
Hello! Our grandfather Matvey lives in our village - an avid hunter. Last week he managed to get a serious trophy. He treated all the neighbors with a moose.
He told me that the hunt ended for him with an attack of numerous insects.
Judging by the descriptions, he got from a deer bloodsucker. Grandfather was still worried that he could pick up what kind of infection from them. Do you want to know whether deer bloodsucker is dangerous for a person? When can you become a victim of these insects? I will share relevant and honest information with you.
The content of the article:
- 1 What is dangerous forest fly
- 2 Moose louse, or fly: what is dangerous, ways to fight
- 2.1 Moose fly: appearance description
- 2.2 What is dangerous deer bloodsucker for animals?
- 2.3 Are moose flies dangerous to humans?
- 2.4 Human response to a bite of a moose tick
- 2.5 How to protect yourself from a deer bloodsucker?
- 2.6 What to do if a moose louse has bitten?
- 2.7 How to get rid of a deer bloodsucker
- 2.8 How to cure a bite of a moose tick?
- 3 Are moose lice dangerous for humans and protection methods
- 4 Moose louse - dangerous or not
- 5 Elk lice: are their bites dangerous for humans?
- 6 Is moose tick dangerous for humans and animals
- 7 How to protect yourself from moose lice in the forest?
What is dangerous forest fly
At the height of summer, people go to the forest for mushrooms, but often come from there with ulcers on the body, and the small fly called the deer bloodsucker is to blame. We will tell you today how to distinguish this dangerous fly from a harmless insect.
We will talk about what threatens the bite of this fly. Our hero is an avid mushroom picker, he came from the forest last year with dermatitis, which he could not cure for a long time. The man was often bitten by insects, but last year the bites itched and hurt, and then red spots appeared.
Some believe that she lives only in the Far East, but lives as a bloodsucker in central Russia. The consequences are very serious, some of which do not go away for months or remain for life.
Campaigns in the forest should not be canceled, but you need to know the rules that will help to avoid a bite of a bloodsucker. Bloodsucker attacks during the day. To protect against a bloodsucker, a repellent will not help, it does not act on it.
A bloodsucker deer does not distinguish colors, so it does not matter if you are in white clothes or not. The bloodsucker reacts to movement and sweat; it bites when you move. Bloodsucker deer can carry a serious infectious disease.
Moose louse, or fly: what is dangerous, ways to fight
Moose fly, or moose tick, is a representative of the Bloodsucker family. Ectoparasite has two more names: moose louse, deer bloodsucker. He feeds on the blood of warm-blooded animals, although it can harm humans, but a competent fight will help to avoid negative consequences.
Natural habitat of a moose fly:
- North America;
- european part of Russia;
- Siberia;
- Primorsky Krai;
- north of china.
The number of insects in a particular area directly depends on the number of moose and deer.
Moose fly: appearance description
The parasite resembles flies until it drops its wings.
What does a fly or elk louse look like:
- individual length - 3–3.5 cm;
- flat body shape with dense shiny leathery cover of light brown color;
- complex eyes, consisting of 2.5-3 thousand facets, are located on the forehead along the sides of the head, occupying 25% of its total surface;
- there are also three simple eyes on the head;
- the oral apparatus is similar to the proboscis of an autumn lighter;
- wings — transparent, developed, dense, 5.5–6 mm long;
- legs with asymmetric claws with thickened hips are located on the sides of the chest;
- the abdomen is elastic, so it can become larger after eating.
What is dangerous deer bloodsucker for animals?
In large quantities, elk mites systematically drink the blood of animals, as a result they become restless, cease to sleep normally and eat food, as a result of which exhaustion occurs, and growth is slowed down in young animals.
Deer bloodsucker can be found on the body of the following animals:
- roe deer, deer, elk, red deer - representatives of the cloven-hoofed mammal family;
- cattle;
- wild boars, bears, dogs, foxes, badgers, goats, sheep and others - their parasitism was noted.
Insects drink the blood of animals somewhere 15-20 times a day. Sexually mature females eat more often than males. If we talk about pets, it is impossible to deliberately prevent the appearance of parasites.
A person can save them from the prolonged presence of deer bloodsuckers with the help of special aerosols and sprays to kill insects such as flies, mosquitoes, ticks.
Are moose flies dangerous to humans?
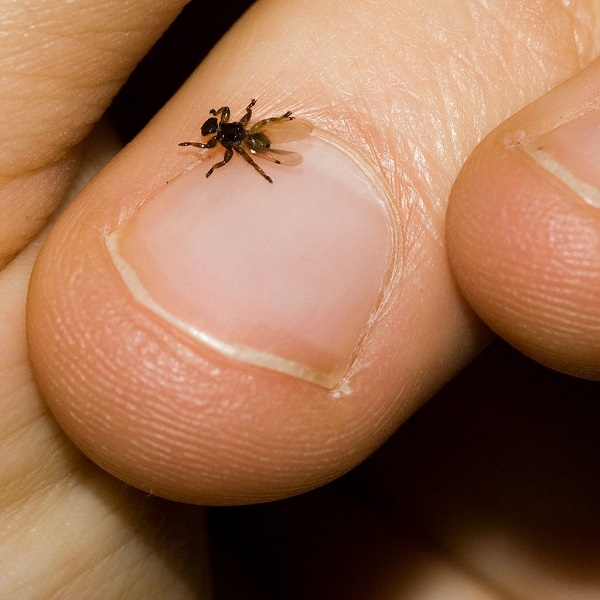

Moose ticks attack not only animals, but also people, usually in forests, during daylight hours and calm weather. Often there is a massive attack of parasites on a person, their number can reach up to 120 pcs. in one minute.
When an insect sits on a person, for the first few seconds it sits motionless, and then it begins to move quickly through the body, mainly trying to get under clothes or in hair. Reset the parasite will not succeed even with sudden movements.
Human response to a bite of a moose tick
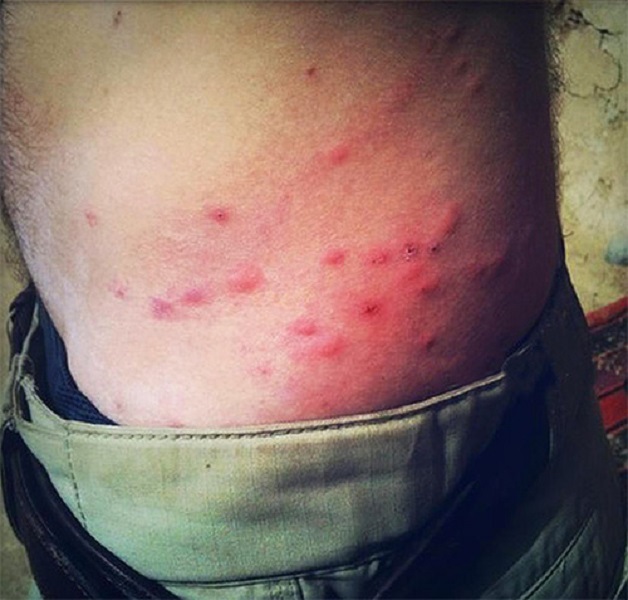
The bloodsucker deer, or moose fly, has a flat body with a dense cover, tenacious nails are located on the legs. When it settles under clothes or in a person’s hair, it immediately begins to drink blood, and in some cases after 30-60 minutes.
Each person can react to a moose tick bite differently: one - does not feel anything, the other - experiences painful sensations, sometimes strong enough, which are accompanied by itching and burning.
And the manifestations on the skin depend on the individual or acquired sensitivity to the saliva of the insect. Observations showed that in people who have been systematically subjected to deer bloodsucker bites for many years, the reaction to the skin is much stronger.
How to protect yourself from a deer bloodsucker?
Jumpsuit and mosquito net - protection against moose flies
Despite the fact that elk mites drink human blood, they are not carriers of serious diseases, for example, encephalitis, Lyme disease. To protect yourself from them in the forest, you must observe safety precautions.
Clothing requirements for protection against deer bloodsucker:
- Items of clothing should cover all areas of the body.The best option is jumpsuit. The cuffs on the jacket and jacket should fit snugly on the wrist or pulled together with an elastic band.
- A mosquito net with a net should be put on the head, which will prevent insects from getting to the skin of the face and hair. If not, you can apply a scarf or hat.
- A moose fly is easier to spot on plain clothes.
- Use repellents in which the content of DETA is at least 20%.
What to do if a moose louse has bitten?
If in the forest the tick got into the hair or under the clothes and dug into the skin, it must be removed immediately.
Three ways to remove deer bloodsucker from your skin:
- With tweezers or thin tweezers, you should take the insect by the abdomen and gently twist counterclockwise, gradually removing it from the wound.
- Time-tested and effective remedy for moose flies - vegetable oil. After the product enters the body of the parasite, the flow of oxygen is blocked, as a result, after about 10-15 minutes, it will begin to break out in search of air.
- You can remove the tick using a conventional nylon thread. To do this, you need to skip it under the abdomen of the insect, tighten the loop, preferably closer to the head. Then swing it in different directions and take it out. The bite site must be disinfected.
How to get rid of a deer bloodsucker
There are two ways to deal with moose flies.
Industrial methods. Processing of the area with various chemicals. Currently, a large number of chemicals have been developed that do not harm plants, animals and people.
Spraying on a site of chemicals in a gaseous state allows even hard-to-reach spots to be treated, leaving no chance for parasites to survive.
Folk methods. To prevent the accumulation of insects on a private territory, it is necessary to regularly mow the grass, since, as a rule, they live among tall plants.
Moose flies do not like moisture, so it is recommended to spray trees, shrubs and lawns with water. You can add alcohol or regular garlic to it. They also successfully help to cope with the parasites of wormwood and tansy.
How to cure a bite of a moose tick?
The elk fly bites quite painfully. On the skin of the bite site may swell, redden, small blood spots remain. In some cases, besides these symptoms it may be itchy.
In the presence of allergies, medications and ointments should be prescribed by a doctor. Do not self-medicate, as this can aggravate the situation.
Are moose lice dangerous for humans and protection methods
Moose louse - this is what the people call a parasitic insect - a deer bloodsucker, which, as a rule, lives on the body of large representatives of artiodactyls - deer, deer, cows, etc., living in the forest.
People who often visit forest zones know firsthand what kind of lice they are, whether they pose a danger to humans, how to protect themselves from them. For the rest, this insect remains a mystery. How can you protect yourself from moose lice and how are they dangerous?
basic information
Moose louse, a fly, and even a tick - all these are the names of the same insect - a deer bloodsucker. This louse looks really more like a fly. Actually, moose lice are nothing more than ectoparasite flies, which always require a host to live and nourish it with warm blood.
Wings to moose parasites are necessary for getting on a victim’s body. After their discharge, the flying muscles atrophy at the insect, and the elk louse lives on the host's body all its life. An external resemblance of deer bloodsucker and lice is noted here.
What is the threat of deer bloodsucker to humans?
Unlike ticks, elk lice are not carriers of pathogens. Therefore, the risk of infection with encephalitis, borreliosis and other serious ailments is absent.
In addition, elk louse does not pose a danger to humans, since it does not lay larvae on its body. The main danger to the human body is that a parasite bite can cause the development of various kinds of dermatological ailments.
The bite itself causes pain and discomfort, but each organism responds individually. In the best case, hyperemia that occurs at the site of penetration of the trunk of a moose bloodsucker passes through 2-3 days.
But in some victims, each bite of a elk louse turns into a blister, the skin is covered with a crust and a rash spreads over the whole body. Numerous swelling is observed. This condition is most often accompanied by severe itching.
This is how multiple bites of a deer bloodsucker may look like. Later, condensed papules form on the body, which disappear only after a week and a half.
Basically, at the first bites, the body exerts resistance, and the person does not have pronounced symptoms. Long-term activity of moose lice on human skin is of great danger, since repeated damage adversely affects the general condition of the body.
Security methods
For a person, being on the body of moose lice, if it does not pose a mortal danger, it causes a certain discomfort. If one mature individual is found on the body, then a second one will be found nearby.
Bloodsuckers do not like to fly and try to do it in suitable weather for flights. The danger is high in quiet, autumn weather, when there is no rain and wind. Lice, in response to movement, select a larger target and attack.
Once on a person, the parasite adheres to clothing and for a certain time is in a frozen state. When there is a company of adults with children in the forest, lice will attack larger objects, and for children there is practically no danger.
Of course, human blood is not suitable for moose lice, they cannot reproduce here, but there is still a certain danger to the body.
It is worth considering the requirements for clothing, so that in the forest she helps to protect herself from various parasites, including moose lice:
- Clothing should be spacious, not restricting movement.
- It is better if it will cover the entire human body, so the most successful option is overalls.
- On the sleeves and bottom of the trousers, the presence of tight cuffs is desirable, this will help protect a person from crawling insects on the skin. If there are no cuffs, you can use elastic bands for these purposes, legs can be tucked under the elastic band of socks.
- It is better to give preference to plain clothes, this helps to quickly detect the danger in the form of lice or ticks.
- You can protect yourself from moose lice with the help of a mosquito net. If there is no such device, then the person’s head must be tightly tied with a scarf or a tight hat worn. If outerwear has a hood, you can protect them.
- Before visiting the forest, it is advisable to use repellent products, which include DET. They do not pose a danger to the people themselves, but will help to reliably protect themselves from various flying and crawling parasites.
How to delete?
What should I do if I failed to defend myself and not only a bite, but also a sucking blood-sucking louse was found on the human body? You must uninstall using one of the following methods:
- Grease a bite with a fat cream or apply a drop of any vegetable oil.
- Without air access, a moose fly will fall off in about 15 minutes.
- You can remove the insect with tweezers, for this you should carefully twist its body counterclockwise, while tracking the extraction of the proboscis.
- An ordinary thread is suitable for removing lice, a loop is made, it is tightened on the body of the parasite and swings by the principle of the pendulum until the fly is pulled out.
After the procedure, the bite should be treated with a disinfectant. It is imperative to seek the advice of an infectious disease specialist or a dermatologist, since bites of bloodsuckers can be dangerous, sometimes a person needs additional treatment.
If the deer of the bloodsucker divorced in a household plot, then you can protect yourself from it with the help of chemicals. Processing is necessary in places with tall grass. Before applying the funds, high vegetation can be mowed, thereby removing places convenient for parasite habitat.
You can also protect yourself from moose lice with the help of repelling plants by planting common tansy on the site of wormwood. To protect yourself indoors, you can use carbon dioxide.
Moose louse - dangerous or not
The elk louse is an insect that is not widely known to the population, although many have not rarely encountered it, simply confused it with a tick. In fact, there are many such moose lice, especially in forests, starting in August. They often climb into the hair, from where it is then very difficult to pull them out.
The elk louse has a flat body, thick tenacious paws, as well as a proboscis with which they are able to pierce the skin and drink blood.
Moose lice also have other names - moose flies or moose mites, but they are scientifically called "deer bloodsucker." In fact, they are adapted for life on moose, getting on them, they drop their wings and live for their pleasure. And moose lice fall on humans by accident, so they die very quickly.
There were no cases of transmission of any diseases by elk louse, so they should not be feared. The only thing is that these insects are very unpleasant and even bite painfully.
Redness may appear at the site of the elk louse bite, and the bite may itch. Therefore, it is sometimes worthwhile to use an antiallergic drug that will help relieve itching and redness.
To protect yourself from the attack of insects, it is necessary to wear such clothes that would cover all parts of the body, and wear a hat on your head, then these insects will not be scary.
Elk lice: are their bites dangerous for humans?
Moose louse, parasitizing on almost all warm-blooded forest dwellers, mammals and birds, systematically feeding on their blood, leads to animal depletion and growth retardation of young animals.
Morphology and developmental biology
Lipoptena cervi has other names: deer bloodsucker, moose fly, moose tick.
The body of the insect is dorsoventrally flattened. Ticks have a soft, leathery abdomen with poorly expressed segmentation.Claws on paws allow them to hold firmly on wool or plumage. By mechanically piercing the skin of an animal, lice can be carriers of blood parasites.
A blood-sucking bloodsucker attacks from trees within a radius of 50 m. It drops wings on the body of an animal. It feeds on blood for 5-7 days, after which copulation (mating) takes place.
In 2-3 months, the female is able to spawn up to 30 ancestors, which, covered with a hardened larval membrane (puparia), then turn into pupae. Pupae fall into the soil, where after 86-160 days they turn into young winged bloodsuckers. By the end of September, the first puparia appear.
The attack on animals begins at the end of July and continues until steady frost sets in. The largest number of bloodsuckers on moose is observed from October to February.
On adult moose, up to 1 thousand bloodsuckers parasitize. Most flies are found in the neck, back and sides.
From February to July, the population of deer bloodsuckers decreases. In July, animals completely get rid of last year's flies. But with the onset of the swimming time, when animals, fleeing from the nest, are completely immersed in the pond, the number of insects increases.
Animals are forced to stand in water bodies for a long time, fleeing from flies, scratching themselves on trees. Because of what they develop extensive dermatitis, complicated by microflora. Infection of animals with moose lice provokes the disease lipoptenosis.
The consequences of a bite for a person
Elk lice bite leads to the development of dermatitis. 4 types of dermatitis of varying severity were identified:
- After a bite, a maculopapular rash appears, which disappears after 5-6 days without consequences.
- Rashes of itchy papules that pass within 2 weeks.
- Papular urticaria - the appearance of small blisters.
- At the first bite of a bloodsucker, no reaction of the body occurs. Subsequent bites develop island-inflammatory exudative blisters, the treatment of which lasts up to six months.
With a repeated bite, an allergic reaction, local or systemic, can develop, since insect allergens persist for a long time in the blood of a person.
When bitten by a deer bloodsucker, a person experiences:
- itching, flushing after 5-10 minutes;
- the formation of a rash after 5-12 hours;
- in place of the rash after 20-25 hours, vesicles with serous contents form;
- the transformation of bubbles into pustules, from which a yellow liquid oozes for 5-15 days;
- as the liquid is released and dried, brown crusts form.
After peel rejection, dark spots remain on the skin that do not resolve for more than 1 month.
Treating parasite bites is easy at home. The surface of the skin is treated with hydrogen peroxide. An antipruritic agent is applied to the bite site, which includes menthol, camphor, kelamine.
Do not allow combing of papules. In this case, the attachment of a secondary infection is possible. What antibiotics should be taken, the doctor will tell you at the reception in the clinic.
The consequences of numerous bites can be mistaken for lice or other skin disease.
The reaction of the body to the bites of a bloodsucker is individual. It is believed that people who constantly go into the woods and are often attacked by lice react more and more sharply to bites over time.
It has been established that bloodsuckers are most active when the weather is wet.
Moose flies during an attack are guided by the size and color of the victim. With good vision, they notice moving figures of people or animals. A large number of bloodsuckers are attacking the one in front. If there is a child in the group, lice may not notice him.
Hunters noticed that elk lice prefer the scalp, especially the occipital. They immediately drop their wings and begin to feed, piercing the skin with a strong proboscis. The elk fly, dropping wings and having a flat body, becomes like a tick.
Despite the fact that Lyme disease pathogens were found in a quarter of the examined bloodsuckers, medical statistics do not confirm the fact that they transmit infectious diseases.
This contributes to the lifestyle of bloodsuckers. It parasitizes all life on one host, unlike ticks, which use several victims for nutrition, including natural reservoirs of infectious diseases - rodents.
Protection methods
Drugs designed to protect against flying insects, mosquitoes and flies do not affect deer bloodsucker.
Ways to protect from moose lice:
- put on a jacket with a blank collar and a light hat in the forest;
- soak clothes with repellents designed to protect against ticks.
Detected lice must be destroyed immediately.
The number of bloodsuckers is directly dependent on the population of animals in the area. Parasites choose for hunting impassable forests of a mixed type, lowlands and wetlands, since it is there that the largest number of forest animals live.
The natural enemies of moose lice are forest birds. It is noticed that tits peck on puparia from the ground in the forest. The harmful value of elk lice is currently poorly understood.
Is moose tick dangerous for humans and animals
The elk tick has another name that very accurately reflects the essence of the insect. In areas where this parasite is widespread, they gave it the definition of "moose fly", in the scientific classification it is presented as "deer bloodsucker." An elk or deer tick is a danger not only to animals, but also to humans.
Appearance
Small, from 3 to 5 mm in size, the fly parasitizes on deer, roe deer, elk, goats and even wild boars. It gets tangled in a person’s hair and can bring a lot of discomfort.
Many of the names of this insect were formed due to the fact that it knows how to adapt perfectly and is content with the blood of the animal that currently lives within reach.
The main part of the body of a moose fly falls on the head. Despite the fact that she has eyes, she sees poorly. The organs of vision of the parasite consist of a pair of eyes and three additional eyes, but it is oriented along the contours. The larger the object, the more interesting it is for the tick.
In the absence of the main hosts, deer ticks do not disdain the blood of dogs, badgers and bears. The deer bloodsucker has wings for the time being. Having found the victim, she discards them and outwardly looks like a tick, although she has nothing to do with him.
On the head of the bloodsucker are located a barely noticeable antennae. Until the parasite has dropped its wings, it differs little from the usual fly. Wings reach a length of 5 mm, they are dense and transparent. Over long distances, the insect does not fly due to the weak development of the wings.
He needs them only in order to fly onto the animal, and then the wings will prevent them from moving in the depths of the coat, so the parasite gets rid of them.His body is flattened, it is protected by a dense shell, making it difficult to accidentally crush an insect.
The tenacious claws at the ends of the legs provide a firm hold on the skin and coat of animals. The elasticity of the abdomen gives the elk mite the opportunity to increase in size when eating and bearing offspring.
Reindeer Bloodsucker Lifestyle
While the weather is warm, elk ticks are undergoing a development process. At the end of summer, they leave the cocoon and begin to look for a suitable host, in whose wool they will spend the whole winter. With the onset of spring, a new cycle will begin.
Adult ticks will die, the larvae will again wait for their term in the cocoon, and after leaving it they will fly from foliage to deer, elk or roe deer, drop their wings and begin to feed and multiply intensively.
One bloodsucker deer can feed up to 20 times a day. If we take into account that there are hundreds and thousands of them in one animal, then the poor animal has a hard time. During the winter, the body of an elk or deer is so depleted that some young and weakened individuals die.
In areas where there are large numbers of wild artiodactyls and cattle, there are many elk mites. Their number directly depends on the availability of food, that is, on whether it will parasitize on whom. In the absence of deer and elk, a moose fly settles down even on foxes and domestic dogs.
Elk tick and man
Moose ticks are most active in warm weather. Ideal conditions for them are considered areas with high humidity and dim light. Usually this is a thicket of forest. Insects lead a daily life, the victim is attacked en masse.
This insect is common in most of Russia. It can be found in the European part, in Siberia and in Primorye. Most elk mite where deer, elk and roe deer are found. The larger the cloven-hoofed population, the greater the number of insects.
Since they calculate the victim according to the shape and at the same time look out for a dimensional object, children are rarely attacked - they are too small for bloodsuckers, especially against the background of an adult who is walking nearby. Bloodsuckers prefer to attack the one who is larger. They act together. They are not shy and completely ignore attempts to beat them off.
It is possible to judge whether this parasite is dangerous to humans by the fact that after the studies, a fifth of the subjects did not have any negative manifestations, but repeated contact that happened a few years later led to the need for long-term treatment. For some patients, treatment took six months.
Getting under the clothes, the insect assimilates there for some time, and it may take at least an hour before the bite follows. The tick itself will not get out and will not leave the body. Its tenacious claws allow you to firmly cling to the skin.
Crushing it under the clothes also does not work, since the body structure and the density of its shell do not allow this to be done, the only way out is to undress and remove the tick, which, surrounded by hundreds of those who are thirsty for human flesh and blood, is equivalent to a feat. But panic is not worth it.
Allergy to the saliva of a deer bloodsucker does not occur in everyone, but if this happens, then taking an antihistamine helps to avoid serious consequences. There are people for whom the bites pass without a trace, in a couple of days there are not even traces left of them.
Elk Tick Protection
Unlike real ticks, a deer bloodsucker is not a carrier of diseases, and at its first bites, the body resists, so basically everything goes without consequences. But when the critical point is passed, the general condition can deteriorate significantly, and it is impossible to predict in advance who this will happen to and who will pass.
Therefore, to go to the forest you need to choose the right equipment: clothing should cover the whole body. The cuffs on the sleeves and trousers should fit snugly against the wrists and ankles.
There are no specialized remedies for the elk mite, but you can try to use tar: apply it in stripes to exposed areas of the body. In this way, the Siberians are protected from the vulture.
It is necessary to cover the hair with a hat, cap or scarf, but it is best to use mosquito nets, they will protect the face, neck, ears. From the attack of a deer bloodsucker, you can use repellents - protection from mosquitoes and other insects, but the result cannot be guaranteed.
Bite places need to be treated with an antiseptic, alcohol or perfume, that is, what is at hand. To make the insect better visible, choose plain light clothing for the forest. Against a motley and dark background, it is more difficult to detect a bug.
How to protect yourself from moose lice in the forest?
Among the insects that cause horror in humans is deer bloodsucker - an animal parasite that feeds only on their blood. Without it, the reproductive cycle is impossible.
Scientists discovered a moose bloodsucker on the bodies of bears, goats, dogs, wild boars, badgers, sheep and other large representatives of the fauna. Are ectoparasites dangerous to humans? What threatens a flea bite? How to protect yourself?
What does the parasite look like: description and habitat
A small moose fly lives in woodlands, where a large population of deer class representatives lives. These are Siberia, North America, Primorsky Krai, the European part of Russia and other regions.
With a decrease in the number of feeders, the moose tick is able to survive by feeding on the blood of birds. And with an increase in the number of insects themselves, they begin an attack on humans. But eating his blood, ectoparasite is not able to give offspring.
This is possible due to the structure of the insect - the densified covers of a strongly flattened body, the length of which reaches 3 mm or more. The largest individuals can have a body length of up to 4 mm. The color of the integument is light brown or amber.
The bloodsucker deer differs from its bloodsucking counterparts in other features:
- strongly forward head with densified covers;
- presence of thick antennae in deep frontal cavities;
- two large eyes (occupy 25% of the surface of the head) with a complex facet;
- three simple eyes;
- piercing-sucking apparatus. He became the reason why the moose fly got such a name among the people, because in its structure it resembles a proboscis (sucking apparatus) of a lighter (type of flies);
- very developed and strong legs;
- thickened hips;
- the presence of asymmetric strong claws on the legs;
- dense, well-developed wings. In a bloodsucker fly, they reach a length of 5-6 mm;
- abdomen. With the bearing of the offspring and during feeding it increases by 1.5-2 times.
Having found its "breadwinner", the bloodsucker drops its wings. Without them, it vaguely resembles a tick with wings, which is why the insect has so many names. To stay on the body of the “victim” insects cling to the hairs like a louse.
One adult eats from 15 to 23 times a day. A sexually mature elk fly female, expecting offspring, eats more often and drinks more. One meal is from 0.3 to 1.5 mg of blood.
Blood-sucking moose fly: what is dangerous for humans and how does it bite?
Despite the fact that human blood is not suitable for starting and ending the reproductive cycle, elk louse attacks people. Moreover, in their habitat, these attacks in 54% of cases are massive. There are cases when a person was overcome by up to 120 adults.
Unlike other ectoparasites, the bloodsucker deer does not synthesize an enzyme that anesthetizes the skin during its bite, so the bite is extremely painful.
The risk group for the most frequently attacked individuals includes:
- hunters. Cutting off dead carcass of a deer or elk will inevitably attract an insect;
- mushroom picking mushrooms in the forest often;
- vacationers.
Scientists have recorded cases of an elk tick attack, but is a bite dangerous for a person? The insect is not considered a carrier of any infections or viruses. But it can not be called harmless, since a bite of a moose louse causes:
- severe pain;
- local hyperemia;
- itching and burning in the bite area.
After a person is bitten by a moose tick, skin manifestations are inevitable. At the same time, in persons sensitive and individually intolerant to parasite saliva enzymes, they are longer and more pronounced.
At the same time, the elk louse is also dangerous for humans because the consequences of bites become more complicated and stronger with each subsequent attack.
Features of a Reindeer Bloodsucker Attack
Scientists have found that the moose fly always chooses a larger object for attack. Therefore, there are very few cases of attacks on babies up to 8-10 years old (if there is an adult nearby, a deer bloodsucker will give preference to him).
The attack takes place after a few seconds and begins with a quick movement through the body of the “victim” in search of the scalp or exposed areas of the body. You are afraid that moose lice bite you in nature, learn how to protect yourself from ectoparasites before entering their habitat.
Finding a place where you can firmly cling to the body, the moose tick does not immediately strike. He will wait, put to sleep the vigilance of the "victim." The waiting period for an attack can last up to an hour.
Do not try to scare away the bloodsucker with a sharp movement or blow to the body - these measures will not scare her away. Removing a biting insect is also not easy. Euthanizing the vigilance of the “victim”, elk lice are dangerous for humans, because he does not expect a bite.
How to identify a deer tick bite on a body?
Less sensitive people may not feel a bite. Having drunk blood, the flat fly itself will fall away and leave the body. Therefore, in the absence of physical symptoms, it is almost impossible to see a skin bite.
The consequences of a fly bite sticking to a person:
- papule formation at the site of the bite - a dense tubercle protruding above the surface of the skin;
- the appearance of severe itching;
- redness of tissues adjacent to the wound;
- the appearance of a macular rash is often with a crust;
- the formation of a papular rash and severe itching without fever;
- blistering;
- the appearance of persistent dermographism.
Figuring out the issue, moose flea, whether it is dangerous for humans, scientists came to the conclusion that an insect bite is dangerous with its unpredictable reaction to it.
Initially, painless tick bites with wings are dangerous for humans by the development of serious and intractable skin ailments. The period of manifestation of papules, blisters and rash in all bitten is different - from 40 minutes-days to 10-21 days.
Deer bloodsucker bites: how to treat and recognize?
It is interesting that the bite of a moose flea is also dangerous for a person with related problems. An itchy place is the cause of infection in the body. A deer fly that bit a person left an open wound on the body.
Its combing with dirty hands in 82.6% of cases leads to the ingestion of pathogenic microflora. Therefore, having discovered the papule on the body, you need:
- to disinfect the bite site and adjacent tissues - hydrogen peroxide, alcohol, etc .;
- take an antihistamine - especially if a tick-like fly has bitten a person prone to allergies;
- glue the wound with a band-aid and grease with a local antipruritic drug;
- see a doctor immediately.
Knowing the results of a bite of elk louse, the treatment of complications should be entrusted to a specialist. An allergic reaction can be very strong, because during feeding the insect does not stop the process of life.
The wound can be contaminated with feces of elk mite, dangerous for humans with increased sensitization of the body to irritants.
Now you know that moose fleas are dangerous for humans, so a trip to the forest should be carefully considered. Experts recommend:
- wear clothes covering the whole body;
- trousers, cuffs and collar must fit snugly, otherwise the moose fly, than the dangerous bloodsucker we described above, will crawl into the openings to the body;
- treat hands and face, neck with repellents. Usually a remedy for moose lice is made on the basis of DET;
- apply a deterrent to clothing. If you have any difficulties with the purchase of a ready-made repellent, you can use ordinary tar soap. This remedy for moose lice in the forest will save no less effective;
- to bring along special devices for removing mites - a lasso pen, a mite clasp or an ordinary strong thread. After the physical sensation of a bite, you need to try as carefully as possible to remove the blood-sucking fly by pulling its proboscis out of the body;
- to take hydrogen peroxide and iodine, hand sanitizers and an antihistamine for moose flies in a backpack - the person who provides help also processes the hands.
Removing an insect will not be easy. It must be remembered that a flat fly adhered, having a body structure such that the classical physical methods of struggle do not work.
It often happens that a moose fly is found in an apartment. In this case, you need to try to kick it or scare it away with a repellent.
leave a comment