
Hello! Once I looked at my country house and remembered all the hardships with its construction.
How much time has been spent choosing suitable building materials. But then I paid the most important attention to the choice of insulation for floors and walls.
Indeed, very often it becomes an object of close attention from mice and rats. I was not mistaken with the choice - these rodents do not bother me. Do you want to know which insulation is not eaten by mice and rats? How to prevent the appearance of these unpleasant neighbors? Then in the article below you will find a detailed answer.
The content of the article:
What kind of insulation do not bite the mouse
During the construction of a country house, thermal insulation work is indispensable. A good owner will always take measures to warm the walls, floors and roof. When choosing the necessary material for this, one of the main questions that arises for the owner of the house is what kind of insulation the mice or their relatives do not bite.
Rodents do not eat any of the existing heaters, but gnaw them with special pleasure, arranging nests and moves inside it, and even if they appear thicker than such material, it is almost impossible to evict them from there. Therefore, choosing a thermal insulation material, you need to carefully study all its characteristics so that you do not have to redo all the work done again.
Insulators used and their properties
It should be noted that for mice there are few barriers that they are not able to overcome - these small rodents penetrate through the narrowest cracks formed at the joints of the walls of the house and concrete tides, and through almost imperceptible cracks in the facade cladding.
If, having penetrated into the insulation, rodents feel comfortable in it, they cannot be smoked from there, therefore, the material for thermal insulation should have such properties that are unacceptable for animals to exist in its thickness. There are several similar materials, and they are quite accessible to any owner of a house under construction.
Expanded clay is made from special grades of clay, which is cleaned, carefully wiped and kneaded into a plastic solution. Then granules are formed from it and hardened in a certain temperature mode, at which swelling of the mass is achieved. When cooling, the insulation becomes light in weight and at the same time very durable, able to withstand significant mechanical stresses.
Expanded clay can have different fractional sizes. So, it is produced in the form of sand, fine and medium gravel, as well as large, up to 10 - 25 mm granules.
It is unlikely that rodents will choose at least some of their similar materials for the construction of nests and accommodation. If they can move along large fractions of the material, then in the insulation in the form of fine gravel and sand, mice, and even more so rats, will simply sink.
Expanded clay is insulated with basements, interfloor and attic floors, but you can also use it for wall insulation.
To do this, a kind of formwork is made near or inside the walls, having the desired thickness, into which expanded clay is poured. It densely fills all spaces without tamping. Expanded clay can be insulated walls or the foundation of the house
To insulate the wooden floor, a vapor barrier material is laid on the rough base, which is fixed to the logs. Expanded clay is poured on it and again it is covered with vapor barrier from above. Further, a finishing floor made of boards or plywood is laid on the logs. It is great for warming wooden floors.
In addition, small expanded clay is used for the installation of a bulk floor using the “dry screed” technology, where it serves as a heater and sound insulator, and in addition, as the basis for gypsum fiber flooring. By arranging such a floor, expanded clay can be poured both on the ground and on the concrete surface.
But before, waterproofing material is laid on any of them, if it is stacked in separate sheets, they are glued together with a special adhesive tape. The waterproofing is raised to the walls by 15–20 cm, and a damper tape is installed on the wall and only then expanded clay is poured.
Gypsum fiber boards laid on expanded clay backfill will create a smooth and durable floor surface. On top of such an embankment, carefully horizontally aligned with the help of a system of temporary beacons, gypsum fiber panels are laid, which create a rigid surface. In such a warmed floor basis, rodents will never start.
Since the mice manage to penetrate the interfloor and attic floors, they are also filled with expanded clay crumb.
Alluvial material has the same properties as expanded clay small fractions, and use it in the same way for walls, floors and ceilings. With the help of granulated foam glass, floors and floors are perfectly insulated
Plates are mounted on the walls from the outside or inside, and also laid on the floors, on concrete mortar, bitumen, building glue, or on foam glass or expanded clay pre-poured under them in small fractions. Blocks of foam glass are used for thermal insulation of the walls of the house.
Foam glass is a heat-insulating material that is made by melting and foaming glass. This process is possible due to the ability of the glass to soften and boil at a temperature of 950 ÷ 1000 degrees. It can also be used indoors, for example, for warming the attic.
Foam glass resists not only rodents, but also the appearance of fungal formations and the appearance of insect nests.
The material is durable, not damaged by moisture and does not decompose from ultraviolet radiation, does not crumble and retains its heat-insulating qualities for many years.
A very important advantage of foam glass is its environmental cleanliness - under any conditions, the material does not emit any harmful fumes that adversely affect the health of residents.
Ecowool. In order to avoid settlement in the insulation of rodents, experts recommend the use of ecowool. This is a relatively new material, but it confidently occupies its niche among the often used effective thermal insulators.
Installation of ecowool takes place using special equipment that helps to distribute the material over the insulated area. After the initial setting, the applied layer is leveled with a special roller.
The question arises as to why rodents bypass the ecowool side, because it is soft and easily lends itself to the teeth of mice and rats. The secret of these animals' dislike for such a heater lies in the fact that during its manufacture, the manufacturer adds orthoboric acid to the mixture, which causes suffocation and dehydration in rodents.
Perhaps some individuals will try to make a nest in the ecowool, but they will not be able to stay in this insulation for a long time, and even more so - to breed, so rodents quickly leave a seemingly comfortable place to live.
Ecowool treated with orthoboric acid, has antiseptic properties, and also well releases moisture when heated strongly, thereby providing a fairly high fire performance.
They produce ecowool from cellulose, which is absolutely harmless to the human body, therefore, insulation can be carried out not only outside the building, but also from the inside, distributing the material between the crate of timber installed on floors and walls.
Ecowool has low thermal conductivity and sound conductivity, therefore, it retains heat well indoors and drowns out all the noise coming from the street, as well as from other rooms, if it is used for interior walls. Ecowool remains functional for many years, as it is not subject to decay and decay.
From the ready-made blocks, the walls are laid, or they are already covered with ready-made brick or wooden walls. The solution is distributed on the surface of the floor or filled with formwork, arranged, for example, from two rows of brickwork.
This material consists of cement, water, sand and a foaming agent. When hardening, it acquires rigidity and a pronounced porous structure. Foam concrete will definitely not be bitten by mice, trying to build a nest in it, since such conditions are unacceptable to them.
The walls are insulated with foam concrete only from the outside of the building, or they are poured into the middle of the masonry when it is erected. Indoors, it is rarely used for wall insulation, since the technological process must be strictly observed, and with the slightest deviation from it, condensation may appear in the piers, which means that the development of mold processes begins.
Floors may well be flooded with foam concrete. With full hardening, it will become a reliable basis for decorative surface design. Floors flooded with this material will get excellent thermal and sound insulation.
Blocks of foam concrete are light in weight, so it is not difficult to lay them. They are environmentally friendly and do not pose any danger to residents of the house. They are easy to handle - cut or drill holes if necessary.The material is absolutely non-combustible and not subject to decay.
And what about the usual heaters?
Penoizol - This is the same polystyrene, only in liquid form, sprayed onto the walls and floor with the help of a special compressor. Many articles indicate that mice do not gnaw this material because of its components, but, unfortunately, this is not true. Rodents work very well on this material. Perhaps they will not arrange moves and nests in it, but they gnaw at it with great pleasure.
The same can be said about extruded polystyrene foam - it is quite dense, and therefore mice or rats will not live in it, but they will not refuse to gnaw it.
All kinds mineral wool also in the teeth of mice and rats, and it doesn’t matter if it is glass wool or stone. Any of them is suitable for rodents to settle in it for living.
They do not eat this material, but skillfully chop it, arranging their houses, and if they have chosen the insulation layer of a certain house, it will be very difficult to remove them. The trouble is that poison cannot be laid out for them, otherwise the rodent can say goodbye to life right in the nest and then it will be very difficult to get rid of the putrid smell. Therefore, it is not recommended to insulate the lower part of the house with these materials.
In order for the house to be protected from rodents, its basement and basement must be insulated with rigid or loose materials, and the joint between the wall and the concrete tint must be very carefully sealed.
It is extremely important that no cracks or cracks form in this place - even the smallest of them will be a good loophole for gray sneakers. And yet - in order for the private house to be protected from mice, it is imperative to get a good active cat that will intercept rodents on the way to the house.
But, choosing a heater, you still need to follow the tips given above, which are based on the operational characteristics of the materials and on the experience of numerous owners of private houses.
Overview of Rodent Protection Materials
If mice are started under the skin of the house, this nullifies all the efforts of the builders in thermal insulation. Rodents arrange nests in the insulation, make moves in it, cold penetrates into the resulting holes, and heating costs increase.
In order not to suffer from this disaster, and not to remodel expensive repairs, it is important to immediately know what kind of insulation mice and rats do not bite.
Unstable materials
To begin with, we will determine what building materials do not need to be used if there is a high probability of rodent damage. All these materials are artificial and not edible, but this does not stop the mice from nibbling them, turning them into dust, and build nests for themselves in the vacant voids.
- Basalt wool, glass wool and other mineral wool.
- Any polystyrene (polystyrene foam, foamed and extruded).
- Fiberboard, particleboard, MDF boards.
The main criterion by which pests choose housing for themselves is that the material should be low density, warm and dry. For example, expanded polystyrene - they especially liked it.
And of course, mice will happily dwell in natural materials such as sawdust, straw, reeds or clay.
Overview of Rodent Resistant Materials
As a rule, mice bypass inorganic materials with a solid and loose structure.
Ecowool. Thermal conductivity = 0.03-0.04 - an excellent indicator comparable to such isolates as polystyrene and glass wool.More than 80% of cotton wool consists of cellulose. The material is non-combustible, well springy, non-toxic, sound insulation is 4 times better than mineral wool.
It can be applied manually and with the help of pneumatic installations. The latter method is 20 times faster, saves half the material due to uniform application, fills all the gaps well, does not form joints. Installation is possible at subzero temperatures. It is possible to insulate both under construction objects and during reconstruction. The service life is about 80 years.
The disadvantages of the material are its high cost and additional costs for pneumatic transport at the installation stage. In addition, she needs to provide conditions for drying (from 2 to 4 days) at a comfortable humidity.
The composition of ecowool is brown salts and boric acid. The concentration of these substances is not large and does not threaten people's health, but it is enough to protect the material from fungi, rot, insects and rodents!
The mass is placed in molds and sintered at very high temperatures. Available in two types: bulk, slabs.
Thermal conductivity = 0.04 - 0.14. The material is absolutely not afraid of moisture, does not lose its properties, even with prolonged contact with water. It does not collapse due to temperature changes, it does not shrink. Plates can be sawn, glued with mastics, plaster, and put on a cement mortar. The service life is 100 years.
The disadvantages of foam glass:
- High cost (1 m3 of tile foam glass costs about 18 thousand rubles. The granular version costs 2500 - 4800 rubles per 1 m3).
- Great weight.
Glass in the composition of the material prevents fungi and mold from developing, it is not damaged by the roots of trees. In addition, foamglass is an excellent abrasive that is too tough for rodents!
Foam concrete. This is a type of cellular concrete. The properties are close to aerated concrete (in foam concrete, a uniform distribution of bubbles is achieved by mixing, in aerated concrete this is a consequence of chemical reactions). The D400 and D500 are heat insulating grades. Thermal conductivity = 0.08 - 0.12.
The material can be sawn and glued with mastics. It is fireproof, durable, mounted quickly enough, environmentally friendly. Lighter and warmer than regular concrete. The cost per 1 m3 is approximately 2500 rubles. But you can purchase individually.
Disadvantages:
- He does not like moisture, it is necessary to protect it from atmospheric precipitation with a vapor barrier layer.
- In a humid environment, mold may develop.
- Not very well plastered.
Expanded clay. Environmentally friendly material is clay exposed to high temperatures. May be expanded clay:
- gravel (brown balls familiar to everyone);
- crushed stone;
- sand.
Thermal conductivity = 0.14-0.18 (comparable with the thermal conductivity of boards and roofing felts; worse than that of ecowool, foam or glass wool). Installation of large objects can be time-consuming - lifting mechanisms are required, private builders do it on their own.
With prolonged contact with water, it loses its properties. Shelf life comparable to the life of the building. One of the most inexpensive heaters (1 m3 will cost 1 - 1.4 thousand rubles.)
Which is better to choose?
Expanded clay. Expanded clay, as the most inexpensive of the listed materials, is the first to attract attention. But its use is not advisable in all situations. It is better not to use expanded clay for wall insulation of a finished wooden house.
It is poured into the void between the main wall and the erected formwork wall; expanded clay layer thickness should be about 20-40 cm.
At the construction stage, it is possible to plan the insulation of expanded clay walls with expanded clay. Then, on a single foundation, two walls are erected in parallel, with the space between them, which is filled with insulation. After a few rows, a bundle is made (it can be a metal mesh, for example).
Foam concrete. Brick walls are lined with foam concrete to create an additional warm layer. Non-standard, but effective method - foam concrete can insulate the house from the inside (including wooden). The insulation layer will serve as a heat accumulator. You can clearly see this if you open the door.
Only air will warm in a wooden house - it will quickly evaporate and the temperature will drop sharply. In a house with foam concrete walls, warm air will also quickly disappear, but after closing the door, the walls will begin to give off heat and warm the room again.
When covering the premises from the street, it will not release moisture outside, from which the walls can rot.
Ecowool. The ideal material that can be applied to the walls of a wooden or stone house. Ecowool has good adhesion, it will repeat the contours of the house and fill all the cracks. At the same time, the material is lightweight, any construction will withstand it. Ecowool is perfect for insulation of ceilings and floors of private houses and any other construction projects.
How to protect polystyrene from mice
As we saw, polystyrene does not stand up to rodents at all, and they spoil it quickly and thoroughly. However, the material is quite popular.
What can be done to protect the foam insulation from pests:
- Polystyrene foam with a dense structure is preferable, such a material is still less susceptible to pests.
- You can cover the foam mats with a fine metal mesh (but this method will be quite expensive).
- There is a technology by which a foam sheet is poured with concrete on both sides, the insulation is obtained in a reliable casing, but it performs its functions.
- If at the construction stage these actions have not been performed, there is only a constant scaring away of rodents from the house. Here, all means are suitable: from a cat to modern electronic repellers.
Poisons (including boric acid) should be used with caution. Mice can die directly in their nests, and an unhygienic zone forms under the skin, which will not be available.
Popular materials such as glass wool or isover, polystyrene foam or even polyurethane foam are very vulnerable to rodent damage.
There are materials that can really be a salvation from adversity - this is foam glass, ecowool, foam concrete or expanded clay. The cost of these heaters is not feasible for everyone, so you can try to defend existing building materials by other methods.
Insulation in the house is a necessary thing
Warming the house with modern materials sets the main goal of maintaining heat in the house and reducing energy costs. But often this goal is leveled by the banal intervention of rodents.
Of course, for them, polystyrene, mineral wool and other heaters do not represent culinary value. But to equip a comfortable place for nesting in a warm mass of material is another matter.
The solution is seen only in the use of heaters, which are not of interest to the sharp teeth of rodents.
Despite the fact that the selected type of insulation must be resistant to attacks by rodents, it is obliged to fulfill its basic functions, having practical parameters:
- Thermal conductivity - the lower the coefficient of this characteristic, the more reliable the house is protected from cold temperature
- Heat capacity - higher values of this parameter provide better heat storage
- Vapor barrier - if the heater meets the standards of this criterion, walls and other structural elements are not at risk of infection by fungus and mold
- Soundproofing is an important argument, especially when warming partitions and walls in multi-storey panel houses
- Resistance to ignition risk
In order not to experiment with the taste of rodents once again, you can immediately determine those heaters for the walls of a wooden house that are suitable for their interests:
- Basalt cotton wool. Here rodents feel very comfortable, arranging breeding nests. Rats are able to live in such a heater until it turns into dust
- Polyfoam - with the cohabitation of rodents, the supply of insulation may not be enough even for a couple of seasons
- Expanded polystyrene is also an attractive place for rodents
But these animals feel discomfort when arranging isolation:
- Penoizolom. This is a type of foam, but with different components and structure.
- Extruded polystyrene foam, the dense structure of which does not crumble, and is not suitable for the residence of mice and rats
- Aerated concrete with a solid structure that is too tough for rodents
- Ecowool, which contains borax, not causing interest in rodents
But more effective heaters in confrontation with a detachment of rodents are expanded clay and foam glass.
Foam glass
Foam glass is a resistant barrier for all types of rodents due to its dense structure and durable components.
This material, unlike the Polinor insulation, is distinguished by an almost unlimited service life. In any case, foam glass will be an effective heater during the entire period of operation of the house.
In addition to unsuitability for rodent life, foamglass has such advantages:
- Immunity to temperature changes
- Inertness to erosion
- The ability to withstand freezing water
- Corrosion Prevention
- Resistance to deformation
- Resistance to negative biological manifestations
Foam glass has excellent vapor permeability. Its use is advisable when warming large areas - public buildings, commercial establishments, as well as private residential buildings.
The arrangement of thermal insulation of private buildings with a long service life with foam glass is not always rational, since the service life of the material is very long. If after a few years it is necessary to repair the insulated surfaces, then you will have to dismantle the insulation layer and use a new one.
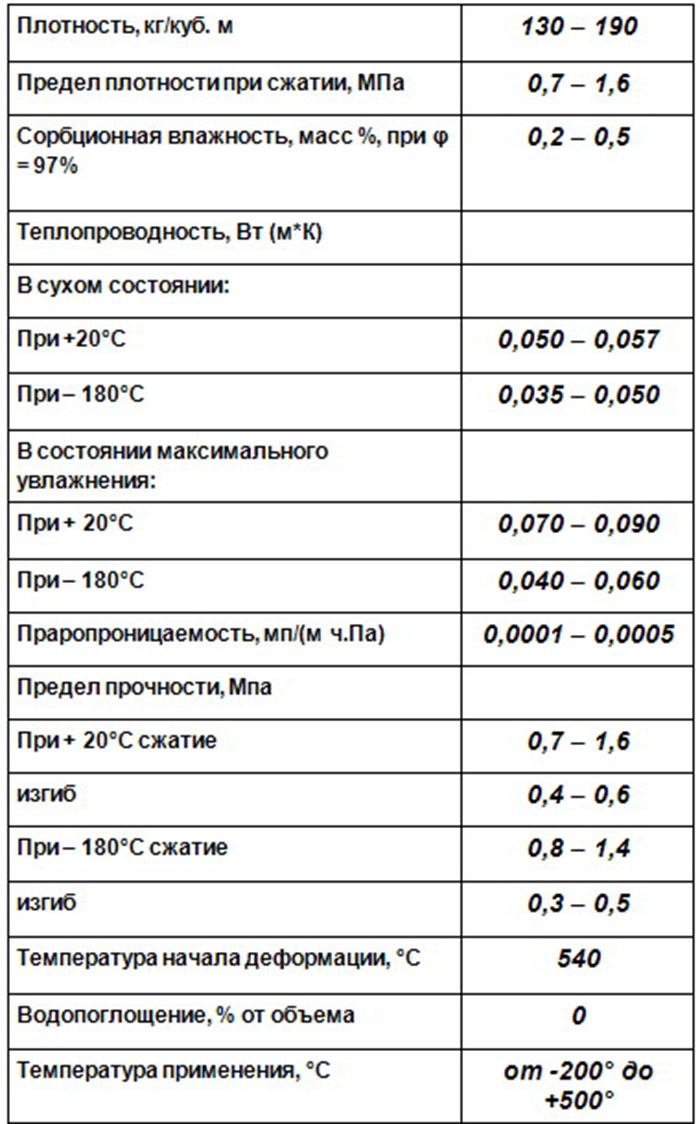
Expanded clay
Expanded clay has a porous structure and light weight. But this is enough to neutralize the interest of rodents in the insulation. This material appears in the form of small granules of a slightly reddish or brown color.
The thermal conductivity of expanded clay is quite suitable for its use when warming floors and attic structures. Although its coefficient is not the highest among similar materials - only 0.12-0.15 W / m * K.
When mixed with cement mortar, expanded clay can also be used for wall insulation. But in this case, due to the use of a cement base, the heat capacity of the thermal insulator will suffer.
But the porous structure of the material also has a side effect - it is able to accumulate moisture in itself. Therefore, when installing thermal insulation using expanded clay, it is necessary to prepare a waterproofing layer.
In order for claydite to truly provide the declared thermal insulation parameters, it is necessary to lay it with a dense mass. The layer of material should be at least 500 mm - only in this case the insulation will be rational.
Among the advantages of this material are light weight and ability to withstand deformation. The strong structure of the granules also provides resistance to chemical factors.
Responses of house owners who have insulated their homes with different types of thermal insulators differ for reasons of importance of priorities. But most reviews with a positive attitude relate to foam glass and expanded clay.
In both cases, according to the results of reviews, with the right insulation device, a high degree of efficiency is noted. One of the priorities of many residents is the low cost of both materials.
Foam glass is a material that is often used to warm the facade of a house. Expanded clay - a product made of clay, which means environmentally friendly.
Novelty in the market of heat insulators
When choosing a heater, many different criteria are taken into account, such as thermal conductivity, durability, environmental cleanliness, etc.
Choosing a heater, all homeowners are wondering: what kind of insulation do not eat mice and rats? This issue is especially relevant for residents of those areas where many rodents live. Do they harm thermal insulation? What kind of insulation do not the mice eat?
What heaters do mice like?
Let's first talk about those heaters that rodents "love." Accordingly, these types of materials are not recommended. The leader among heaters that mice eagerly eat is foam.
Styrofoam. This material in the presence of rodents in the house becomes worthless after a few years. When opening the insulation, it is found that up to 80% of the insulation is eaten and damaged by mice. Rodents do not eat polystyrene, but they love to chew.
Extruded Styrofoam. Its rodents do not eat so willingly, but consider it a great habitat. When dismantling a heat insulator from extruded polystyrene foam, nests of pests are usually found, although the material itself is much less damaged than polystyrene.
Mineral wool. Mineral wool is considered environmentally friendly and safe material. Unfortunately, rodents also understand this. Mice do not eat this insulation, however, reproduce well in it.
With all the advantages of mineral and basalt wool, it is dangerous to use it in areas where rodents live. It is better to leave this insulation for urban high-rise buildings, where the concentration of mice and rats is less.The only, rather dubious, plus is that mineral wool has excellent sound insulation, so you most likely will not hear the presence of mice.
Stone wool is not included in the diet of rodents, but nests are built in it willingly. Since they have to gnaw it to build nests, they spoil it for all this.
As you can see, the most common types of insulation were also popular and loved by rodents. This led builders and homeowners to look for new insulation materials that would not be exposed to rodents.
Types of heaters that are not afraid of rodents
Such insulation today is quite enough. They differ more in density and sometimes low environmental friendliness, but among them there are completely unique materials that not only are not exposed to rodents, but also have excellent thermal insulation and environmental characteristics.
Expanded clay. Well-known heat insulator for floors, floors, foundations - it is not combustible, absorbs noise, is relatively cheap. Mice and rats do not live in expanded clay, which, of course, is also its advantage. However, this material has two significant drawbacks:
- low environmental friendliness; when heated, expanded clay releases toxic fumes;
- the complexity of the installation of the insulation system, for expanded clay, it is necessary to construct the formwork into which it is poured.
Ecowool. A relatively new material used for insulation of walls, floors, ceilings. Although ecowool is soft and safe, rats and smaller animals bypass it.
For humans, such an acid is absolutely safe, therefore, eco-friendly cotton wool can be safely used as a heat insulator. However, it is worth knowing that ecowool has its drawbacks: combustibility and high cost.
Do mice eat Velit insulation
This material does not attract rodents and insects at all, despite the fact that it has a low specific gravity. Most of it is occupied by air pores, and the structure itself is porous. The material is a very low density cellular concrete. In addition, Velit has high heat-preserving and noise-absorbing characteristics.
No toxic substances are used in its production, therefore, the material belongs to the class of environmentally friendly. Another advantage is the low cost, which is important for consumers.
As you see, when choosing a heater it is very important that it does not suit the taste of rats and other animals, otherwise the thermal insulation will not last long. We recommend using materials that meet two criteria: resistance to rodents and environmental safety.
We advise you to pay attention to the new Velit heat insulator - inexpensive and reliable, with all the required properties.
Overview of materials, characteristics and methods of protection against rodents
All the advantages of modern insulation can come to naught if rodents are chosen as their goal. They use the material as feed or arrange nests in it. What kind of insulation do not bite mice and rats and how to protect thermal insulation from them?
A heater that can resist mice
There are a number of signs by which mice choose insulation material: low density, lack of moisture, warmth, and the possibility of being used as feed. Therefore, to protect against rodents, these factors must be excluded.
The insulation, which can withstand the attacks of rats and similar animals, must have the following properties:
- High density.This is the main obstacle for rodents.
- Processing with special means, the concentration of which is safe for human health.
- The loose structure of the insulation. It does not allow pests to make nests in the material.
These requirements are met by a number of heat insulators, which need to be considered in more detail.
Foam glass. For the manufacture of foam glass, glass break is used, which passes the stage of heat treatment. Foaming agents are added to create voids - anthracite, coke.
When choosing foam glass as a heater, it is necessary to take into account its properties:
- Large specific gravity. Depending on the manufacturing technology, the density of the material varies from 100 to 600 kg / m³. This is a high figure, which negatively affects the conditions of installation and processing.
- The thermal conductivity coefficient is one of the lowest among heaters - from 0.043 W / m * C. For bulk types of foam glass, it is higher, since tight contact of the granules with each other is not ensured.
- Fire safety and soundproofing. They are due to the properties of the material of manufacture and its structure.
- High price. The average price for 1 m³ of block foam glass is 17,500 rubles.
- This insulation is chosen if the problem of rodents is relevant and it is required to provide a high degree of protection against them.
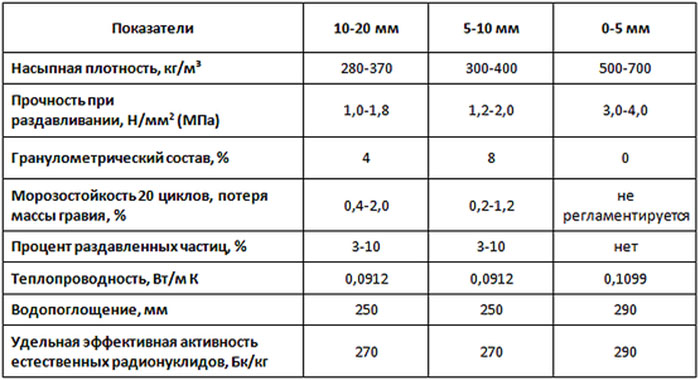
Expanded clay. Expanded clay is made from special grades of clay using a technology similar to foam glass. But in contrast to it, the formed granules cannot be compressed into a single block, since they have low mechanical strength and elasticity. This insulation is not bitten by mice and rats because of its flowability.
To analyze the relevance of the use of expanded clay, its characteristics are taken into account:
- The nominal thermal conductivity for one granule is from 0.01 W / m * C. But in fact, it is higher for the expanded clay layer, since “cold bridges” are formed between the components. It all depends on the density of the backfill.
- The compaction ratio is 1.15.
- Fraction 10-20. It is this granule size that is used for insulation.
- Water absorption from 8 to 20%.
- The average cost is from 1300 r per 1 m³.
- Expanded clay can only be used as bulk insulation on horizontal surfaces.
Ecowool. It is made from paper industry waste. After processing, ecowool is treated with compounds of brown salt and boric acid. Their concentration is dangerous for rodents, but does not affect human health.
For the application of ecowool on the surface of walls or floors, special pneumatic equipment is used. The final drying time of the protective layer varies from 2 to 4 days, depending on its thickness.
The main characteristics of ecowool:
- Insulation is classified as moderately combustible materials. When exposed to open fire, it does not melt, if you remove the source of ignition, attenuation is observed.
- The average density is up to 55 kg / m³.
- Thermal conductivity - up to 41 W / m * С.
- The price includes work on applying material - from 600 p. For 1 m² with a thickness of 100 mm.
- Ecowool is advisable to apply for large volumes of insulation.
That mice and rats rarely gnaw
There are a number of insulating materials that rodents rarely spoil. But it depends on the thickness of the insulation, its actual density, the structure of the wall (ceiling). If you apply additional protection measures (processing with special compounds), then the mice will not gnaw the following types of heat insulators:
- Mineral wool or glass wool. The material attracts rodents of low density, they can use it to arrange nests. Glass wool negatively affects the health of rats, which is why they are afraid to come into direct contact with it.
- Extruded polystyrene foam.Unlike foam, it has a higher density, which prevents rodents from making moves in the material.
- Mice and similar animals like to chew on polystyrene, fiberboard, particleboard, penoizol. This must be considered with a high concentration of rodents.
Additional protection methods
If the thermal insulation layer is already installed, and the problem with rodents has appeared recently, additional protective measures must be taken. It is important to exclude mouse access to the layer. This can be done without dismantling the insulation.
To create additional protection, it is recommended to use the following methods:
- Installation of steel mesh. It is installed in front of the insulation. The method is expensive, but effective.
- The use of chemical compounds - “Krysid”, “Goliath”, “Mortorat”. Processing is done in accordance with the instructions. It is important that the properties of the insulation do not change.
- The use of alternative heat insulators. Rodents are afraid of sounds, so a layer of fallen leaves will scare them away.
The choice of insulation that mice and rats do not gnaw on must be taken care of before buying it. It is possible to use standard types of heat insulators, but with additional protective measures.
leave a comment