to begin the prophylactic administration of a special antibiotic.
A doctor may prescribe doxycycline, but it can be another antibiotic, taking into account the characteristics of each individual person, because each drug has its own side effects. So, doxycycline, for example, is contraindicated in children under 8 years of age, pregnant and suffering from liver disease, in addition, it very “hits” a weak stomach.
Try not to provoke an attack of bees, bumblebees and wasps by your actions: do not make sudden movements in the immediate vicinity of these insects, do not apply strong smelling substances, try to accidentally or deliberately grab insects with your hand.
Use repellents.
Cypermethrin (cypermethrin)
International Nonproprietary Name (INN): BAN accepted in the UK.
Pharmacological (biological) properties and effects
Insecticide drug. Cypermethrin, which is part of the Biorex-GC preparation, belongs to the second generation pyrethroids, has a wide spectrum of insectoacaricidal action, is active against sarcoptoid, ixodid ticks and insects.
By the degree of exposure to the body, Biorex-GC belongs to moderately hazardous substances (hazard class 3 according to GOST 12.1.007-76), in the recommended doses and concentrations it does not exert a locally irritating and sensitizing effect. Toxic to fish and bees.
Indications for use of the drug BIOREX-GC:
- for the treatment and prevention of sheep psoroptosis;
- for the treatment and prevention of psoroptosis, chorioptosis, sarcoptosis, sifunculosis, ixodid tick infections in cattle;
- for the treatment of pigs with sarcoptosis and hematopinosis;
- for treating birds against chickens and Persian ticks, bed bugs and downy eaters, as well as for pest and pest disinfestation;
- for the treatment and prevention of sarcoptosis, notodedrosis and otodectosis of foxes, arctic foxes, raccoon dogs and other fur-bearing animals, as well as rabbit notoedrosis and psoroptosis;
- treatment of animals against blood-sucking dipterans insects (mosquitoes, midges, woodlings, horseflies) and pasture flies in quantities that cause anxiety, disturbance of normal grazing or rest and a decrease in the productivity of animals, or that pose a risk of the spread of infectious and invasive diseases.
Application procedure
Before mass treatments, each batch of Biorex-GC is tested on 10-15 animal heads. If the animals do not show signs of toxicosis within 2 days after treatment, proceed to the processing of the entire livestock.
At the same time, the volume of the working emulsion required for processing and the amount of Biorex-GC preparation required for its preparation are determined (see table).
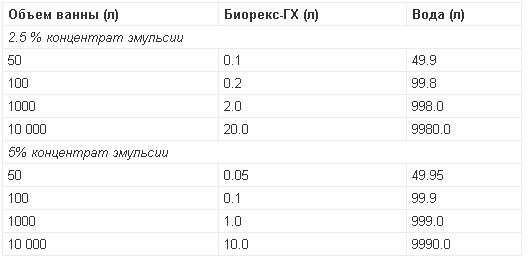
Sheep with psoroptosis is bathed in a swim bath using Biorex-GC 0.005% aqueous emulsion for therapeutic purposes twice with an interval of 10-14 days, for the purpose of prevention - once.
The required amount of Biorex-GC is thoroughly mixed with 2-3 volumes of warm water (28-32 ° C), and then poured into a floating bath with water, adding water to the required volume with stirring.
The treatment is carried out in dry weather at an air temperature of at least 18 ° C and emulsion emulsion - 18-25 ° C. Duration of bathing sheep - 50-60 sec. Before processing, the sheep are kept on a starvation diet for 10 hours. 2 hours before the treatment, the animals need to be fed. After shearing, sheep should be bathed no earlier than 3 days later.
After exiting the bath, the sheep are left for 10-15 minutes in a special area for draining the emulsion, after which they are distilled into the pen.
Refueling the bath is carried out after processing 300-400 unshorn sheep or 400-500 sheared sheep, while for every 1000 liters of water added to the bath with careful stirring, 4 l of 2.5% or 2 l of 5% Biorex-GC is added.
After processing 1000 sheep, the used emulsion is poured into the sump wells, avoiding environmental pollution, the bath is cleaned of dirt and filled with a newly prepared batch emulsion.
Animals are sprayed, moisturizing the entire body, especially carefully treating the lesion sites and areas in the ears, limbs, abdomen and tail. The biorex-GC working emulsion consumption rate, depending on the weight of the animal, is 1.5-3.0 l.
Repeated treatment of cattle with entomoses and ixodid tick damage during the parasitic season is carried out according to indications, with sarcoptoidosis twice with an interval of 7-10 days.
Pigs with sarcoptosis and pig hematopinosis are sprayed with 0.025% Biorex-GC aqueous emulsion with a flow rate of 300-500 ml per animal. For example, to prepare 100 L of a 0.025% aqueous emulsion, you should take 1 L of 2.5% Biorex-GC and 99 L of water or 0.5 L of 5% Biorex-GC and 99.5 L of water.
In dysfunctional sarcoptoidosis farms, simultaneously with the processing of animals, deacacification of the premises is carried out using Biorex-GC 0.005% aqueous emulsion with a flow rate of 200-400 ml / m2 of the treated surface.
Spraying the premises is carried out in the absence of animals, the residues of feed, water and dairy equipment are pre-cleaned, milking equipment is covered with plastic wrap.
1-1.5 hours after treatment, the room is ventilated for at least 1 hour, the treated surfaces are washed with water, the feeders and drinkers are thoroughly washed with a 3% solution of soda ash and rinsed with water, after which the animals are placed in the room.
The treatment of birds against lint, chicken and Persian ticks, bed bugs is carried out with Biorex-GC by spraying birds with directed aerosols of 0.005% aqueous emulsion (cypermethrin). Processing is carried out after collecting eggs in a dose of 15-30 ml per bird twice with an interval of 8-10 days.
Pest control and deacarization is carried out with a 0.005% Biorex-GC aqueous emulsion (according to cypermethrin) twice, taking into account the development cycle of ectoparasites and the air temperature in the house during the technological break:
- for the destruction of chicken mites at an air temperature of 15-17 ° C, the interval between treatments is 10-12 days, at a temperature of 18-20 ° C - 8-10 days, at a temperature above 20 ° C - 5-6 days;
- for the destruction of bed bugs and Persian ticks at an air temperature of 17-20 ° C, the interval between treatments is 15-21 days, at a temperature of 21-25 ° C - 10-15 days, at a temperature of 26 ° C and above - 8-10 days .
The first treatment of poultry houses in order to destroy the bulk of ectoparasites and prevent their creep or transfer to other objects is carried out before mechanical cleaning of the premises immediately after removal of the bird. The consumption rate of the working emulsion is 100-200 ml / m2 of the treated surface.
The second treatment is carried out after sanitary preparation (washing, repair and whitewashing) of the poultry house with a working emulsion consumption rate of 50-75 ml / m2 of the treated surface.
The exposure of the treatment is 24 hours. After the exposure, the room is ventilated for at least 1 hour, the dead ectoparasites are swept away and destroyed, the treated surfaces are washed with water, feeders and drinkers are thoroughly washed with 3% soda ash solution and rinsed with water, after which the bird is placed in the room.
To kill bestial flies in closed production rooms (poultry houses), spraying is carried out with 0.005% Biorex-GC water emulsion with a flow rate of 50-100 ml / m2 of the treated surface. Repeated processing is carried out according to entomological indications.
In case of sarcoptosis, notohedrosis and otodectosis of foxes, arctic foxes, raccoon dogs and other fur animals, as well as notodedrosis and psoroptosis of rabbits, Biorex-GC is used for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes with a concentration of 0.005% for cypermethrin (see table).
Fur animals and rabbits are bathed in a bath placed in insulated rooms, for therapeutic purposes twice with an interval of 7-8 days, for the purpose of prevention - once.
Before processing, in order to avoid the bites of the people conducting the treatment, the jaws are fixed with a loop from the braid and immersed in a bucket emulsion.
In order for the acaricidal liquid to reach the skin surface, the hairline of animals and rabbits when bathing is massaged by stroking in the direction from the tail to the head, and the limbs - from the bottom up.
The head of the animal during bathing is twice immersed for 2-3 seconds in the emulsion of the bucket, pinching the nostrils and the oral cavity with a palm. After bathing, the fur cover is wrung out, providing a drain of liquid back into the bath, and then animals are placed in warm, disinfected cells.
After processing 20 fur-bearing animals or 30 rabbits in a bath containing 50 l of working emulsion, the treatment is stopped, and the used emulsion is poured into the sump wells, avoiding environmental pollution, the bath is cleaned of dirt and filled with a newly prepared batch emulsion.
Spraying the premises is carried out in the absence of animals, the residues of feed and water are previously removed.
The exposure of the treatment is 1-1.5 hours, after which the room is ventilated for at least 1 hour, the treated surfaces are washed with water, the feeders and drinkers are thoroughly washed with a 3% solution of soda ash and rinsed with water, after which the animals are placed in the room.
For sarcoptosis, notodedrosis and otodectosis of fur-bearing animals, as well as for rabbit notoedrosis and psoroptosis, 0.005% (cypermethrin) Biorex-GC oil emulsion is used. As oily solvents, liquid paraffin or sunflower oil is used.
In order to more fully treat the entire surface of the ear and ear canal, the auricle is folded in half and lightly massaged at its base. Processing is carried out twice with a 7-10-day interval. An oil emulsion must be introduced into both ears, even in cases of mite damage of only one ear.
In order to combat vaginosis (mosquitoes, midges, midges, horseflies), treatment of cattle with Biorex-GC is carried out by spraying with a 0.008% aqueous emulsion (according to cypermethrin) with a consumption rate: young animals up to 1 year old - 230-270 ml, older than 1 year old - 480-520 ml per animal.
For example, to prepare 100 l of a 0.008% aqueous emulsion, you should take 320 ml of a 2.5% solution of Biorex-GC and 99.68 l of water or 160 ml of a 5% solution of Biorex-GC and 99.84 l of water.
The time of treatment and the need for their implementation is determined depending on the dominant components of the midge.
With a high number of horseflies and midges, animal treatments are carried out daily after morning milking, and with a high number of mosquitoes and biting midges after evening.
With a moderate number of blood-sucking insects, treatments are carried out once every 2-3 days, and with an attack of only pasture flies - after 7-10 days.
Cattle are sprayed using a PER apparatus, an OP-8 knapsack sprayer, a DUK or other spraying devices that provide small-drop spraying.
In case of non-observance of the established period of repeated treatments, the use of the drug should be resumed in the same dosage according to the same scheme.
Side effects
Side effects and complications when using the drug in accordance with the instructions, as a rule, are not observed. With increased individual sensitivity of the animal to the components of the drug and the appearance of individual reactions (redness of the skin, itching), treatment is stopped.
Symptoms of an overdose when using the drug have not been established.
Contraindications to the use of the drug BIOREX-GC:
- patients with infectious diseases and malnourished animals;
- females in the second half of pregnancy;
- increased individual sensitivity to the components of the drug.
special instructions
You should not use insectoacaricidal drugs of other groups at the same time.
Slaughter for meat of sheep and rabbits is permitted no earlier than 15 days, cattle and pigs - no earlier than 25 days after the last treatment with Biorex-GC.
In the event of forced slaughter of previously established terms, the meat can be used to feed animals or for the production of meat and bone meal. Eggs obtained from Biorex-GC-treated chickens are used without restriction.
Milking cows and the use of milk is allowed 12 hours after treatment with Biorex-GC. Milk obtained at an earlier date is used for animal feed.
Personal Prevention
When working with Biorex-GC, the general rules of personal hygiene and safety precautions provided for when working with medicines should be observed:
- During work, it is forbidden to smoke, drink or eat food.
- After work, overalls must be removed, wash your face and hands with warm water and soap, and rinse your mouth with water.
- All types of work using Biorex-GC are carried out using personal protective equipment: a cotton dressing gown or a suit, a hat; rubber gloves and boots, an apron and sleeves made of rubberized fabric.To protect the eyes, airtight goggles are used, and respirators of the ШБ-1 type “Petal”, “Kama”, and “RPG-67” are used for respiratory protection.
- In case of accidental contact of Biorex-GC with skin or mucous membranes of the eyes, they must be washed with plenty of water.
- People with hypersensitivity to the drug should avoid direct contact with Biorex-GC.
- In case of allergic reactions or in case of accidental ingestion of the drug into the human body, you should immediately contact a medical institution (you should have the instructions for use of the drug or a label with you).
- Empty packaging for a medicinal product is prohibited for domestic use, they must be disposed of with household waste.
Terms and conditions of storage
The drug should be stored in closed original packaging, in a dry place protected from direct sunlight, inaccessible to children, separately from food and feed, at a temperature of from -25 ° C to + 40 ° C. Shelf life under storage conditions is 2 years. It is forbidden to use the drug after the expiration date.
Working emulsions, drainage water and wash water generated during cleaning and neutralization of premises, vehicles, containers, equipment and work clothing are collected in a concrete tank and treated with bleach (500 g per 10 l of waste water).
How to use Cypermethrin
Cypermethrin is a broad-spectrum insecticide. It is used in agriculture and forestry to protect plants from pests. At home, it is effective against cockroaches, fleas, ants and other unwanted guests.
Insects do not develop immunity to Cypermethrin, but its active substance is toxic to humans. Therefore, the drug should be used strictly according to the instructions.
Composition
Cypermethrin is made on the basis of the active substance of the same name - pyrethroid of the second generation. Its molecule contains 3 asymmetric carbon atoms, which allows the existence of 8 isomers.
The properties of the isomers are slightly different: some act on lepidopteran insects, others on hard-winged insects. Therefore, depending on the isomeric composition, the labeling of the drug will also change.
The active substance is found under various trade names. For example, it is part of the Tetriks, Tsifoks, Kukaracha, Medilis Zipper, Klopomor, Raid, Clean House, Sychlor, Sipaz Super funds. On its basis, the insecticidal chalk "Mashenka" is made.
Release form
Cypermethrin has three forms of release. In everyday life, an emulsion with a concentration of cypermethrin equal to 5–25% is used. In liquid form, the drug is a viscous substance with a consistency of honey from yellow to light brown in color with a specific smell. Other forms of release are tablets and powder for solution preparation.
Application area
At home, Cypermethrin is used against fleas, cockroaches, ants, bedbugs, and mosquitoes. In this case, the working concentration of the emulsion and the treatment area will vary, since each type of insect prefers its habitat.
To treat cockroaches, you need 0.1% aqueous emulsion of the substance. Spraying is carried out on all surfaces except textiles. The kitchen is usually processed, especially the areas near sinks, pipes (access to water), the bin and the area around it, as well as access routes to food.
Processing from ants is carried out using a 0.01% emulsion. The active substance is applied to ant pathways, as well as areas of accumulation and habitat of insects.
In the presence of bugs, an emulsion is prepared in a concentration of 0.01%. Slots are processed in furniture, floor, baseboard and wall area. The tool should not get on bedding: this can cause an allergic or even neurotoxic effect.
To process the room from mosquitoes, a 0.01% emulsion is taken. The tool is sprayed in places of accumulation of insects.
How does it affect insects?
Cypermethrin acts on insects at different stages of development. The product enters the body through direct contact with the substance and through the digestive system.
For insects, this is a neurotoxin that blocks sodium channels, disrupts the transmission of nerve impulses and the functioning of the central nervous system as a whole. This leads to paralysis: the insect loses its ability to move, eat, and reproduce.
Instructions for use
Before using Cypermethrin, the dose must be calculated taking into account the type of insects and the area of the treated surface. Before spraying, remove people and pets from the premises, remove aquariums and terrariums, hide food, personal hygiene items and utensils.
It is better to prepare the working solution on the street, and if this is not possible, then in a well-ventilated area. Do not dilute the product by eye, always accurately measure the amount. Exceeding the dosage can be dangerous to your health.
Keep in mind that after processing insects can begin mass migration, so spray not only your favorite habitats recommended by the Cypermetrin instruction, but also other surfaces. At the end of the work, open the windows and leave the room for 1.5 hours. During this time, the rooms will be ventilated, and insects will die.
When working with Zipermetrin, be sure to use personal protective equipment.
Healthy adults can return to the house after one and a half hours of airing to complete the cleaning. And children, pregnant women, allergy sufferers and people with severe illnesses are better to go in a day.
Human impact
Cypermethrin in high concentration can be dangerous to humans. Poisoning with this agent causes increased salivation, convulsions, impaired coordination of movements and concentration of attention, pupil reflex.
Therefore, when processing rooms, it is important to protect the skin, mucous membranes, respiratory tract. The clothes in which the treatment was carried out will have to be removed and washed in hot water or discarded. During processing, you can not drink, eat or smoke, and at the end of the work you need to wash your hands with soap and rinse your mouth.
Cypermethrin is easy to use, effective and rarely requires repeated disinsection. But when handling the product, be careful not to exceed the recommended dosage.
leave a comment