
Hello! For most of the year, cycling is my primary means of transportation.
I keep my vehicle in a small garage. Without locks, without bolts - we have no small thieves. But I was scared the day before yesterday for a completely different reason.
I went behind the bicycle, extended my hands to it and immediately flew out of the garage with a bullet. On the seat was a spider with long slender legs. It was later that I already knew all the details about him, and at first I was very scared. I want to tell you in detail about this type of spiders so that you are not afraid of it.
The content of the article:
Is it worth it to be afraid of a haymaker (kosinozku)?
The haymaker is a strange land animal (class Arachnids) with very long legs. It has an ovoid body, cephalothorax.
About 60 species of hayfields live in Russia, although there are much more of them in the world. The most common species in our country is the common haymaker (Phalangium opilio).
Common haymaker
Mowers are not considered spiders, but arachnids. Sometimes they are called false science. Scientists note that haymakers are perfectly adapted to life on land. They usually hunt at dusk or at night. Day less mobile.
They can usually be seen in their characteristic pose with legs spread wide. There are species that feed on snails and slugs, using special claws. Many haymakers are content with small insects, plant foods and ... animal corpses.
At dusk and in the first half of the night, the haymaker searches for and absorbs food: not only plant, but also animal: eats small insects. This species is common in Eurasia and North America. A similar species (Opilio parietinus) is found in the steppe strip.
It is easy to recognize the female haymaker by the dark spot (with a bright white border) on the back. The male "saddle" does not have such clear boundaries and looks vague.
The female has a longer body (9 mm) than the male (up to 7 mm). But her legs are shorter. The female lays eggs in the soil, dry leaves, moss. Before that, she studied the place for a long time, after which she plunged a long ovipositor into a loose substrate.
It will take time, more precisely, 5 - 7 molts, before the little rhino-boots can reproduce themselves. This happens from July to October. Only young and eggs hibernate.
Who needs long legs?
The haymaker has long legs that are easy to handle. Nature has devised a unique principle for controlling these limbs.The legs are bent with a muscle that tightens the tendon (muscular-mechanical action). They are unbent due to hemolymph pressure, which accumulates inside (hydraulic effect).
Such a debugged mechanism is incredibly economical: it avoids the need to have many small muscles. The haymaker can calmly entwine with his paw any blade of grass or small pebble. A walking rhinestone easily overcomes obstacles and can move even in hot or cool times, carrying the body high above the surface.
The movement mechanism of the haymaker was of interest to specialists in the field of bionics (an applied science that studies the use of the principles of functioning of living forms in technology). Snowflakes give ideas to writers and artists, they are developed by experts who work on the creation of ... walking devices for exploring other planets.
Such an automatic machine is thought of as a walking device, which has a number of advantages over an automatic machine on a wheeled or caterpillar track, especially in the sense of orientation and overcoming obstacles.
The equipment intended for research and movement is concentrated in a sealed capsule, towering on several elbow-shaped long legs.
At the ends of the legs and joints there are sensors that send information about touching the foot to the substrate and its relative positions, according to which further coordinated movements are programmed at each moment.
For example, it is believed that the most appropriate combination of mechanical and hydraulic principles that is observed in the foot of the haymill is most appropriate for bringing the legs into motion: flexion due to the cord passing through the joints to the end of the leg, and extension of the pressure of the fluid filling the leg (“Animal Life” Volume III).
At the first danger, the haymaker can easily part with his limbs. The wound instantly heals, so hemolymph loss does not occur. The torn leg continues to twitch for some time (up to half an hour). This is due to the arbitrary contraction of special muscles.
Similarly, lizards act that give their tails to the enemy. An autotomy (this is what the “voluntary” loss of body parts is called) often saves the animal from death.
The longest, as a rule, is the second pair of legs. The male haymaker ordinary - up to 54 mm. These legs read information about the condition of the ground, stone or other support. The red dots on the legs or body are the larvae of ticks that have stuck to the rhizomes.
Fear of Spiders - Arachnophobia
Many people suffer from fear of spiders (arachnophobia) and all kinds of arachnids. Some simply do not like them, others cannot touch them or fall into a state of panic in contact with these animals. Haymowers, completely harmless to humans, are no exception. Especially when they are on the human body.
Psychologists give a lot of advice. The simplest and most interesting one seemed to me to be that it helps to reduce the degree of tension, to change the negative attitude to the hayers on a positive or neglect. There are many different game options. For example, give a name to a specific kinozinki. Call her Anyuta. Or Clara.
To come up with the life story of this cute rhino, sympathize with her. It is said that such a "dialogue" often leads to the fact that a particular haymaker ceases to be nasty and becomes quite cute.And this is the first step towards overcoming arachnophobia.
Haymaking Spiders
Haymaking spiders, or so-called centipedes, belong to the family of spiders from the infraorder araneomorphic. The family received this name because of the similarity of long-legged spiders in the shape of a body with hayers.
This family includes over 1000 species, which are combined into 84 genera.
Haymakers live on the earth for about 0.5 billion years, and during this time they have not changed at all, which indicates that they are perfectly adapted to living in the harsh conditions of the world of invertebrates.
Structure
Hay mowing spiders are common throughout the world. The vast majority of them live in the tropics. They often coexist with people in their homes. In the middle zone of Russia, in Ukraine, Belarus, the Pholcus species is widespread.
Haymakers are small spiders that have a wide variety of shapes (from spherical to elongated) and body length from 2 to 10 mm.
We will never meet a haymaker weaving a web, equipping a den or descending on a thin thread of web, as these arthropods do not have spider warts.
There are eight eyes on the round millet (two small medial and six lateral, forming triads), but some spiders have fewer eyes, mainly those living in caves. Haymen have eight long thin legs on the cephalothorax.
The length of the legs varies from species to species, from short legs to very long, up to 0.5 cm. Many haymakers have a pair of excessively long legs that are adapted, like antennas, to touch surrounding objects, find food, and avoid danger, since a pair of eyes on the crown of the head does not provide clear vision.
Long, clumsy legs help to preserve their life, because they raise the body of spiders above the level where most invertebrate predators hunt.
Breeding
Haymakers are dioecious animals with internal insemination. After fertilization, the female lays eggs in the soil from an elongated ovipositor, extending from the base of the abdomen, and then buries them. In most species of hayfields, the full development cycle is 1-2 years.
A feature of the copulative organ (cymbium) is the presence of a distal process - a procursus with teeth, between which there is a plastic membrane that swells during mating.
Food
Haymaking spiders weave snare-shaped hunting nets, which are randomly-tangled jagged cobwebs, and hang upside down on them. Spiders build their cobwebs in dark, moist caves, on trees, under stones, and in various buildings.
In a person’s dwelling, they are located in warm and dry places near the windows. Hayers mainly hunt at night. The networks of hayfire spiders do not have sticky properties, so they are messy. When it enters the network, the victim tries to leave it and becomes increasingly entangled in them.
The spider approaches it with great speed, envelops it and inflicts a fatal bite, after which it can eat prey right away, and can leave it for the future. Hay mowing spiders are omnivorous, except for spiders, small insects, ticks, they can feed on plants, mushrooms, living and dead animals, etc.
It is not necessary for haymakers to pre-prepare their prey for use, as they can tear the victim and eat small portions of solid food, unlike other spiders. These arachnids are not poisonous.
Haymaker
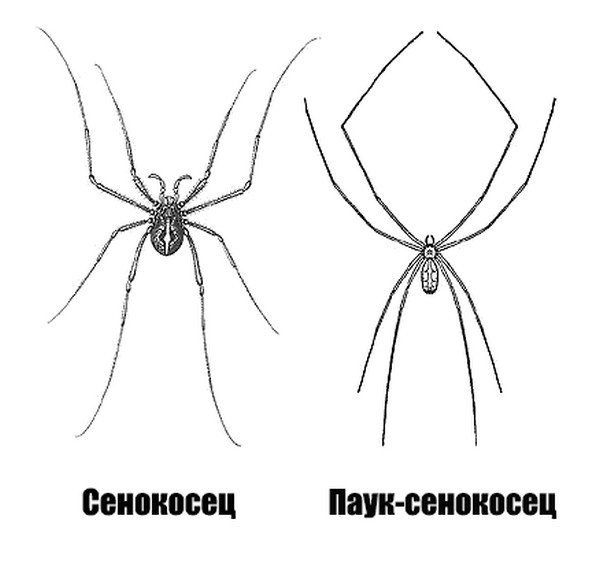
The haymaker (Opiliones sp.) Or reaper is also known by other names, such as Papa long legs, or Grandfather long legs. They are a bit like spiders, having eight long thin legs and a cephalothorax, and therefore are with them in the class of arachnids (Arachnida).
On this, the similarity with spiders ends with the hayers, since most of them have only two eyes (some cave species do not have them at all), are not poisonous, do not produce a thread to weave a web, and it is obvious that the body is not divided into two segments, and they don’t drop the esoskilet when they grow.
The hayfields have come a long way - more than 400 million years, and have not changed at all during this time, which indicates that they are well adapted for life in the harsh conditions of the invertebrate mini-world.
This success may still be related to their omnivorous nature. In addition to small insects, spiders, ticks, they eat everything: plants, mushrooms, living and dead animals, etc.
Unlike spiders, who still have to get to the insides of invertebrates, and pre-prepare them so that they become digestible, hayers can tear off and eat small portions of solid food, therefore, have another advantage for survival.
The legs, if the predator grabs the haymaker, fall off easily and continue to contract for a long time, distracting attention from the animal itself. These continuous reductions are very reminiscent of mowing, hence its popular name.
Unlike spiders, torn limbs from them are not restored, and therefore it is so often possible to meet a haymaker on five, and sometimes on four legs.
Long clumsy legs also help to save life because they raise the body above the level where most invertebrate predators hunt. Therefore, despite the relatively simple structure in form, it nevertheless proved to be a very effective means for finding food and defense.
The color is dark, although there are species and light. They can live anywhere, and since they hunt mainly at night, they can be met only by chance, turning their shelters among the leaves, under the bark, under logs, stones, etc.
Hayman spider: long-legged spider description
Among the representatives of the class of arthropods, often penetrating the human dwelling, it is worth noting the spider of a haymaker, a meeting with which is unlikely to be pleasant.
This is a common family that includes about a thousand species. You can also find other names for the spider: a centipede, a reaper, a warbler, a false spider. Get to know him better.
Who is it?
An ordinary hayman most often comes across in apartments and houses as an uninvited guest. What does he look like?
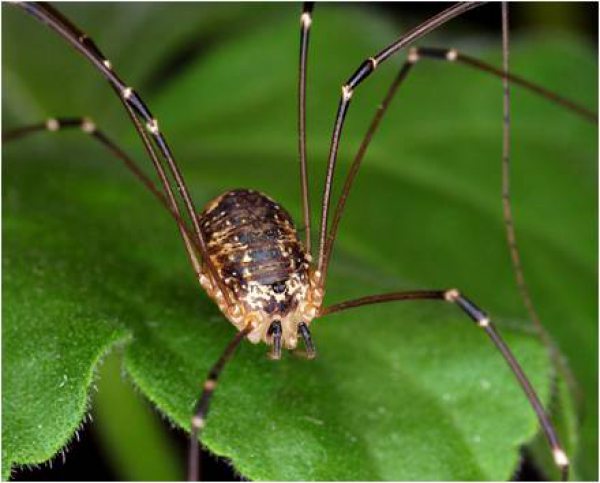

In the photo you can see that the cosine has eight long legs, which are surprisingly curved. Also, this representative of spiders can be recognized by such signs:
- the body resembles an egg in shape, consists of two departments - cephalothorax and abdomen;
- body length can be from 10 mm to 20 mm;
- the body covers the shell;
- the abdomen consists of segments tightly adjacent to each other;
the articulation of the cephalothorax and abdomen is very thin, almost imperceptible; - there are eight eyes;
- mustache is absent;
- legs are pairwise located in the cephalothorax, absent on the abdomen;
- the largest is the second pair of limbs. Average leg length up to 5 cm;
- four legs are used for walking, two for grabbing food;
- the limbs are hollow inside, filled with hemolymph, which replaces the blood;
- at the ends of the legs of the claw;
- Glands are located on the lateral sides of the cephalothorax: in case of danger, they secrete a special substance with an unpleasant odor that scares away predators. That is why such spiders have very few enemies;
- no teeth, food is ground with chelicera.
Interestingly, the species that live in the forests have short legs, while urban residents have long, thin legs.
DNA research revealed an interesting fact: hayfields are much closer to scorpions than to spiders.
Of particular interest is the hayfoot web, which is devoid of a sticky enzyme. However, once the victim is in the network, the victim will not be able to break out of it - the messy weaves are so cunningly executed.
When injured, the wound heals in a few moments, preventing hemolymph from leaking. However, in place of a damaged or torn limb, a new one will not grow. Due to the nerve endings, the torn leg will impulsively twitch.
The movement of the limb resembles haying, hence the name of the arthropod. Loss of limbs for spiders is not fatal, often they themselves tear off the leg as a distraction to escape from danger.
Life expectancy of reaper spiders in favorable conditions is up to 2 years.
Types of Snowflakes
There are several thousand species of hayfields, which are divided into daytime and nighttime: daytime have a variegated color; nightly painted black, gray or brown.
It is customary to distinguish four suborders:
- Eupnoi are distinguished by very long legs and large eyes. It is the representatives of this suborder who find refuge in the home of man;
- Cyphophthalmi - these are the most primitive representatives of rhinoids, resembling ticks in appearance. They have a short body length - up to 3 mm, short legs and an oval, slightly elongated body. You can meet such spiders in tropical and subtropical countries;
- Dyspnoi - owners of short legs and developed chelicera, prefer to live in the southern latitudes. Due to their “claws”, these spiders can easily get mollusks from their shells;
- Laniatores are the inhabitants of the tropics, the suborder, despite its impressive size, is among the little studied. The body often has a bright unusual color and bizarre growths.
Habitat
The haymaker spider is found almost throughout the globe, but the most comfortable conditions for it are southern and temperate latitudes, forests. Certain species inhabit cities.
Food
Spiders belong to predators, catch prey with the help of their intricate web. The insect, getting into the network, gets confused, and the haymaker quickly gets to the victim from his shelter, killing her.
The haymaker eats various living creatures:
- slugs;
- ants;
- snails;
- caterpillars
- Zhukov;
- even other arthropods.
Often spiders are forced to use carrion, excrement, rotting organic remains, mushrooms.
This arthropod can get into the apartment in several ways:
- through holes and crevices in the walls and floor;
- on people's clothes and shoes.
Having entered the room, spiders choose warm, dry places and begin to weave their network. For the winter, they prefer to rise higher, closer to the ceiling.
Lifestyle
The spider prefers to hunt at night, hides during the day, can sit for many hours completely motionless, spreading out along the wall.
The haymaker moves well and easily on his long legs, feeling quite stable. The speed of movement is quite fast.
Breeding
Moths spiders begin to mate in the last weeks of summer, mating dances are absent, but fierce battles of males for a female are often observed. The breeding method is internal insemination, after which the female lays more than 500 eggs in the soil.
During the season, the female manages to postpone several clutches with a break of about 21 days. Young spiders molt about 5-6 times, after which they enter puberty.
Is a haymaker dangerous for humans?
Despite the fact that this spider is poisonous, the strength of its poison is enough only to paralyze victims caught in the web, poison is completely unafraid for humans. But at the same time, such a neighborhood is not always pleasant, and for some people, the appearance of a haying spider causes a real panic attack - this fear is known to science and is called arachnophobia.
How to rid your home of these unpleasant neighbors? First of all, you should get rid of the cause of their appearance, that is, remove cockroaches, flies and other insects attractive to spiders. Also, the elimination of their cobwebs will be an effective way to destroy hayfields, for this you can use a broom or vacuum cleaner.
After harvesting, it is necessary to carefully close all the cracks so that the spiders of the hayfields could not return. For preventive purposes, citrus peels have proven themselves well: their aroma repels arthropods.
Also for this purpose, you can use spray guns with tinctures of peppermint, eucalyptus. In the corners, you can put small containers with a solution of vinegar.
Do not forget that hayfields often bring benefits, helping to clean the apartment from unpleasant insects such as bugs or cockroaches. Despite the unattractive appearance, these creatures are absolutely safe for humans and cannot harm him.
Haymaker - description, characteristics, structure
Why in common people a haymaker is called a kinozhenka? The haymaker got this name because of the special structure of the limbs. The torn paw of the rhino continues to make movements resembling mowing.
A hayfare (rhinozoot) is similar to a spider, but unlike spiders, the external structure of the hayfields is different: they have an abdomen, consisting of tightly closed segments with a wide rigid base that passes into the cephalothorax.
In spiders, the connection between the abdomen and cephalothorax is thin. Also, do not confuse the haymaker with mowing mites, although these three species of animals belong to the arachnid class.
Structure
The body of the haymaker is small (1-5 mm), covered with a shell. Some individuals have a large, ovoid body, up to 22 mm long. One pair of simple eyes with low vision is located on the protruding part of the cephalothorax. Long legs end with claws.
Due to the absence of extensor muscles, the haymakers have a hydraulic principle of movement. Hollow inside the limbs are filled with hemolymph, replacing blood milliflowers. The legs straighten when pressure builds up inside.
Short pedipalps (the second pair of limbs) and legs perform the functions of smell and touch.Hayers feel objects with the longest limb.
Types of mowing grass
The world population has nearly 7 thousand species of hayfields. Nocturnal species of rhinoceros have a black, brown or grayish color. Daytime individuals are colorful.
The classification of hayfields is divided into 4 main suborders:
Cyphophthalmi: primitive small trinkets. Outwardly resemble ticks, 2-3 mm long, with short legs and an oval oblong body. The habitat is the tropics and subtropics of Africa, America and Eurasia. The suborder includes the families Sironidae and Stylocellidae;
This suborder includes mittens that we meet on the walls of residential buildings: Phalangium opilio and Opilio parietinus. The suborder consists of 2 families: Phalangiidae and Caddidae;
Dyspnoi: Slow suborder of haymakers with short legs. Some families of the suborder have powerful chelicerae (oral appendages in the form of claws), which allow hayers to extract mollusks from shells.
The subspecies is distributed throughout the world, including in the southern regions of Russia. The suborder consists of 4 families: Ischyropsalidae, Nemastomatidae, Trogulidae and Dicranolasmatidae;
They live in tropical America, Africa, India and Australia. The suborder consists of 5 families: Cosmetidae, Gonyleptidae, Triaenonychidae, Oncopodidae, Phalangodidae.
Where does it live?
Haymakers can be found in all countries of the world. They are most common in southern and temperate climatic zones. The bulk of the population inhabits meadows and forests. Some species prefer megacities, during the day they can be seen on the walls of buildings.
What does a haymaker eat?
The structure of the oral apparatus allows hayers to chew and digest food. Like any predators, rhinoceroses feed on animal food: caterpillars, mosquitoes, bugs, ants. Do not shun carrion, excrement, the remains of rotting organic matter. "Gourmets" prefer snails and slugs. They can eat mushrooms and other plant foods.
Breeding trunks
The mating period begins near the end of summer. There are no mating dances among the haymakers. Fierce battles of males for a female are frequent.
Reproduction occurs as a result of internal insemination. With the help of an ovipositor, a fertilized female haymaker lays eggs in the soil. One clutch can count over 500 eggs.
Some species of male hayfields are endowed with a maternal instinct: they protect the clutch after mating and protect the eggs from voracious and indiscriminate females in food.
Hatched young rhizomes molt 5-7 times, after which puberty sets in. During the season, the female manages to lay eggs several times, with a break of 3 weeks. Under favorable conditions, the life cycle of the haymaker is 2 years.
Interesting Facts
Not dangerous for humans, the haymaker brings invaluable benefits, destroying many types of insect pests, and is also an excellent nurse, absorbing and processing waste and decaying organic matter.
Loss of limb is not fatal for the haymaker. Sometimes kosinozhki themselves seperate their own legs, distracting the enemy with a twitching foot, thereby gaining time for retreat.
Rhinoceros is sometimes confused with hayfire spiders and mowing mites. The Snowflake only resembles a spider due to its long legs, but does not weave webs, does not catch victims in them and does not kill them with the help of poison.Myths and confusion, caused by the similarity of kerozhezhok with dangerous relatives, do harm only to themselves.
The squad of haymakers
Among our other arachnids, hayfields stand out for their exorbitantly long and thin legs supporting a relatively small body. In the afternoon they are inactive and sit in cracks of a bark on trees, in grooves of log walls and in other secluded corners; by night, they become more lively and go hunting for small insects and spiders.
If, in order to catch the haymaker, we grab him by one of his long legs, then the leg easily comes off and remains in our hands, and he himself escapes danger on the remaining legs.
"Spider-mow-hay" is common everywhere and is often found on the walls of our houses, so it is very easy to observe and study it.
First of all, we can see that the body of the haymaker has an ovoid shape as a whole and there is no interception between the cephalothorax and abdomen, which is available for the cross. We will never see a haymaker weaving a web, arranging a lair for himself or descending on a thin cobweb; we will never find females with an egg cocoon, which wandering wolf spiders carry with them.
If we look at it through a magnifying glass, we will see that the abdomen of the haymaker is divided into segments, that it does not have gossamer warts, and that the first pair of mouth limbs looks like small claws.
All these essential features that distinguish hayers from the cross and from other spider webs make us attribute them to another group - to a special detachment of hayers.
Excessively long legs, as you can easily see, do not give much speed to running the haymaker, and the value of their peculiar features, apparently, is different: both in the sitting and crawling haymakers the body is always surrounded by a whole palisade of limbs, with which the attacker first of all meets me predator.
The grabbed leg, as you know, easily comes off and with its convulsive twitches it distracts the attention of the pursuer, while the haymaker continues to leave on his surviving legs: he still has enough of them. Therefore, it is often necessary to meet hayfields with an incomplete number of limbs (their lost legs do not regenerate).
The ease with which a leg cutter comes off has the impression that it sits very “weakly”, and we pulled it too carelessly. However, in fact, the legs are firmly attached to the body of the haymaker, and their rejection depends on the special muscular movement that the haymaker makes when his legs are very irritated.
Such self-mutilation (or autotomy) is also observed in many other animals, for example, the Crimean flycatcher centipede, some cancers, and our ordinary lizards.
Sometimes in the garden or in the forest there are hayfields, in which on the body or on the legs you can notice small roundish little bodies of bright red color. These red bodies are representatives of another order of arachnids - tick larvae that live on the body of hayfields as external parasites.
Who is a spider with long thin legs, and how is it still different from its relatives?
This is a haying spider, or a long-legged spider. This is a family of spiders Pholcidae, which includes more than 1000 species that live across the globe. Many of them often settle in houses, apartments, in sheds and garages, preferring to coexist with people. First of all, we are talking about Pholcus phalangioides.
The body of this spider with long legs can reach a length of 2 to 10 mm, look like a ball or have a fusiform shape.In this case, males are usually a couple of millimeters less than females.
In Pholcus phalangioides, the most common type of haying spider, the abdomen is painted in beige or brown, and the scutellum covering the body is painted with a grayish pattern. The real pride of this spider family is its long legs with a shiny surface. Their length can be several centimeters, and sometimes reaches 9 cm in the tropics.
It is important not only to know the name of the spider with long legs, but also how it differs from rhinoceros.
For example, a centipede, which is a true spider, weaves a cobweb, while rhinoceros do not. In addition, in a haying spider on a round body - millet - there are 8 eyes: two of them are in the middle (medial), and the rest are along the edges of the abdomen on small outgrowths.
In some specimens living in dark caves, the number of eyes can be reduced as unnecessary. Haymakers have only two eyes.
Another difference between the centipede spider and the haymower can be seen if you carefully examine their torso. In both it consists of a rounded abdomen and chest, smoothly passing into the head. These two significant parts are connected by a peculiar neck-stalk.
But in a true haymaker, unlike a spider, this transition is very wide, so it seems that the whole body consists of one single section in a snow cutter, while each of the centipedes is pronounced.
There are 8 legs on the cephalothorax. Moreover, their size is often uneven: the longest pair of spider-mowing is actively using as antennas. He perceives with them the objects surrounding him, restores order in his web.
At the same time, each of the legs can fall off in danger: for example, if a lizard grabbed it. Although the lost limb is not regenerated, the centipedes can do fine without them: there are often individuals who move at a fast pace even on 4 legs.
Haymaking Spider Life
Spiders with long legs, belonging to the family Pholcidae, are spread all over the world, as well as its famous representative phalanx folkul (Pholcus phalangioides), which is so often found in houses and buildings on adjacent sites.
Every person at least once in his life met a spider with long legs
Hay mowing spiders move very quickly due to their long legs. Their height allows this arthropod to grab onto the blades of grass, easily climb over logs, cross impressive distances in a short time.
In this case, the body itself is located at a relatively large distance above the ground, so the risk of injuries is minimal. These qualities allow haying spiders to hide from numerous ill-wishers.
Hunting
A haymaker - a spider with long legs - is quite undemanding to food. The process of eating is slow because the creature has no teeth. He tears off pieces of his food - snails, small insects and other arthropods with strong chelicera, and then carefully grinds the food in his mouth.
Chelicerae are processes in the oral cavity in the form of small ticks.
In the diet of the haying spider there is not only animal food, but also vegetable. Sometimes he does not disdain even carrion, eating dead insects. Solid, soft, and semi-liquid foods are suitable for long-legged women.
But the main way to get food from a haying spider is hunting. Like all real spiders, he, unlike grasshoppers, weaves a web.
But he does not secrete the sticky enzyme that his brothers have, so the hunting net works in a different way: it is interwoven randomly and firmly, and the victim, fluttering, strives with all his might to get out of the trap, only getting more entangled in it.
The haying spider is often active at night, when it weaves its chaotic web and awaits prey. In the daytime, centipedes prefer to sit on the walls, windows and foundations of houses, and their wide and long legs serve as an excellent support, allowing the arthropod to feel confident on any surface.
Cobweb web is not accurate and symmetrical
If too much prey gets into the network to the hay spider, which it can’t handle (for example, a bumblebee), or unnecessary garbage, then the centipede begins to move the web, causing it to vibrate, thereby helping the prey to get out of the trap.
Breeding
Hayfields are dioecious animals. Their mating season begins around the end of August. The exact “start” depends on the type, region of residence and weather. Males after fertilization, the females do not stop, but immediately begin to look for a new girlfriend. Sometimes males fight for the right to leave offspring.
Females lay several clutches during the season, which is a cocoon containing up to 50 eggs. The optimal substrate for this is the fallen foliage of trees, less often, moderately moist moss or well-loosened soil.
Usually, young hay spiders hatch from overwintered eggs with the onset of spring, although in warm regions this can happen in the fall.
Until the end of summer, they manage to become sexually mature after several links. In individuals living in the tropics, two such generations per year are possible. The maximum lifespan of a haying spider from emergence from eggs is 3 years.
Is he harmful in the house?
Haying spiders, despite their peculiar appearance, are completely safe for humans. Their poison is unable to cause harm to health, with the exception of the rarest cases of individual intolerance to substances that cause slight local redness.
Hay mowing spiders have been living in human homes for a long time and around the world. In the West they were nicknamed "Cellar spider", which is translated from English as "Basement Spider".
The main reason why people strive to rid themselves of the neighborhood of centipedes and their relatives is arachnophobia, that is, fear of spiders. It represents an irrational fear of these creatures; and treatment is done by psychologists or psychotherapists.
But, if there are many hayfire spiders in the house, there is still cause for concern. This means that a lot of food has appeared in the room for the centipedes, often parasites. Therefore, you need to find the reason for this "neighborhood", eliminate it and conduct treatment at home from spiders.
leave a comment