
Hello! Recently I went with my friend Catherine to our lake to sunbathe. At the very beginning, she asked me to smear her back with suntan lotion.
And there she was in horror! In the sense that there was some kind of rash all over the back.
Then a friend told me about the causes of this phenomenon on her skin. I consider it important to share this information with you, friends. Now I’ll tell you about the subcutaneous tick in humans, symptoms of its activity and possible consequences for the human body. You need to be very careful about your health.
The content of the article:
Subcutaneous tick
The microscopic subcutaneous tick Demodex folliculorum (“long” tick) or Demodex brevis (“short” tick) lives on the scalp and on the skin of the face. This tiny parasite can completely ruin the life of anyone.
A subcutaneous tick causes a skin lesion in people and animals - demodicosis. The tick settles in the hair follicles of the head, eyelashes and eyebrows, in the ducts and secretion of the sebaceous glands of the skin of the face.
According to researchers, women are more likely to experience this disease.
FACT: it is believed that more than 20% of people are carriers of demodicosis, however, no clinical signs are detected.
Signs of illness
In its manifestations, a subcutaneous mite lesion is very similar to rosacea or acne. Peeling of the skin and its redness are noted, itching may occur, constant or intensifying after applying tonics or washing with cold water.
When a skin tick is affected, the following parts of the face are more likely to suffer: eyelids, forehead, chin, nasolabial folds and superciliary arches. Exacerbations of demodicosis occur in autumn and spring.
Infection
Infection with a subcutaneous tick occurs from a person or from pets by contact. Household infection is also likely: through bedding, hygiene items, clothing. You can pick up a tick in hairdressing salons, massage rooms.
Risk factors
As mentioned above, it is not unpleasant to have a subcutaneous tick as such - in itself, it cannot harm a healthy person - but demodecosis, which is caused by a tick.
Risk factors include:
- dysfunction of the sebaceous glands, changes in the composition of sebum, vascular changes;
- some skin diseases (rosacea, acne, seborrhea);
- prolonged use of hormonal corticosteroid ointments;
- teenage years;
- pregnancy;
- stress.
Unfortunately, non-specialists react with unacceptable ease to the appearance of acne on the face and body. The appearance of such problems is attributed to age and ordinary acne, which sooner or later should disappear by themselves.
Forced to grieve: demodicosis caused by a subcutaneous tick does not pass by itself. A disease can travel from one part of the skin to another, existing for years and spoiling the life of its "donor".
Extrusion of acne in case of damage by a subcutaneous tick only leads to an exacerbation of the infection, since during this process ticks are pressed into healthy areas of the skin and affect them.
Diagnostics
To diagnose demodecosis caused by a subcutaneous tick, scraping is performed from any affected area of the skin. Then, a study of the taken material is carried out under a microscope to identify the presence of tick-pathogens.
Treatment
The treatment of demodicosis caused by a subcutaneous tick is a long and difficult process. Its complexity is that often this disease develops against the background of a decrease in the body's defenses and has concomitant skin problems. The tactics of therapy include suppression of the parasite, treatment of background diseases and increase immunity.
An important point in the course of treatment is diet. It is necessary to exclude from the diet spicy, spicy and salty foods, foods rich in carbohydrates and fats. Those who are treated for damage by a subcutaneous tick are recommended to consume a large number of fruits, vegetables, trace elements, fiber, dairy products.
During treatment, face masks, especially those containing honey, should not be used. It is necessary to limit sun exposure. With a visit to the baths and saunas, you should also wait a while until better times.
Subcutaneous tick in humans
This disease causes irritation of the skin, caused by the ingestion of a subcutaneous tick in the inner layers of the skin. The demodex tick lives in the sebaceous glands of the skin and is considered conditionally pathogenic.
A subcutaneous tick is found during analysis on the body of almost all people, treatment is required only in cases where the tick penetrates the inner layers of the skin and causes harm to humans. During normal functioning of the immune system, the Demodex tick is not dangerous to human health and does not require treatment.
Symptoms of demodicosis in humans
A tick under the skin in most cases settles on the head, this behavior is due to the fact that the sebaceous glands on the face are more active. In more serious stages, the tick may appear on the back and arms, can be seen in detail in the photo.
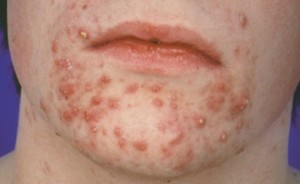
The main signs of a subcutaneous tick:
- Rash on the face - the first stage is redness of the skin, rash of acne, ulcers, papules.
- Redness of the skin - often the face acquires a persistent redness that does not go away over time.
- Demodecosis of the eyelids - can cause eye irritation, tearing, hardening of the skin.
- Unpleasant itching - on the skin where the tick has spread, itching and dryness of the skin occur.
- Vasodilation - the patient forms a vascular network, which remains and requires additional treatment even after successful treatment of the skin from ticks.
In the process of the development of the disease, four stages of erythematous, pustular, papular and combined forms of the disease pass.
Long-term illness can lead to visual impairment due to damage to the cornea and iris.
How to diagnose a disease
To remove parasites, you first need to make sure that the acne is caused by ticks. Symptoms may vary in different people, so you need to resort to a special analysis that will show the real cause of the disease.
To identify parasites, scraping of the sebaceous glands located on the body should be done from the contents of acne or hair follicles should be used for analysis. These methods allow you to detect and make an accurate diagnosis of the patient.
Before taking tests for demodicosis of the eyes, you should refrain from hygiene procedures a few days before the tests. In the clinic, the doctor will carefully take particles of keratinized skin of the eyelid with a cotton swab and, after analysis, will make a diagnosis.
To check the skin of the face does not require special preparation, you can take the analysis in any form.
Many are interested in what a subcutaneous tick looks like, but the fact is that this parasite can only be examined under a microscope. In its form, it resembles an ordinary tick, but with the back of the body from the worm.
How to get rid of ailment
It should be treated not only the skin in which the parasite has settled, but also the very reason why the subcutaneous tick was able to penetrate inside. Treatment consists of an integrated approach, and not just the destruction of subcutaneous ticks.
If the patient has found subcutaneous mites in an acceptable amount, there is no need to carry out treatment since a tick under the skin is observed in many people and does not cause troubles and symptoms of the disease.
Diet - to cure the disease, you should improve the diet, for this you need to abandon fried, spicy, salty, fatty and smoked foods. Sour-milk products (kefir, yogurt, sour cream, fermented baked milk and others) should be added to the menu; vegetables and fruits in large quantities must be present in the diet.
Proper and healthy nutrition will improve the condition of the body, raise immunity, which will increase the chances of a speedy recovery.
Drugs - prescribe an internal intake of antihistamines (diphenhydramine, tavegil, suprastin), they should be taken 3 times a day. Long-acting drugs are taken 1 time per day (zyrtec, clarithin).
To prevent subcutaneous mites, it is enough to monitor the cleanliness of the skin, regular water procedures with skin care products will reduce the likelihood of infection by several times.
Who is attacked
If a subcutaneous tick was found on the skin and does not cause trouble, then you do not need to fight it.
The parasite itself cannot penetrate the skin of a healthy person and harm him, but there are still some conditions under which the body is weakened and more susceptible to the attack of the parasite, and during this period you should be very careful and use a skin care product so that had to further treat the disease.
Factors that increase the risk of the disease:
- Skin diseases (seborrhea, acne);
- The use of hormonal corticosteroid ointments;
- Incorrect work of the sebaceous glands;
- Teenage years;
- Pregnancy;
- Constant stress.
Often people ignore the appearance of acne and acne on the skin, thinking that they will pass on their own after a while, but in cases of similar symptoms with a subcutaneous tick, you should rather seek help from a specialist so that he prescribes drugs to treat the disease.
Sulfuric ointment
This tool helps to cure various skin diseases well, sulfuric ointment has proven itself in the treatment of subcutaneous ticks. Sulfur ointment has a drying effect so that the skin does not dry out, moisturizing ointments should be used.
Sulfur ointment has antimicrobial and healing properties and, if it comes into contact with the skin, causes the death of the tick and other parasites. The healing effect accelerates the restoration of the skin.
Sulfur ointment is often used to treat scabies in children older than 2 months. This tool is the safest for children, and given the fact that the subcutaneous tick is afraid of this ointment, its use in the fight against parasites is simply invaluable especially for children.
In the case of a subcutaneous tick, the ointment is applied to the affected areas of the skin, or the entire damaged part of the body is smeared.
The product is applied to the skin and is not washed off for 3-5 hours, the drug must be used once a day. Some recommend rinsing off the product with oil, but you can also use boiled water, having previously cooled it to room temperature.
The course of treatment with a subcutaneous tick lasts 7-10 days.
Demodecosis: causes, symptoms and treatment of a subcutaneous tick in humans
Demodecosis in humans is a chronic inflammatory disease of the skin, the cause of the development of which is a small tick.
The development of the pathological process begins only if the local immunity of the skin in a limited area is reduced and the subcutaneous tick is able to penetrate deeper.
That is why a simple detection of a demodex tick in a skin scraping or secretion of the sebaceous gland cannot become the reason for establishing a diagnosis of demodecosis - with the correct study, the pathogen is detected in almost all people.
Causes of the disease
Typical places for preserving the tick population are facial skin - the pathogen can live there indefinitely. The subcutaneous tick population will be maintained throughout the life of the host, but outside the body, the tick very quickly dies.
Recent studies have not confirmed that demodicosis in humans depends on the patient’s gender - the state of immunity and the physiology of the skin are much more important.
A predisposing condition for the development of the disease is a change in the regimen of sebum secretion, its composition, and the presence of concomitant skin diseases (allergies, pyoderma).
The life cycle of the parasite proceeds in the thickness of the skin - the fertilization of the female and the maturation of the eggs takes place there, after that with tick oil, the tick larvae stand out on the surface of the skin, where most of them die for one reason or another.
The remaining amount with the preserved immune status of the body is clearly not enough for the development of the clinical picture of the disease - subcutaneous mites can only spread over the skin, but do not have the ability to penetrate inside.
Active development of the parasite is possible only in those areas where the sebaceous glands of the skin produce an increased amount of fat - a tendency to seborrhea is a predisposing factor.
In recent years, several studies have been conducted, the purpose of which was to study the development of the disease. Their results prove that a subcutaneous tick in humans, due to its own enzymes, changes skin fat and secretes a special substance into it that can cause deep skin edema, but local protective mechanisms compensate for this effect.
In the case when the number of the pathogen exceeds the critical (30 pieces per sebaceous gland), the body’s reserves are exhausted, and the patient has a clinical picture of the disease.
That is why some dermatologists believe that a characteristic change in the skin, which was previously considered different forms of demodicosis, is a manifestation of the underlying disease (rosacea).
It should be noted that the unjustified or prolonged use of medications (including those containing steroid hormones and antibiotics), improperly selected cosmetics can provoke an active inflammatory process, if the skin type is incorrectly determined and the cosmetic product is chosen incorrectly, the production of sebum increases several times.
Poor nutrition, which includes a large amount of carbohydrates and preservatives, excessive consumption of coffee or tea, excess salt, spices and pepper, smoking and alcohol abuse can change the production of skin secretion and cause a large number of diseases that can also provoke demodecosis.
Important in understanding the causes of the development of the disease is the fact that suggests that only a subcutaneous tick that lives in humans can become the cause of demodicosis.
A subcutaneous tick from person to person is transmitted only through close contact or with household items, but a vivid clinical picture of the disease occurs only with a progressive increase in the number of pathogens in a particular patient, so there is no need to isolate the person from others.
Symptoms
In the vast majority of cases, the main manifestations of the pathological process are concentrated on the patient’s head, and only in severe cases can the manifestations of demodecosis spread to the upper back and chest.
Demodecosis of the head arises precisely because the sebaceous glands of the skin are very active in this area and the composition of the sebum is sensitive to the slightest changes in the hormonal profile of the body, the state of internal organs and systems, and the immune status of the patient.
The main signs of facial demodicosis, most dermatologists consider the appearance of rosacea. In this case, the patient is found:
- Persistent hyperemia of the skin - most often it focuses in the central region, but can spread to the chest and back.
- A variety of rashes on the face - in the initial stage of the pathological process, small pink papules form on the background of reddened skin, which turn into elements of an abscess rash (pustules, acne, acne).
- A sharp tightening of the skin in the affected area, which is felt in the later stages of the disease.
- The formation of various convoluted vascular networks and diffuse or local vasodilation - the patient develops telangiectasia, which persists even after the cure of the main inflammation.
- Compaction and marked redness of the skin of the nose (rhinophyma), often detected in men;
- Demodecosis of the eyes - occurring in about half the cases, the main manifestations of which are dryness, pain in the eyes, severe redness, sensations of the presence of a start-up or foreign body, often with severe lacrimation.
Acute itching, burning, a pronounced feeling of tightening of the skin may occur throughout the skin of the face.
Demodecosis of the eyelids often causes the patient to go to the ophthalmologist for blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelid) or blephoroconjunctivitis.
In this case, patients notice that pustules and scales form on the eyelids, thin out and become brittle eyelashes, and when the disease progresses, itching, sharp redness, lacrimation, and the appearance of a foamy discharge appear.
Patients often experience barley, which in its development does not reach the resolution stage and on the eyelid a halazion forms (a cicatricial change in the tissue of the eyelid of a spherical shape).
Very often, against the background of eye demodicosis, infection of a bacterial infection (bacterial, fungal, chlamydial, viral) penetrates - the inflammatory process is very difficult and standard therapy is poorly delivered.
With a prolonged course of the disease, damage to the surface layers of the sclera, cornea of the eye, iris, ciliary body can occur, which can lead to a sharp decrease in vision due to clouding of the cornea and a change in the density of the transparent media of the eye.
Diagnosis of demodicosis and detection of subcutaneous tick
To establish the diagnosis of demodicosis, the symptoms of which can vary in different people, it is necessary not only to detect a subcutaneous tick in patients, but also to see the characteristic clinical picture of the pathological process.
For laboratory research, you can use the secret of the sebaceous glands of the skin, the contents of the blackheads that are secreted on the mucous membrane of the eyes, and also examine the eyelashes or hair follicles - this is where the subcutaneous tick is most often determined.
When examining a patient with suspected demodicosis of the eyes, it is necessary to advise the patient in advance not to make a hygienic toilet of the eyes within the next 2-3 days before the study. Only after this, with the help of tweezers and a cotton swab, the scales taken at the edge of the eyelid or several eyelashes are taken.
The resulting material can be examined without preliminary staining, most often the doctor can make a diagnosis in the presence of the patient, but it is possible to consider that the cause of this skin condition is a subcutaneous tick, only if a sufficient amount of the pathogen is detected in the laboratory.
Treatment
In the vast majority of cases, it is impossible to cure demodicosis only using local drugs. The main goal of treatment is the elimination of the causative agent of the disease, the exclusion of exposure to skin irritating factors, the restoration of general and local immunity, the normalization of blood circulation and skin metabolism.
Treatment of demodicosis necessarily involves a diet.In the patient's diet, the consumption of fried, fatty, spicy, salty, spicy and smoked foods, foods rich in simple carbohydrates is limited. Mandatory use of dairy products, an additional introduction to the diet of vegetables and fruits.
During treatment, the patient is recommended to abandon the use of cosmetics, which in themselves can provoke the accelerated development of the pathogen. Excess insolation, thermal procedures are prohibited, the patient is recommended to protect the skin from the effects of damaging factors
Most dermatologists recommend that, when detecting demodicosis, treatment should begin with the appointment of drugs from the metronidazole group (Trichopolum, Tiberal).
Most often, the duration of therapy is 4-6 weeks. Such treatment necessarily takes place under the control of the general condition of the patient, a clinical and biochemical blood test.
In addition, it is necessary to prescribe antihistamines inside - both short-acting drugs (tavegil, suprastin, diphenhydramine, diazolin), which are taken 2-3 times a day, and prolonged-action drugs (clarithin, zyrtec), which are taken 1 time per day.
For external treatment of demodicosis, standard acaricidal therapy (anti-mite) is used. In this case, the same drugs are prescribed as for the treatment of scabies, a water-soap emulsion or benzyl benzoate ointment, Wilconson ointment, sulfur ointment, metronidazole ointment.
An obligatory component of treatment is the use of cryoprocedures, during which the main focus of inflammation in the skin is removed.
Demodecosis disease - symptoms, causes, treatment
Demodecosis is a skin lesion caused by an acne mite tick. This pathology is more common in women. Ticks live in the hair follicles, duct and secretion of the sebaceous glands of the skin, often with seborrhea. The favorite localization of the tick is the eyelids, facial skin, the area of the superciliary arches, forehead, nasolabial folds and chin, ears.
Mite vital products contribute to the development of allergies, acne (acne), rosacea on the face; cause a specific eye lesion - demodectic blepharitis and blepharoconjunctivitis.
The disease is chronic in nature with seasonal exacerbations in spring and autumn.
The complexity of the fight against subcutaneous ticks is determined by the fact that it is our symbiont, that is, its presence is the norm, and not pathology. However, these mites bring trouble only when they begin to multiply rapidly.
These ticks are found in 90% of people and animals and usually do not cause any troubles, since the body's immune system maintains their number at an acceptable level.
It also occurs with certain skin diseases, such as rosacea, vascular diseases or oily porous skin.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a subcutaneous tick bring the patient a lot of inconvenience and aesthetic problems. In the primary form of infection of the skin with demodex, redness, rash and peeling are characteristic at the sites of localization of the tick.
The primary symptoms of demodicosis are not always visible. Often, the patient does not even suspect that he is a demodex carrier. Signs of a subcutaneous tick in a person do not manifest themselves, the integument remains clean, the general appearance is satisfactory, and there are no complaints.
It can only be detected by scraping from the upper layer of the skin and laboratory tests.
The manifestations of demodicosis are such that it can be confused with other skin diseases. But there are signs of demodex, the presence of which gives a good reason to suspect the presence of demodicosis:
- itching, which intensifies at night;
- acne, peeling, redness, ulcers and ulcers;
- unpleasant tuberosity on the skin of the face, forehead and cheeks;
- the feeling of a “mask" on the face;
- unhealthy earthy gray shade of the skin;
- permanent shine on the skin, which remains even after washing and special cosmetics;
- enlarged pores;
- the wings of the nose increase in size, the nose becomes swollen, takes the form of “potato” (this symptom of a subcutaneous tick is characteristic of an advanced stage of the disease).
The following signs indicate eyelid demodicosis:
- redness of the eyes, itching, feeling of “sand in the eyes”,
- loss and fragility of eyelashes,
- inflammation of the edge of the eyelid,
- mucous discharge from the eyes, adhesion of eyelashes,
- scaly formations at the roots of the eyelashes.
The presence of demodex in the scalp should be suspected with the following symptoms:
- redness, bumps and inflammation on the scalp;
- thinning and hair loss;
- small white scales at the roots.
Symptoms of a subcutaneous tick on the arms and legs include red spots, persistent itching (especially in the evening), inflammation, pustules, pimples.
Causes of Demodecosis
Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The cause of demodicosis may lie in pathological disorders of the intestines: chronic gastritis, pancreatitis, peptic ulcer, dysbiosis. These factors provoke an increase in the number of parasite in the sebaceous and meibomian glands of a person.
Thermal effect on the skin. The demodex mite is a thermophilic microorganism, and frequent visits to saunas, steam rooms and tanning salons, taking hot baths and prolonged exposure to direct sunlight create a favorable atmosphere for the parasite.
The skin demodex recognizes electromagnetic radiation as a factor that threatens its life, as a result the process of active reproduction is launched in order to reproduce new offspring.
Wrong way of life. In people who abuse alcohol, foods high in fat, spices, salt, sugar, Demodex disease is twice as common as in patients who prefer a healthy diet. This is one of the most common infections with demodicosis.
Environmental pollution. Malicious external factors gradually reduce the protective functions of the body, from which a subcutaneous tick appears, actively multiplies and penetrates into the deeper layers of the skin. Therefore, poor ecology can cause demodicosis in humans.
Based on the above causes of demodex, treatment of the disease demodecosis begins with the settlement of disorders in the body and reduce the influence of external stimuli.
The longer you refuse competent diagnosis and treatment, the more actively the disease progresses, and the more difficult it will be to get rid of it. In order not to aggravate the course of demodicosis and minimize the time of treatment, consult a competent dermatologist.
Factors determining the effectiveness of treatment
Treatment should be aimed not only at eliminating the tick, but also at normalizing the functioning of the immune system, regulating the protective functions of the body, increasing skin resistance, improving the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
There are many schemes for the treatment of demodicosis, but all of them are based on the use of antibacterial and antiparasitic drugs, agents for regulating the functioning of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract and agents that increase immunity.
Self-medication for demodicosis is contraindicated. To enhance the effectiveness of local skin products, the doctor may prescribe adjuvants in the form of soaps, shampoos, conditioners and tonics. As a rule, these are specialized anti-demodectic drugs.
The recommended duration of treatment for demodicosis may not be effective with short-term use. And although the results are noticeable in the first weeks, it is important to complete the therapy, otherwise relapse is possible, and all symptoms will return again.
Strengthening personal hygiene with frequent changes of bed linen and towels is strongly recommended. You should also avoid exposure to hot air, visiting saunas and tanning salons, taking hot baths.
Subcutaneous tick - symptoms of infection and treatment of demodicosis
Subcutaneous tick (Acne zheleznitsa) is a parasite that lives in the sebaceous glands or human hair follicles and has sizes up to 0.4 mm. It has an elongated and translucent body. He actively moves, mainly at night, as he seeks to avoid sunlight. Demodecosis causes a disease that does not pose a threat to human life and health.
To some extent, the subcutaneous tick even protects the skin, as it feeds on bacteria that are harmful to the human body. However, under favorable conditions, the tick begins to multiply rapidly, penetrating into the deeper layers of the skin, supporting its life with sebum and dead cells.
The body of the parasite consists of dense scales, which are a kind of shell. He does not allow medicines to penetrate into it. Therefore, if a tick gets under the skin, even the most modern drugs do not always cope with it.
Causes and ways of infection
A subcutaneous tick can live in the human body for years and does not declare itself in any way. Therefore, it is very important to know under what conditions he will begin active life, bringing a lot of trouble to his carrier.
The subcutaneous tick becomes active in the presence of the following factors:
Weakening of the immune system, which is provoked by such moments:
- Long-term use of antibiotics and hormonal drugs;
- chronic diseases;
- severe stress.
Gastrointestinal tract diseases:
- The abuse of carbohydrate and fatty foods;
- Frequent use of alcohol and a large amount of coffee;
- The use of hot seasonings.
- Hormonal changes and malfunctions in the endocrine system.
Violation of the rules of personal hygiene:
- Use of other people's personal hygiene items;
- Excessive hobby for a sunbed and a bath;
- Long exposure to the sun.
- Increased production of sebum and sweat.
This is facilitated by such factors:
- Stress
- Insomnia or lack of sleep;
- Low level of physical activity;
- Nervous breakdowns.
- Continuous use of low-quality cosmetics.
All these causes excite the sexual instincts of ticks. Females strive to lay eggs in the deeper layers of the skin in order to protect their offspring as much as possible. Three days later, the larvae turn into adults.
The subcutaneous tick, inhabiting the subcutaneous layers, feeds, multiplies and dies.At the same time, decomposing, releases a huge amount of toxic substances into the skin.
And since it settles in colonies and multiplies very quickly, the body responds to such an invasion with a persistent allergic reaction. Moreover, inflammation of the skin does not cause the parasite itself, but the products of its vital activity.
It is very simple to get infected with demodicosis: the disease is transmitted from person to person. A subcutaneous tick living in the skin comes out with sweat and sebum.
The use of the same towel, common dishes, even a kiss or a handshake will result in the parasite moving to a new host. Sometimes infection may not occur, but a person will become a tick carrier.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The subcutaneous tick settles in the sebaceous glands, and then continues on its way. Therefore, the symptoms of the parasite can be found on almost any part of the body. However, the face, eyes and back of a person suffer most from him. A pimpled red rash appears on the skin, which is then converted to whiteheads.
You will need to see a doctor if the following symptoms are found:
- areas of the skin turn red and rashes appear on them, red pimples become purulent over time and turn into papules;
- the skin in the affected area turns red, the normal color does not return for a long time;
- the skin becomes very dry or, conversely, oily, constantly itching, and itching intensifies in the evening and at night;
- a distinctly visible vascular red net appears on the skin, which occurs due to vasodilation.
- intense hair loss, which is accompanied by the appearance of dandruff near the roots;
- the skin on the face shrinks and becomes like a mask, thickenings similar to tubercles appear;
- if the tick populated in the nose, the skin on it becomes very inflamed, the nose becomes like a huge potato;
- complexion becomes earthy, grayish, pores expand. This is due to the fact that the waste products of the tick are secrets and toxins that the parasite actively secretes into the skin. Moreover, every evening ticks go outside, and when they return, they bring with them countless other pathogenic bacteria;
- the occurrence of a feeling of subcutaneous movement;
- in the most advanced cases, the appearance of a serous or blood-pustular crust can be observed.
If a subcutaneous tick reaches the eye area, the symptoms will be more characteristic:
- intense eyelash loss begins;
- fog is increasingly appearing in front of my eyes, objects are not clearly visible (persistent visual impairment);
- conjunctivitis and tearing appear;
- dandruff occurs on the eyelashes;
- the eyelids turn red and harden;
- there is a feeling of severe itching, especially at night;
- hair loss from the eyebrow area is observed;
- mucus is released from the eyes.
The use of decorative cosmetics is also erroneous, with the help of which many women try to hide the manifestation of the disease on the face. Poor quality products will clog pores, which will provide additional favorable conditions for the reproduction of parasites.
The only correct solution for detecting these symptoms is to see a doctor.
To diagnose the disease, not only particles of the skin, but also eyelashes are taken for analysis. The disease is confirmed if the number of viable ticks exceeds five per one centimeter of skin.
It is important to recognize the disease on time. Indeed, in advanced cases, the disease flows into a chronic form. Small spots with pimples turn into abscesses, ulcers, are covered with scars and pigmentation. The face becomes swollen and covered with serous crusts.
The more neglected the disease, the more difficult it is to treat!
Treatment
The fight against the parasite will be long and difficult. The treatment regimen is selected individually by a dermatologist and depends on the degree of skin lesion and the presence of other diseases that, quite possibly, provoked the occurrence of demodecosis.
Most often, a treatment complex is used, which includes the following components:
- medication treatment;
- physiotherapy;
- special medical diet;
- hygiene procedures;
- a complete rejection of makeup.
Drug treatment is prescribed to cleanse the blood vessels, normalize the gastrointestinal tract, and increase immunity. The most commonly used therapy is the following drugs:
- Antiparasitic drugs that have a wide spectrum of action.
- Antibiotics.
- Preparations for the restoration of intestinal microflora.
- Drugs designed to strengthen blood vessels. They must be used, since parasites in the process of their life make the vessels that surround them very fragile.
- Immunity enhancers.
- If the body cannot cope with the disease itself, hormonal drugs can be prescribed.
It is important to remember that the use of all drugs should be agreed with the attending physician. You need to use them according to the instructions or those prescriptions that the dermatologist suggested.
Successfully apply ointments containing sulfur. The agent is applied to the affected area with a thick layer. After 6-8 hours, it must be removed with purified vegetable oil.
After that, it will be effective to apply steroid preparations to the skin, such as Flucinar or Elokom. Ointments containing metronidazole and benzyl benzoate will have an antimicrobial effect.
To normalize the microflora of the skin and relieve inflammation, drugs that contain azelaic acid are used. If demodicosis is in an advanced stage, dermatologists will recommend the use of tar ointments. These products have a pungent odor, but are very effective.
Despite the use of sufficiently effective medications and adjuvants, the cure for the disease will not come if you do not adhere to a special diet. It is necessary to exclude sweets and flour, alcohol, honey and chocolate.
Minimize the intake of fatty and carbohydrate foods. The diet must include as many fresh vegetables and fruits as possible. You need to eat low-calorie dishes, boiled meat. Drinking 2 liters of water per day is another necessary condition for a therapeutic diet.
Various procedures aimed at hardening will also be useful in the treatment of subcutaneous mites. In summer, you need to swim in open water, sunbathe under natural sunlight, and be treated with mud. Cryomassage will be very useful for skin restoration.
One of the important directions in the treatment of the disease is strict adherence to the rules of personal hygiene. Every day you need to rinse your face with infusions of medicinal herbs and wipe with alcohol tinctures. If possible, use only tar soap.
If treatment is started on time, at the initial stage of the disease, when the females of the subcutaneous tick have not yet acquired offspring, the condition will improve by 7-8 days. However, unfortunately, few can recognize the disease so early. In the chronic stage, demodicosis is treated for a very long and difficult time.
Complete the treatment by re-diagnosis.
Folk remedies
Our distant ancestors did not have modern medicines to combat subcutaneous ticks. However, they successfully treated this disease with the help of drugs that were in every home.
Yellow clay. When the first signs of the disease appear, you can use yellow clay. It must be mixed with warm water until thick sour cream and applied to the skin in those places where there are lesions with a tick. It is advisable to keep the mask on your face all night. Yellow clay has an antimicrobial effect, provides good nutrition and whitening the skin.
Laundry soap. The subcutaneous tick is very afraid of ordinary laundry soap. You need to grate it, and then foam well. Foam is applied to the face and left there until completely dry. The procedure must be repeated several times.
Mask of solid oil. A very effective mask made with your own hands from solid oil, olive oil and birch tar. All components are mixed and applied to the face.
Prevention
The subcutaneous tick in humans is highly contagious. These parasites cannot be seen without special devices, but they are at any moment ready to move from one carrier to another. To prevent the disease, do not break simple, but very important rules:
- bed linen must be changed as often as possible;
- feather-based blankets and pillows should be heat treated as often as possible;
- use only your towels, bedding, etc .;
- after playing sports, as soon as possible, change clothes wet from sweat to dry;
- be sure to take a shower after exercise;
- you can’t always use decorative cosmetics, since powder and some greasy creams provoke the spread of the parasite (under no circumstances should anyone use other people's cosmetics);
- if there is a disease of the gastrointestinal tract, do not postpone their treatment;
- proper nutrition is the key to a healthy body, watch your diet, and this will help prevent many problems;
- maintain immunity with fresh vegetables and fruits, drink herbal teas;
- if any rashes are found on the skin, consult a dermatologist immediately;
- never try to cure a subcutaneous tick by yourself, as you will lose precious time and the disease will go into a chronic stage.
By following these simple recommendations, you eliminate the likelihood of infection with a subcutaneous tick to a minimum.
leave a comment