
Hello! It was a long time ago. I once went with my daughter on a short trip to our forest.
Without any specific purpose, just wander around. As soon as we moved a few meters from each other, our daughter had already come running screaming. Something bit her. She decided it was a tick.
But there was no insect bite at the site, and there were no characteristic traces after tick activity. Want to know what a tick bite looks like on a person’s body? Now I’ll try to describe everything in detail, so that you can determine at a glance.
The content of the article:
What does a tick and tick bite look like?
Probably, each person heard exactly the common version that a forest tick always falls on a person only from a tree, for example, from an oak. However, oddly enough, this version is erroneous. Ticks usually hide where people do not expect to see them. In thickets, on branches of bushes, along the edges of paths in the forest, in the grass.
In the period from mid-spring until the first frost, ticks become more active. The most dangerous period is the end of April - July. Ticks live in forest zones and parks, where there is no hot direct sunlight, and the temperature rises over twenty degrees.
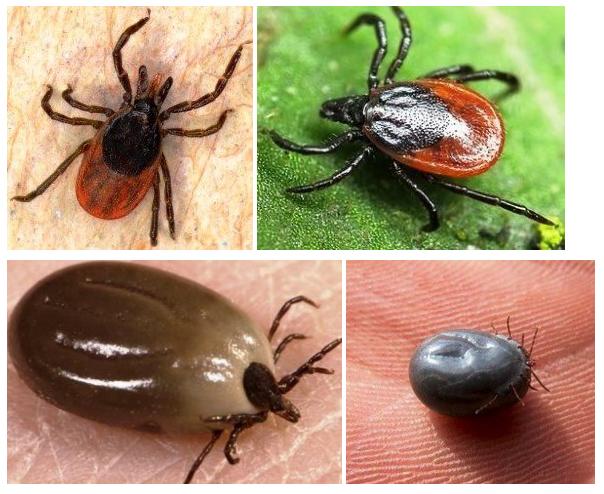
What does a parasite look like?
Ticks - a small spider with the size of a match head. A female who has gained blood can reach the size of a pea. Ticks are absorbed into the skin of an animal or person with the help of their proboscis. The male, as a rule, does this for a short time and soon disappears by himself.
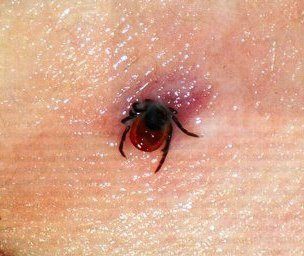
More dangerous is the female. To get rid of it, human intervention from outside is necessary. What the tick looks like you can see in the photo.

A tick, when bitten, secretes a specific substance that acts on the principle of anesthesia. That is, a person will not feel the very moment of the bite. That is why it is not possible to quickly respond to a tick attack.
What does his bite look like?
Basically, a person finds a tick bite before the tick has time to fall off. A noticeable red spot appears on the skin - this is the usual reaction of the body to a bite. Then, a person sees a protruding little body on top of the spot. As a rule, the diameter of the redness does not exceed one centimeter.
If you are unable to pull out the tick completely, and you have torn it, for example, the trunk and legs, you should not try to dig out the rest of the skin. The body itself can tear it away as soon as you grease the lesion with green.
If the spot does not start to disappear or decrease over the next few days - this is an occasion to go to the hospital.
You do not need to try to remove the arachnid as soon as you find it, especially if the tick has already managed to suck into the skin. It should be carefully loosened, because the tick is fixed by a bite inside the wound.
If you rush into action, it is possible that you separate the body of the tick, but leave the head of the parasite in your skin.
No need to use tweezers or forceps, the reason is the same. Only with your hands, carefully and slowly try to pull the tick, but counterclockwise. You can also try to bite the site of the bite with ordinary sunflower oil and wait fifteen minutes. Perhaps this will greatly simplify the procedure for extracting the tick.
In general, try not to kill the insect so that its saliva and stomach contents cannot get into your wound, and with it a dangerous virus.
Going hysterical if you are bitten by a tick is not worth it. Naturally, not every tick is an infected representative of the virus encephalitis. And even if the tick is contagious, then it releases the viral substance for about three days, but during this time it is quite possible to get rid of it.
If redness does not go away after getting rid of the parasite, and there is a feeling of deterioration in well-being, it is worth visiting a doctor. Since encephalitis in the incubation (hidden) period can occur up to three months. You should be more careful about your body after a tick bite.
In the near future, headache, drowsiness, weakness, loss of appetite, apathy and fever up to thirty-seven degrees and above may appear.
Further, the disease, as a rule, begins to develop sharply: there is a fever, cramps, severe pain in the muscles, a disorder of the nervous system.
Post-Bite Prevention
To protect yourself, prepare carefully before heading out into the forest. Choose clothing only from thick fabrics and with long legs and sleeves.
Of course, in our time there are many special tools that are designed to repel ticks. They need to handle places where the tick can penetrate. For example, wrists, lower back, neck, ankle.
Symptoms after a tick bite in humans
A tick is a small arachnid insect that feeds on blood. Basically, they parasitize on the body of animals. But there are situations when a tick is attached to a person.
Every year the number of cases when the tick has become a carrier of these diseases is growing. This means that you need to be more attentive to yourself and your health. Take into account the places where the tick most often lives, and also know the symptoms that indicate a bite.
What symptoms appear if a person is bitten by a tick
Hypostam is a special organ of the tick, with the help of which it is attached to a person.As a rule, due to the fact that the tick lives in the grass, less often on low bushes, and is a sedentary insect, it is sucked from the bottom up.
Most often, he selects a tender skin as a bite site, located in the groin, lower back, abdomen, ears, neck and armpits.
This spot is grown quickly enough. Sometimes its diameter can reach 60 cm. So, how to determine that a person has been bitten by a tick?
How many symptoms after a tick bite appear? What to do if this insect has bitten you? Each of these issues requires close examination, since the number of cases of damage by severe infectious diseases, the carriers of which are insects, is constantly growing.
First signs
A tick bite does not hurt. That is why people can not always immediately identify the cause of their poor health. If you are visitors to a park or forest, then you should carefully examine your body and eliminate the likelihood of damage. Certain symptoms may indicate that tick poison has entered the body. These include:
- Chills;
- Weakness;
- Drowsiness;
- Fear of light;
- Joint pain.
It should be noted that signs may not be pronounced. It all depends on how many ticks sucked on the person, to which place, whether the person has health problems and a tendency to allergic reactions.
The very first and important sign that it is worth the alarm is the detection of a sucking tick.
The insect must be removed and sent for research. If it is clean, then no further treatment is required. If the tick is a carrier of dangerous diseases, then timely detection is a guarantee of eliminating serious consequences.
Symptoms the next day
If a person did not timely notice a tick affection and did not pay attention to the first symptoms, which can easily be confused with fatigue, then the next day his condition can worsen significantly.
Separately, the symptoms are similar to the first signs of a cold, however, it is worth remembering that the combination of such factors can speak precisely of a tick bite. What to look for?
In rare cases, additional symptoms may be added:
- Severe headaches dizziness;
- Vomiting and nausea;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Hallucinations.
If the temperature rises immediately after the bite, then this may indicate the development of an allergic reaction to saliva. If the temperature lasts for a week, then this may be a sign of an infectious lesion.
Signs of tick-borne encephalitis
Tick-borne encephalitis is a viral disease that affects the nervous system. With untimely treatment, disastrous consequences can occur. The disease progresses very quickly.
After the disease covers the entire brain, a person may notice the following symptoms:
- Headache;
- Fainting;
- Disruption of the cardiovascular system;
- Increased irritability;
- Digestive system problems;
- Increase in body temperature up to 40 degrees.
Complications of this disease lead to flaccid paralysis of the upper limbs. The percentage of deaths depends on the country in the world.In Europe, this figure does not exceed 2 percent. In the countries of the Far East, it is 20%. Mortality occurs one week after the defeat.
With Lyme Borreliosis
Lyme Borreliosis is an infectious disease that affects the work of the heart, nervous system and musculoskeletal system. The carrier of the virus is a tick. The skin turns red at the site of the bite.
A month later, symptoms of damage to the cardiovascular and nervous system are noted, joint pain occurs. A person’s condition corresponds to the state at the initial stage of a cold: headache, aching muscles, weakness and fatigue, as well as sore throat.
To all this are added symptoms from neurology - paralysis, hearing loss, insomnia. Complications of this disease rarely cause death. However, it is they that can provoke the development of dangerous diseases, which in the future can lead to death.
What does a tick bite look like on a body?
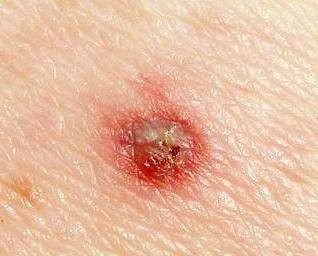
As practice shows, basically a person discovers a bite after the tick has time to fall off. The bite site is a red speck from which the body of the insect sticks out. The diameter of the redness is about one centimeter.
Many try to pull the tick out on their own. If the legs or tentacles of an insect remain in the wound, then you should not worry.
The body itself will reject them. Another thing is the head. In the photos presented in this section, you can get acquainted with how the places of bites look in practice.
What to do after a bite?
Since the tick is a carrier of serious diseases, then returning home after going to the park or forest, do not immediately lie down on the sofa. It is important to carefully examine yourself and your loved ones for the presence of a tick on the body.
Immediately it is worth noting measures that will avoid biting this insect. First of all, it is worth knowing the places that they choose for themselves. These are grasses and low shrubs. Do not wander unnecessarily through such landscapes.
Thirdly, going to the nature, choose tight clothes. Weather permitting, wear long sleeves and a throat. Pants should be as long as possible. It is best when clothes fit the body completely.
Treat exposed areas of the body with a special tick remover. If the above measures did not allow to avoid a tick bite, then the following must be done:
- Remove the parasite on its own or by contacting the emergency room;
- Take the tick to the sanitary service for analysis, which will let you know if it is sterile or is a carrier of certain infectious diseases;
- Lubricate the bite site with an antiseptic: iodine, alcohol, brilliant green.
It is worth emphasizing that only a living insect is suitable for analysis. That is why it is necessary to trust the doctor to extract it, since at home it is not possible to correctly extract the tick.
Antibiotics may be prescribed depending on age, as well as antihistamines. Signs of infection begin to appear only after a few weeks, but a general blood test after 10 days already allows us to conclude that there is an infection in the human body.
What does a stain look like after a tick bite?
Tick-borne parasite is a potentially dangerous carrier of pathogens of many infectious conditions that cause the development of serious disorders in the human body, including death.
In addition, ticks transmit pathogens of diseases such as borreliosis, ehrlichiosis, anaplasmosis through a bite, and in the absence of carriage, they contribute to the development of an allergenic reaction in humans, which begins with the formation of a spot after a tick bite.
General information
Ticks are carriers of one or several pathogens at once, which include not only bacteria, but also viruses. The parasite lives in the driest area, activating in the warm and arid weather season.
In the process of penetrating deep into the human integument, a tick injects anesthetic into the tissues, so the bite does not have a pain factor by which it is possible to determine the foreign introduction into the body.
Typical bite areas are skin patches hidden under clothing:
- bend of the elbow region;
- limbs
- inguinal zone.
Blood is their nutrient medium; upon absorption, it begins to stretch the chitin shell of the tick, which immediately becomes visible on the integument of the body as a large bean.
The interval during which the parasite can become saturated with blood takes from an hour or more. The tick smells a person for several meters, in the complete absence of a visual element.
The process of reproduction of an adult takes a range from 3 to 5 years, which begins with the laying of eggs and until the development of the stage of a blood-sucking parasite. Over the life span, an individual is only several times saturated with blood. After performing the nutritional function, it falls away from the integument, on the surface of which a red spot remains after a tick bite.
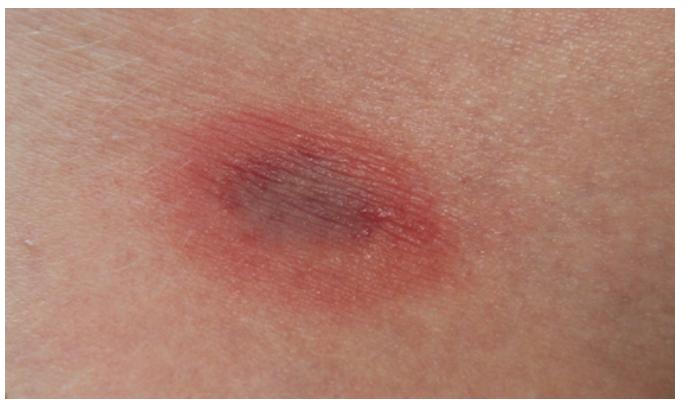
The mechanism of spotting on the skin
The process of penetration of a tick into tissues occurs when its salivary secretion is exposed, provoking the development of a localized inflammatory process in the affected area with the manifestation of an allergenic response. Therefore, a local reaction to a parasite bite is local swelling and swelling of the tissues.
With a normal recovery, these phenomena disappear spontaneously in the interval of several days after a bite. When using antihistamine drugs, redness disappears much faster.
Spot Specific Features
When the parasite carries a certain infectious pathogen, the manifestation of the reaction of the skin integument has some specificity, according to which infection with the corresponding representative of the pathogenic world can be previously assumed. It is much more difficult if several microbes are present in his body at once.
Features of the skin reaction, with the penetration of the causative agent of Lyme pathology, have the following differences:
- Infection with borreliosis (erythema) is characterized by the formation of a spot after a tick bite, which does not appear immediately, but only a week after the incident.
- The bite site has characteristic differences, representing the formation of a specific erythema in the form of a spot, which gradually grows in size, reaching a circumference of up to 60 cm in diameter.
- The shape of the spot is round, oval, or it may have irregular and fuzzy borders.
- After some time, the contours of the spots begin to gradually rise above the surface of the covers, while their shade becomes intensely red.
- When the spot after a tick bite stops growing, its central area acquires a bluish tint or gradually turns white.
- After a day, it becomes in the form of an oval elevation or growth, and a scar and a cortical layer of tissues form on its covers.
- After two weeks, the bite marks completely disappear.
In other cases, a typical picture of redness and staining after a parasitic lesion appears, which characterizes the manifestation of a local allergic response to the introduction of the pathogen.
Characteristic signs and atypical stain outcome
It is difficult to detect the parasite immediately on the integument; therefore, in most cases it is visually determined after the insect is completely saturated with blood, when the full abdomen becomes clearly visible on the human skin. Signs of a bite include the following stepwise process characteristics:
- the absence of pain when the tick penetrates into the layers of the dermis;
- visually you can detect an incomprehensible dark spot;
- the subsequent formation of the elevation of the abdomen of the tick above the surface of the skin;
- self-dropping of the parasite after saturation or its forced extraction;
- the formation of an allergic manifestation in the form of a localized red spot;
- the appearance of pain discomfort in the problem area.
If the stain after a tick bite does not go away on its own, this may indicate an infection in the affected area and the development of local inflammation with a complication in the form of a purulent process. In this case, it is necessary to consult with a specialized specialist to exclude the development of aggravating consequences.
Danger of conditions after infection
In the most deplorable case, when an infected insect bites, a person has a very high risk of developing a serious disease. One of them is the tick-borne form of encephalitis.
In the form of a bite complication, Lyme pathologies, ehrlichiosis, anaplasmosis are much less common. Borreliosis causes damage to the nervous, cardiac, immune and motor systems of the body, while the pathogen is not always determined by laboratory methods.
In the absence of timely therapeutic measures, the lesion process goes into a protracted sluggish form, provoking the development of consequences irreparable for the body.
What does a tick bite look like?
Ticks belong to the class of arachnids, they are one of its most numerous orders. The most dangerous for humans are forest ticks. As a rule, they are found in shady moist forests.
In fact, their main habitat is grass and undersized shrubs up to one meter high. A tick can easily catch you when you walk along a forest path.
When bloodsuckers appear
The most active period of tick reproduction occurs in May, and then their number decreases. Ticks can be found before the first frost. The most careful should be between April and July. Ticks like to live in coolness and shade, so be especially careful when you want to hide from the heat in a cool forest.
The forest tick is very tiny in size - only 3-4 millimeters. But pumping blood, the female tick can become the size of a pea. Ticks are absorbed into the skin of a person with the help of a proboscis.
During a bite, a tick releases a special substance - anesthetic, which relieves pain, so a person does not feel the moment of a bite. The most dangerous are female ticks, because they bite into the skin for a long time and cannot be eliminated without external intervention. Males, as a rule, fall away themselves.
What does the bite site look like?
Usually a tick has time to detect before it has fallen.You will see a red spot on the skin and a tick abdomen sticking out of it. If the tick has already managed to decently get a drink of blood, then it will not be difficult to notice.
After you come home from a park or forest, carefully examine your body. As soon as you find a sucking tick on yourself, you need to remove it.
Therefore, if you find a tick on yourself, be sure to mark the day on the calendar when this happened and carefully monitor your well-being.
Tick-borne encephalitis
Tick-borne encephalitis is a serious disease that affects the nervous system. It progresses very quickly, so without treatment it can cause paralysis or death. Literally 10 days after a tick bite in a person, some muscle groups can be paralyzed. The main symptoms of the disease are:
- dizziness;
- fainting
- problems with the cardiovascular system;
- digestive system problems;
- temperature increase.
Tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme disease) is an infectious disease affecting the nervous system, cardiovascular system and musculoskeletal system. A sign of the disease is considered to be the appearance of a migrating erythema at the site of the bite - a round red spot.
At the initial stage of the disease, a person can feel:
- General weakness and fatigue;
- Headache;
- Muscle pain;
- Sore throat.
As soon as you feel unwell, seek medical help immediately. Timely treatment will help you maintain your health and life.
Tick bite: human symptoms
Every year, starting in May, epidemiologists warn of the danger of tick bites. This blood-sucking parasite can be a carrier of such dangerous diseases as encephalitis, anaplasmosis, ehrlichiosis, borreliosis, and also cause allergic reactions in people with a tendency to such.
The tick has a peculiar organ - a hypostome (proboscis), which pierces the victim’s skin and is attached inside the wound with the help of special saliva, which also anesthetizes (which is why a person does not feel the moment of a bite) and fixes the proboscis in the wound. The size of the tick is about 0.3-0.4 mm, the females are 1 mm larger. Sucking blood, the tick increases in size by 2-3 times.
The main symptoms are:
- a state of chills and a sudden increase in temperature to 37-38 degrees;
- tachycardia (heart palpitations);
- weakness and drowsiness;
- an increase in lymph nodes located near the site of the bite;
- joint aches;
- the manifestation of an allergic reaction in the form of skin rashes is possible.
Signs
If you notice one or more of these symptoms, you should carefully examine the skin. To do this, it is better to go to an open area (so that tree branches do not hang on which parasites can also be) and carefully examine the whole body.
It is better if another person does it, because it is difficult to detect a tick on the back. The most obvious sign of a tick bite is its sucked body. Attention! It is absolutely impossible to tear off the protruding part, since then it will be extremely difficult to extract the remaining half.
It happens that at the time of inspection the tick fell off.But the place of the bite will be clearly visible and the trace is different from the bite of a mosquito or other insect.
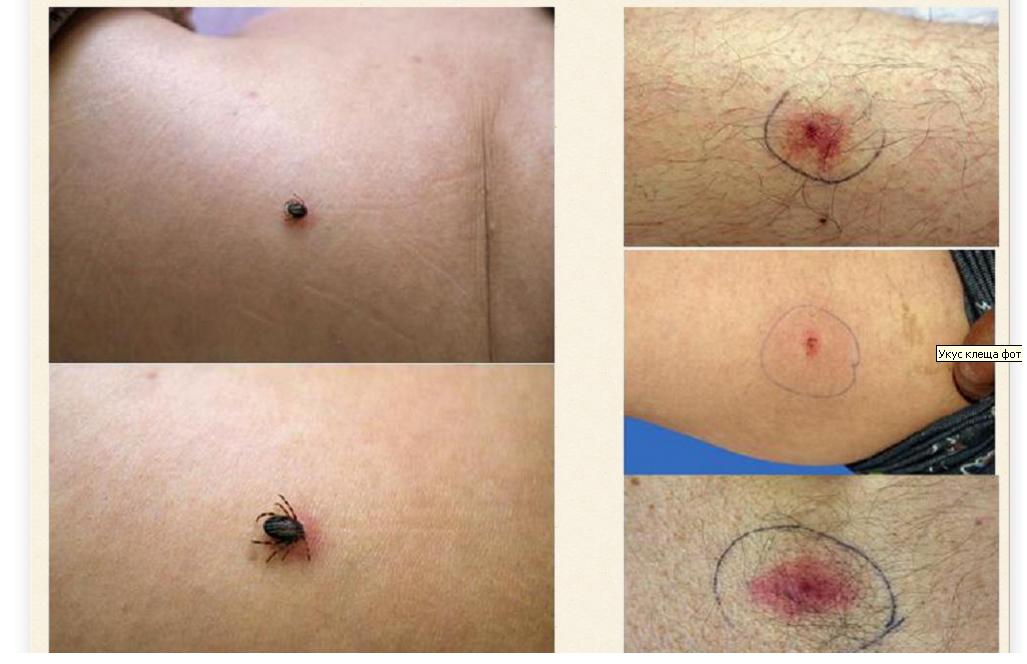
The place around the bite has a color from pink to reddish, it depends on the reaction of the body. In the center there will be a noticeable deepening deep into the skin. With borreliosis, erythema with a diameter of 10-15 cm (sometimes up to half a meter) can form.
Then a sublime ring of red color appears, in the center of which there remains a spot of white or cyanotic color. Then a scar forms, which will pass in two weeks.
Consequences for humans
Practice shows that about 20% of ticks are carriers of monoinfection, and from 7 to 15% carry a range of diseases. In most cases, it is enough to remove the insect and treat the wound.
But a visit to a doctor is mandatory in each case, especially if the temperature rises for 2-3 days - this is a sign of infection in the body. The most dangerous consequences of a tick bite include:
In severe forms, there are epileptic seizures, impaired consciousness, polio syndrome. In severe form, it leads to the development of paralysis and paresis. Transmitted by ixodid ticks. Sometimes infection through the milk of infected goats is possible.
Ehrlichiosis monocytic. One week after the bite, a fever begins, which can last up to three weeks.
Anaplasmosis granulocytic. It is transmitted by ixodid ticks along with saliva when bitten. The incubation period is from 3 days to 3 weeks. General symptoms are very reminiscent of influenza, so patients do not suspect this infection: chills, headaches and muscle pains, vomiting.
When analyzing a blood, a drop in the level of leukocytes and platelets is observed against the background of an increase in urea, liver enzymes and creatine. Allergic reactions are of a very different nature: from itching and rashes to shortness of breath and cramping.
In severe forms of these infections, a loss of self-care ability, reduced ability to work (up to group 1 disability), epileptic seizures and the development of dementia are possible.
What to do?
Remove the tick from the body. Gently grab the fingers with the fingers of the body and pull out the insect with swinging movements. Do not pull sharply, otherwise you risked breaking the tick, while the head and saliva in possible microbes will remain inside. You can wrap the tick with a thread and gently pull it out.
You can remove it with tweezers (blunt, preferably plastic, so as not to damage the insect - it is necessary for analysis). Treat the bite site with alcohol, "green stuff", an antiseptic.
If an allergic reaction develops within a few minutes (difficulty breathing, swelling of the eyelids and lips), immediately call an ambulance. To prevent the development of allergic reactions, antihistamines can be given: erius, suprastin, clarithin, etc.
Be sure to take a blood test to identify a possible infection. In the presence of infection, strictly adhere to the doctor's recommendations.
Where to go?
Report the symptoms to the clinic at the place of residence (if they are observed), where you can also find out about the laboratory where to take the insect.
An accredited laboratory detects infections in the body of the tick. If they are not, the likelihood of infection is almost excluded, but after three weeks it is better to take a second blood test.
If the tick is recognized as a carrier of infections, it is imperative to undergo the necessary course of treatment in order to prevent the development of serious pathologies and death.
When an encephalitis infection is detected, human globulin is administered, the address of such an item is usually indicated on the medical policy. Further treatment is determined by the nature of the infection detected.
First aid
- Remove the blood-sucking insect from the victim (without damaging the body of the tick), treat the bite site.
- With the development of swelling and other allergic reactions, give an antihistamine and call an ambulance.
- If a person felt weak, palpitations, dizziness, help to get home and call a doctor.
- Take the insect in a container to the nearest laboratory for testing. The results are ready either in the evening or the next day.
- Observe the condition of the person, because the symptoms of infections appear 2-4 days or later.
Antibiotics
Since the tick carries infections, antibiotics do not have the desired effect on them, so they are usually not prescribed for tick infections. However, in the form of an agent that suppresses inflammatory processes in the lungs, kidneys, and liver that arise as a result of the development of tick-borne infection, the appointment of antibiotics is very likely.
For encephalitis, the treatment plan is usually:
- hospital and bed rest;
- 1-3 day - human immunoglobulin injection;
- add hemodez, ribonuclease, prednisone and other drugs;
- B and C vitamins;
- with respiratory disorders - intensive ventilation of the lungs;
- for the speedy recovery of the body, the appointment of nootropic drugs, anabolitics, or tranquilizers is possible.
To remove local erythema, tetracycline, chloramphenicol and other drugs of this group are recommended.
Question answer
Question: How to protect yourself from bites?
Question: When should I donate blood for analysis?
Answer: Usually within 10 days after sucking the tick, the analysis lasts about 2.5 hours.
Question: Does oil help remove ticks?
Answer: If you find a tick at home and there is any vegetable oil, it is enough to grease a place in an insect or apply an inverted plastic cork with oil to a place of vinegar. This blocks the access of air and the tick itself will begin to come out.
Symptoms of a tick bite in humans
We are always looking forward to spring sunshine. Unfortunately, with the first warming already at temperatures above +5 degrees., Arachnids, including ticks, wake up to life. For a very long time, from March to November, these tiny arachnids are active.
Can this be avoided? What to do when it is detected on the body? What are the symptoms after a tick bite in a person?
How a tick attacks a person
Ticks feed on the blood of mammals, including humans. They are most active in the morning and afternoon. The parasite from a distance of several meters feels its prey by the smell of sweat and body temperature.
Once it falls on the victim’s skin, the insect begins to roam around in search of a place where the skin is thin and wet. Most often, this is the skin behind the ears, under the armpits and under the knees and in the groin, but can be anywhere else.
The tick bite is painless because the bloodsucker injects an anesthetic substance that inhibits inflammation. Without causing pain, itching or irritation even for several days, the insect eats quietly and increases significantly in size, thanks to sucked blood.
When choosing habitats for live ticks for walking, you must definitely get dressed. You should wear long pants, boots, clothes with long sleeves. In addition, people who are especially vulnerable to tick bites (anglers, mushroom pickers, small children) should be protected with drugs against these insects.
Such drugs can be purchased in pharmacies in the form of creams or sprays. Using cream, you should especially carefully smear the places around the edges of the clothing: around the collar and cuffs. Often, however, this is insufficient protection, so after such a walk, you need to carefully examine the entire body.
The tick is a fairly small insect and is difficult to notice immediately.
What is a parasite dangerous?
Not all ticks spread pathogens. It is estimated that infection after a parasite bite is between 10 and 40 percent, depending on the region. In addition, even in the case of infected bites, the disease does not always occur.
However, the risk of contracting a dangerous disease after a tick bite is still very high, so you should not underestimate it. They usually transmit Lyme disease (Lyme borreliosis), tick-borne encephalitis, and rarely anaplasmosis, babesiosis, or bartonellosis.
Symptoms in humans
It is important to emphasize that the symptoms after a tick bite in a person can be different, depending on the immunity and type of parasite. Often no signs are found at all, or they are local - a slight redness on the body. But if a tick infected with borreliosis bites, the symptoms will be different.
Migrating erythema has a characteristic appearance - blurred in the middle, it gradually fades and redness is again observed outside. In some cases, despite Lyme disease infection, there is no erythema or it is very mild. Other symptoms of infection may indicate the flu:
- enlargement of the nearest lymph nodes,
- headache,
- joint and muscle pain
- general weakness
- fever.
The second stage occurs a few months after the bite. Symptoms
- unexplained fatigue
- red spots on the skin,
- changes in cardiac function,
- neurological and ocular problems.
The third stage is the manifestation of symptoms described by damage to the function of the brain, musculoskeletal system, and cardiovascular activity.
A consequence of untreated Lyme disease can be an infection of the nervous system - paralysis and / or neuritis.
Signs of an encephalitis tick bite
Tick-borne encephalitis, in turn, produces flu-like symptoms. In the first phase appear:
- fever,
- muscle pain
- headaches.
Usually, within a week, the body itself fights the infection. Unfortunately, some patients develop a second stage of the disease and the appearance of neurological symptoms. Yet again,
- fever,
- severe headaches
- may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- loss of consciousness,
- meningitis or encephalitis
This can lead to inflammation of the spinal cord or brain, paresis, impaired consciousness. The outcome of the disease can be fatal, in 1-2 percent of patients. Therefore, people who often live in the forest should be vaccinated.
What to do
If a tick is found on the body, the most important thing is to remove it as soon as possible. The shorter the period that the parasite is on the body, the lower the risk of contracting a dangerous infection.
Very easy to use special tweezers with grooves in the corners of all sizes. Tools must be disinfected with hydrogen peroxide or alcohol before use. It is necessary to capture the tick as close to the skin as possible, trying not to squeeze its abdomen, filled with blood, and not to push it back into our body.
There is a risk that part of the insect will remain in the skin. Therefore, after removing the parasite, laying on a white sheet of paper, you should check whether you deleted it completely.
After removing the insect, thoroughly disinfect and wash your hands. In case you are not able to remove the parasite yourself, or if part of it is inside, you should contact the nearest hospital. After any tick bite, even if you managed to quickly pull it out, you need to consult a doctor.
After removal, place it in a sealed vial. Write the date on the bottle. Keep it for at least one month so that, if necessary, show it to a specialist to determine the type (i.e. whether it is a dangerous Ixodes species).
After a bite, monitoring of the victim is established if there are no signs of infection, migratory erythema or other diseases. If migrating skin erythema appears within 30 days (usually 3-7 days) after removal of the tick, there is no point in conducting laboratory tests confirming the infection.
In this case, the doctor prescribes treatment - an antibiotic. Unfortunately, in some cases, erythema and other symptoms are less severe or no symptoms at all.
Therefore, even if alarming symptoms do not appear, tests must be done. Recommended test ELISA test, which is carried out after 4-6 weeks. If required, another positive Western blot test is performed that detects IgM and IgG antibodies to Lyme disease.
Symptoms of the first phase are observed for approximately a week. After several days of well-being, the second phase of the disease occurs, associated with the spread of the virus into the central nervous system.
Symptoms include headaches, fever, vomiting, nausea, loss of consciousness, meningitis, or encephalitis. Symptoms usually disappear after 2-3 weeks. However, in almost 60% of patients, complications can occur.
Tick-borne encephalitis is diagnosed by detecting IgM antibodies (found in patients with CE after about 7-10 days) in serum and cerebrospinal fluid and IgG (detected after about 10-14 days) in serum and cerebrospinal fluid.
First aid: how to remove a tick?
Tick bites do not always require medical intervention, since in most cases the bloodsucker can fall off by itself.
Removing a tick step by step:
- sterilize pointed tweezers to remove ticks (available at pharmacies)
- capture the tick as close to the skin surface as possible
- gently but firmly pull up
- after removal, place it on a piece of paper and make sure that you have deleted everything
- disinfection of the bite area with alcohol and dressing
- After removing the parasite, wash your hands thoroughly, disinfect the bite site with hydrogen peroxide or 40 percent alcohol.
- if there is an alarming change, consult a doctor
If you are unable to remove the tick correctly, consult your doctor.What should not be done when removing the tick:
- never squeeze his swollen abdomen, because the infected fluid will get under your skin through the wound
- Do not try to strangle a bloodsucker with petroleum jelly, oil, nail polish, gasoline or alcohol. Oil and other substances stop the oxygen supply to the insect and so, it is only possible to provoke tick vomiting and increase the risk of infection
- never remove the insect with bare hands, nail tongs, etc. - if only the abdomen is removed, the head and body of the insect remain in the skin, which are hazardous to health
The risk of Lyme disease is low if the tick is removed within 24-36 hours.
Treatment after removal
Some authors recommend that if a tick of the genus Ixodes has been on your body for a long time (this is determined by the size of a bloodsucker), a prophylactically single dose of 200 mg of doxycycline should be taken within 72 hours of its removal.
After removal of the insect, a month of observation should pass. After this time may occur:
- the so-called migratory erythema (creeping), which is usually observed from 3-30 days after a tick bite. Erythema is the first symptom of one of the tick-borne diseases - Lyme disease. Initially, erythema looks like red spots that grow rapidly. However, you should be aware that in more than half the cases, a skin reaction does not occur.
- fever and flu-like symptoms (severe headache, muscle and joint pain, cough), which may be a sign of anaplasmosis (HGA) - tick-borne encephalitis
After the onset of these symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor.
This skin allergic reaction does not exceed 5 cm in diameter and disappears after a month, regardless of whether you took the medicine or not.
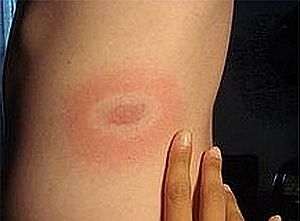
Migratory erythema is caused by the bacterium Borrelia and is one of the symptoms of severe tick-borne disease - Lyme disease. As a rule, it appears within 7-14 days after a tick bite infected with borreliosis. Usually disappears spontaneously after about 1 month.
The characteristic rash resembles a blasting shield: in the middle there is an oval or round spot after a parasite bite, and then a white circle. Erythema ends with a red rim, which every day, "goes" further and becomes larger. Erythema can be accompanied by flu-like symptoms.
It is difficult to miss this type of rash, since the diameter of the migrating erythema is at least 5 cm. A sign by which we can distinguish it from an allergic reaction that appears after a tick or insect bite.
It should be noted, however, that the rash appears only in some infected (30-40 percent.) Its absence does not mean the absence of Lyme disease infection.
Erythema is not always present, but when it appears, forms around the tick bite, although sometimes it occurs in other places. Each patient has an individual form, and even the color of redness.
As a rule, a tick bite is painless and does not manifest itself. However, in some patients, after removal of a blood-sucking insect, the bite site begins to itch.
Causes of itching at the site of a tick bite:
- Burning and itching at the site of the bite may indicate the initial stage of development of borreliosis - Lyme disease. Even before the onset of migratory erythema, characteristic of the disease. You should immediately consult a doctor.
- Itching can occur with the development of an allergic reaction or the attachment of a simple infection, due to poor disinfection when the parasite is removed.
- If the tick bite site is very itchy, perhaps you did not completely remove the insect and parts of it remained in the skin. This is very dangerous - you need to immediately seek medical help.
With proper treatment in the early stages of the disease, most patients achieve rapid improvement (usually within 4-6 weeks) and minimal complications.
In patients in the later stages (second and third), treatment can also lead to significant improvement and lack of consequences.
Some develop persistent muscle and joint pain, constant fatigue and a weakening of concentration, despite the absence of Borrelia in the blood, cerebrospinal fluid and synovial fluid.
With tick-borne encephalitis, the consequences are more serious:
- paresis
- depression
- muscular dystrophy
- persistent headaches.
Meningitis, as a rule, proceeds without complications and is associated with a good prognosis. However, in patients with inflammation of the brain and spinal cord, sometimes there are paresis, paralysis, memory impairment and concentration, which can persist for many months.
Mortality in Europe does not exceed 1%, this primarily applies to patients with paralysis of the extremities and respiratory failure.
By themselves, all arthropods are unpleasant and dangerous creatures. As for the tick bite, then everything depends on the human immunity, if it is weakened, then it is not fatal. Again, it all depends on a timely visit to a medical specialist.
Many are trying to independently pull out the sucked parasite.
But not everyone knows that the tick is breathing, sorry, ass.
I am in such cases. when you need to pull out a bloodsucker, I put a cotton swab on it, abundantly moistened with vodka or alcohol, and after a couple of minutes, he climbs out from under the skin.
Thanks to the author of this important and necessary article.