
Hello! It’s rather strange now to hear from people that they have difficulties in getting rid of cockroaches or bugs.
Dozens of tools are available in free access that will help to quickly get rid of the problem. What can I say, if even about 15 years ago these parasites could be safely removed with the help of Dust.
Already he rescued thousands of people and helped to live a calmer life. Want to know all the details about Dust - what is it and what is the main feature? I will share with you valuable and useful information about this tool.
The content of the article:
Interesting facts about dust
In 1873, the Austrian chemist Otmar Zeidler added chlorobenzene (C6H5Cl) with chloral (Cl3CCHO) to concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and synthesized a white crystalline substance (C14H9Cl5), which was later called DDT or dust, from the English dust - dust.
DDT is an external insecticide, that is, causing death by external contact; it affects the nervous system of the insect. For a person, prolonged contact with dust can result in poisoning or even death.
It's no secret that a decade ago, dust was used as an insecticide to protect crops from insect pests. Dust equally quickly deals with both domestic cockroaches and with pests of crops by butterflies, bugs and locusts.
But now it is banned for use in many countries due to the fact that it can accumulate in the body of animals, humans. High solubility in fats and low solubility in water cause a delay in DDT in adipose tissue.
Few people know that the World Health Organization (WHO) in some cases recommends access to use !!! No kidding, it turns out that dust saved millions of lives in many countries.
In January 1944, with the help of DDT, the typhoid epidemic in Naples was prevented.
In addition to the efficacy of DDT against typhoid, the relative harmlessness of this insecticide was found: 1.3 million people were sprayed with an approximately 15-gram dose with a 5% content of “dust”, and no harmful effects for people were recorded, except for a few cases of skin irritation.
In Greece in 1938 there were a million patients with malaria, and in 1959 only 1,200 people.
During the five years of the campaign to eradicate malaria in Italy, launched by A. Missiroli, by 1949, mosquitoes carrying malaria had practically disappeared in the country.
The use of DDT as part of the malaria control program has largely relieved India of visceral leishmaniasis (mosquito-borne transmission) in the 1950s.
Despite the properties of dust, which at one time helped to almost double crop yields, its use as an insecticide is currently limited. DDT is part of the “dirty dozen” of substances approved by the International Convention under the auspices of the UN.
The Convention, containing a program on chemical safety and restrictions on the production of harmful substances, entered into force on May 17, 2004 and was signed by 15 countries.
Dust (DDT) and its analogues: benefits and dangers of use
The cultivation of some crops on large areas today is unthinkable without the use of insecticides. But still alive are people who collected the Colorado potato beetle in bottles with kerosene, and collective farm leaders with children paid for the number of bugs collected per day.
Of the proposed measures, the use of “dust” powder or DDT was recognized as the most effective.
Discovery story
The word "dust" in translation from English - dust. A white crystalline substance was developed and invented in the distant 1873 by O. Zeidler, an Austrian chemist.
Only after more than half a century in 1939, the Swiss chemist P. Muller, studying the properties of an unknown powder, discovered its ability to negatively affect insects in direct contact. The discovery was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1948, and DDT, as an insecticide, stepped into the fields and in the life of people.
The structure and properties of the world's first insecticide
The abbreviated formula of dust (DDT) is the classic insecticide C14H9Cl5.
Preparation: In concentrated H2SO4 (sulfuric acid), chlorobenzene (C6H5Cl) is condensed with chloral (Cl3CCHO). The result is dichloro diphenyl trichloromethylmethane or 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis (n-chlorophenyl) ethane. In everyday life, the powder is known under the common name DDT or just dust.
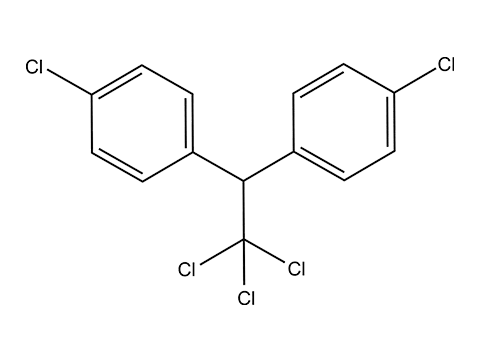
Chemically pure DDT is a crystalline powder, odorless. Quickly soluble in organic solvents. It only forms an emulsion in water.
According to the results of numerous studies, chemists have come to the conclusion that the chemically pure drug DDT is toxic to fish, insects, cold-blooded and small warm-blooded representatives of the animal world. The drug is toxic to large warm-blooded and human, but without death.
At one time, chemically pure DDT saved the lives of millions of people. The use of this drug stopped the typhoid epidemic in Naples (1944), malaria in Greece (1938), Italy (1945), India (1965). In 1950-1960, the population of India got rid of visceral leishmaniasis forever.
Negative examples of the use of DDT gradually accumulated, which led to its complete prohibition on the use (1970).
How DDT affects the environment
The chemically pure DDT insecticide was developed to be highly effective in controlling epidemic diseases (mosquitoes, fleas, mosquitoes) and crop pests, including locusts, which condemned people and animals to starvation.
Its high toxicity is confirmed by the following example: for the death of a housefly larva, the contact of one millionth of a milligram of powder is sufficient.The drug turned out to be economically viable: once the treated surface remains lethal for insects for a long time and does not require re-treatment.
But chemically pure DDT has the ability to accumulate in the body and is highly resistant to decomposition. It negatively affects large warm-blooded people and when a large amount enters the human outer integument, the lungs, digestive tract, and circulatory system.
Properties of insecticides developed on its basis
To give DDT new properties in terms of accelerating decomposition processes, new synthesis methods have been developed. New methods for the synthesis of the technical preparation DDT included mixtures of various substances that accelerate its decomposition. However, the new drug was toxic to humans and low toxic, almost harmless to insects.
In connection with the acquisition by the drug of new properties that are very toxic to humans, in 1970 a decision was made to ban the use of DDT everywhere.
Organophosphorus compounds replaced the chemically pure highly effective insecticide on insects. They were developed on the basis of DDT (dichlorvos, karbofos) and were mistakenly accepted by the population as (in due time) pure DDT harmless to health.
By the way, organophosphorus compounds are part of deadly OM. Considering harmless, the population used dichlorvos and chlorophos everywhere. It got to the point that they poured into the bed the children and themselves in the fight against household insects (fleas, bugs, lice).

Organophosphorus compounds differed from technical DDT in very rapid decomposition, which required repeated repetitions for the destruction of insect pests and were economically very profitable, and the fatal poisoning caused by them was still attributed to the influence of the original chemically pure DDT.
In the media and scientific articles, reports appeared, to some extent rehabilitating DDT. The articles suggested that the damage was not caused by the source material itself, but by impurities, mainly dioxins.
DDT is still used in the disinfection of rooms from rats, mosquitoes, mosquitoes.
The health risks of DDT
The main danger of exposure to chemically pure DDT on a person lies in his ability to accumulate in organs, not succumbing to any decomposition methods. Water, temperature, light, enzymes are not able to accelerate its decomposition or remove from the body. This is terrible DDT.
When using an insecticide to kill insects, it enters the food chain, which closes a person or large warm-blooded representatives of the fauna.
According to the results of studies, it was proved that in each link of the food chain, the concentration of DDT increases by 10 times. When DDT gets into the soil after being washed away by rain, the soil – silt – algae – small aquatic organisms – fish – predators (fish and other animals) are included in the food chain. DDT has practically no effect on soil worms.
The repeated use of infected fish as food by humans undoubtedly contributes to the accumulation of DDT in the body.
Residual quantities of an unusual (unrelated) substance accumulate over time, although extremely slowly, but constantly.
DDT is excreted from the human body only with mother's milk and is transmitted to the newborn. Therefore, it is found in the second and subsequent generations, whose ancestors received certain amounts of DDT with food or in another way.
Its accumulation helps to reduce the reproductive function of birds and some mammals, including bats. Highly toxic to cold-blooded invertebrates and fish. The high danger of DDT is that it accumulates in the body and migrates over long distances around the world.
Can i use dust today
DDT - an insecticide from the group of organochlorine compounds was used in a chemically pure form, later in compounds with other chemicals, such as an insecticide and pesticide to kill plant pests.
It is currently banned and absent in the annual lists of drugs approved for use in agriculture.
The chemical industry has developed and found practical application of DDT analogues, such as Methoxychlor, DDD, Pertan, DPDT and others. In their effect on insects and warm-blooded pests (rats), they are similar to DDT and its derivatives.
They decompose faster in the soil, but are stably strong poisons for humans and are limited in use.
Protective measures for handling pesticides
When working with all chemical pesticides, insecticides, acaricides, you must comply with your own sanitary safety measures.
Work in a respirator, goggles, clothing covering the whole body (trousers, jacket, boots). At the end of work, take a shower, change clothes, drink milk.
DDT is back
In 1946, entire neighborhoods of Athens pollinated DDT dust with an airplane to destroy flies and stop the cholera epidemic that began in the Greek capital.
Dichlorodiphenyl trichloroethane, better known as DDT, was synthesized as early as 1874, but it was not until 1937 that this compound was very toxic to insects.
This paratrooper was protected from malaria, dengue fever and other tropical diseases carried by insects. In the winter of 1944, American soldiers in Naples were pollinated with dust in order to destroy lice.
After World War II, the new insecticide began to be widely used to kill agricultural pests, but after a while it turned out that this substance decomposes extremely slowly in nature, is transmitted to other organisms through the food chain, accumulates in them and slowly poisons them.
In addition, insect lines resistant to DDT appeared, withstanding even ten-fold doses of the drug. Therefore, for almost thirty years in most countries the use of DDT has been banned (Sweden was the first to prohibit this insecticide in 1969).
However, it now appears that there is no better way to fight malaria mosquitoes than DDT. When this insecticide was banned in South Africa, which lagged far behind other countries in 1996, the incidence of malaria increased more than six times, and five years later it was again allowed.
Just do not spray it with tons of airplanes flying over cities, ponds, swamps and agricultural land.
Cautious use inside dwellings, experts now believe, is perfectly acceptable. According to the WHO, two grams of DDT per square meter of mud wall reduce the likelihood of house residents becoming infected with malaria by 90%. Spraying should be repeated only once a year.
Therefore, the World Health Organization has approved the use of DDT for indoor spraying, indicating that it is not only the best weapon for controlling malaria mosquitoes, but also the cheapest and most effective of the insecticides. If used DDT correctly, it does not pose a threat to nature or man.
In addition, recently, data on the accumulation of DDT and toxic products of its decay in living nature had to be called into question.
About twenty years ago, environmentalists monitoring the toxic substances in marine mammals' fats began to detect unknown organic compounds with chlorine atoms in the molecule in their fat samples.
In structure, they resembled DDT, and it was concluded that the drug and its decomposition products are carried by the rivers into the ocean, and there they accumulate in mammals.
And recently, in a vial of whale oil, preserved in the last whaling sailboat, put on an eternal joke off the coast of Connecticut (USA), the same compounds were found - as many as 11 of their varieties.
Where exactly - it is not yet clear, it is only known that something like DDT is produced by symbiotic bacteria living in sea sponges and, apparently, protecting their owners from eating.
Insecticide "Dust clean home" bedbug powder
The appearance of bed bugs at home can turn a person’s life into real hell. Their night attacks will be accompanied by lack of sleep, irritability, depression may appear on this soil.
It is by the location of the red tubercles that you can find out that these are bedbugs, and not other biting insects, such as fleas or mosquitoes. Some people have an allergic reaction to the saliva of parasites, which they anesthetize the skin before biting.
If you find at home the first signs of bugs, you must immediately begin to take action. Most often, residents notice bugs when they are already well settled in the room.
If you are lucky, you saw them before breeding, then getting rid of bed bugs will not be as difficult as in the case of increasing their number.
People have long been trying to completely destroy them, but it doesn’t work out. The market for insecticides is bursting with a variety of different drugs that promise to destroy them forever - gels, aerosols, friable, microencapsulated products.
Our grandmothers also used powders - dusts. But what is it? They helped to save the house from bloodsuckers. Previously, the composition was a dangerous DDT, which was then banned, because it is very toxic to humans, practically it is not excreted from the body.
The new generation of dusts has a completely different composition. It has more pyrethroids that have natural analogues (chamomile), so the popularity of friable chemicals has increased.
Some customer reviews say other forms of chemicals are much more effective than this.
To get a positive result, you need to know what a quality dust is and how to choose the right one, and strictly follow the instructions for use.
Basic properties
A mandatory requirement for dust bugs is the presence of contact exposure. After all, if the drug can only poison the rubber through the stomach, it will not kill him. These parasites eat only blood, nothing else enters their stomach.
Therefore, particles of a substance must enter its abdomen or legs in order to enter the body through the chitinous membrane and begin to act.
Pineronyl butoxide is added to the main active ingredients. It is he who gives a prolonged effect to the rest of the compounds. Dust continues to remain active at any room temperature, the main thing is that there is no increased humidity.
You can buy 50-gram bags with a chemical in Moscow in any gardening or hardware stores, as well as supermarkets. Their price is low. One pack is usually enough for 10 square meters, so you need to correctly calculate how many packages you need.
In addition to bugs, the drug perfectly destroys many other insects that live in the human home - ants, fleas, cockroaches. Only for the persecution of this parasite will require a little more money. Bed bugs have the ability to be resistant to various chemicals, so be prepared to buy several types of poisons.
Most popular friable chemicals
There are many powdered poisons, so choosing a person who does not understand this can be a little difficult. Consider some of the most famous friable chemicals:
Dust Clean House. This drug is one of the effective if used correctly. They are even poisoned by special services for the destruction of insects. It has some toxicity, so you need to be careful when working with it.
Klopoveron. This drug was used to destroy parasites in the premises where the Soviet army was located. Now this is one of the most powerful means that effectively and for a long time destroys bloodsuckers.
But for such a result, you need to pay a lot - a 250-gram pack costs 1800 rubles. For such a price, it is easiest to call a pest control service.
Pyrethrum. Very effective poison. It has a completely natural composition.
Riapan. The main active ingredient is permethrin. It has a neuroparalytic effect. The prolonged result is about three weeks. One 125 gram pack can etch 20 square meters.
Fas double. The composition and result is similar to the drug described above, but there are much more customer reviews. Cost - 20 rubles per 125 gram pack.
Particular attention in the choice of a chemical should be paid to the date of manufacture, effectiveness, toxicity to warm-blooded animals, and prolongation of the result.
Proper insect killing
Before the beginning of pest control, it is necessary to make preparations to obtain the desired effect.
Find all the clusters of bugs to fill there with more dust. If you miss a nest, and these parasites do not have time to go to places treated with a chemical, the pests will multiply further.
Do a little wet cleaning to remove traces of other chemicals that you might have previously applied.
Bed linen, clothes and other fabric items must be washed in 50-degree hot water or boiled. After that, you need to put it in vacuum bags so that the bloodsuckers could not hide in them.
If the treatment affects the kitchen or bathroom, pack the food, utensils and personal care products in bags as well.
It is necessary to move all the cabinets, beds, sofas, household appliances and furniture away from the walls in order to apply the drug on all surfaces without leaving a single clean centimeter.
If the bullying is to be carried out only with powder, dilute part with water so that all cracks and crevices can be sprayed on which it is difficult to pour the product. You can also trick a brush into the resulting liquid and apply it to hard-to-reach places.
Before starting bullying, wear a respirator, goggles, long-sleeved clothing, and rubber gloves. The respirator must be of good quality to avoid getting poison in the airways.
After proper preparations, disinfestation takes place. Sprinkle with a chemical all available surfaces: under carpets, baseboards, floors, shelves, ventilation, cabinets. When you start to pour poison on furniture, pay special attention to all the seams and folds, it is there that parasites love to hide.
Destroying bugs with the help of dust, do not expect quick results, parasites will disappear within a week. Therefore, if there is no strength to endure night attacks anymore, buy a more powerful tool that has an instant effect.
The disadvantage of friable poisons is a low concentration of active compounds and inconvenient operation.
The plus can be considered the effectiveness of the drugs with proper operation, relative safety for the human body, because now they produce chemicals that do not evaporate poison into the air, and the prolonged activity of the active substances, which will help to avoid a new insecticide.
What is dust
Dust has long established itself as an effective tool against parasites.
To date, there are plenty of modern similar tools, but I must admit that they are not competitors. But before using this tool for its intended purpose, many are wondering about how dust affects a person.
Dust has been used to kill parasites and pests since the mid-19th century, but at the end of the 20th century it was banned in Europe and then in the CIS countries. To date, there is dust on sale, but manufacturers only indicate pyrethrum and boric acid in its composition, and one can only guess about the content of DDT in it.
Absolutely precisely, the content of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane in Chinese dust can be stated. Why is it so forbidden to use such an effective pest control agent all over the world? Apparently, this is due to how dust affects a person.
How does dust affect a person?
In the course of numerous studies, scientists have found that DDT causes irreparable harm not only to insects, but also to humans. Namely:
- Once he gets into the atmosphere, poisons all the links in the ecological chain.
- Penetrating into the human body with ease, it is not excreted from there, but accumulates in the tissues.
- Significantly increases the likelihood of developing cancer.
- It affects the human genetic apparatus, that is, it can be dangerous not only for a specific person, but also for his descendants.
Using dusts on the farm is not recommended, since its half-life is from 15 to 20 years, and during this time it can cause a lot of trouble.
Observations of how dust affects a person gave the following results:
- When receiving a dose of DDT in an amount of from 6 to 10 mg / kg, a person experienced moderate intoxication.
- When from 16 to 286 mg / kg dust was ingested, severe intoxication was observed, accompanied by instant vomiting and convulsions.
- Scientists believe that a person receiving a higher dose of DDT than 286 mg / kg can cause death.
The triumph and tragedy of DDT
This is not about Shevchuk, but about the world-famous chlorohydrocarbon 1, 1, 1-trichloro-2,2-bis- (4-chlorophenyl) ethane, aka dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, DDT, in common language - dust.
There were times when humanity could not imagine its life without this pesticide or pesticide. Dust powders containing DDT were sprayed in the fields, in forests, in swamps, in apartments; they were added to soap, fabrics, and water that wiped the floors.
DDT appeared in 1874 in the laboratory of the Austrian chemist Omar Zeidler. "Birth certificate" was the "Reports of the German Society of Chemists." Nobody noticed this.
As before, harmful insects destroyed up to half the crop and spread dangerous diseases. Farmers in the tropical zone, who suffered more from these scourges than Europeans, did not read chemical journals, and organic chemists did not engage in agriculture.
The First World War found a fundamentally new application to the ideas of scientists involved in organic synthesis. They began to create chemical warfare agents.
Finally made peace. Mustard and phosgene are no longer required, conversion of production is necessary. At this time, insect pests bred until extreme.
Organic chemists, hardened in the battles of the imperialist war, met a new enemy fully armed, and when in 1939 the Swiss Paul Muller reported that 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis- (4-chlorophenyl) -ethane it has insecticidal properties, it didn’t surprise anyone with this - tens of thousands of compounds have already been tested for this purpose, and thousands have been prepared for production. Nevertheless, the choice fell on DDT.
He “won” because of his toxicity to all insects without exception. The Second World War was already on, and the danger of hunger was added by the threat of epidemics - typhus, malaria, and other diseases spread by arthropods. Universal poison was required - against locusts, lice, tsetse flies, cockroaches.
The smell of dust did not frighten off insects; they calmly sat on the surfaces treated with the preparation, where they ended their life's journey. By the way, DDT did not spoil the polished furniture at all, which matters when fighting with household insects.
Another advantage that distinguishes DDT from other candidates for the “main” insecticides is its relatively low toxicity to humans and other warm-blooded animals.
A single dose of 500 to 700 mg was considered completely safe, so it was almost impossible to accidentally poison. Note that there have been no cases of fatal poisoning of DDT in the entire history of its use.
The last trump card for doubting owners of chemical companies was the extreme simplicity and cheapness of the production of this toxic chemical.
C2H5OH + 4Cl2 -> CCl3CHO + 5HCl
Then, chloral in the presence of a dewatering agent reacted with chlorobenzene:
CCl3CHO + 2C6H5Cl -> CCl3CH (C6H5Cl) 2 + H2O
and the desired dichlorodiphenyl trichloroethane was obtained.
Since all reagents were cheap and affordable, DDT quickly began to be produced in many countries around the world. A new era has come - the era of the total chemical struggle of man against the representatives of the animal and plant world that prevent him from living quietly.
Indeed, DDT has saved millions of lives. The terrible scourge of all the warm lands, the malarial plasmodium, has almost lost its distributor - a mosquito. The tsetse fly and other insects - carriers of dangerous diseases were not in the best position.
The 1948 Nobel Prize in medicine was awarded to Paul Muller deservedly.
DDT in utilities, veterinary medicine, and crop production was by no means out of place. It seemed that humanity had opened the way to a well-fed and healthy future.
Only here, house flies, the first to experience the insecticidal properties of DDT, suddenly stopped responding even to horse doses of dust, which was first noticed in 1946. But since exceptions should only confirm the rule, nobody seriously thought about this fact.
The first dark spots on the reputation of DDT began to appear in the mid-50s. Especially diligently they were "examined" by US scientists.
Indeed, if in 1942 there was no DDT in the tissues of the inhabitants of this country, then in 1950 its content jumped to 5.3 mg / kg, and in 1953 it tripled. There were more and more insects resistant to the drug: 36 in 1956, 85 in 1958.
Some toxicologists have found a clear relationship between the amount of the drug used and the increase in the incidence of hepatitis and pneumonia in agricultural districts.
Of particular concern was the ability of the drug to increase its concentration as it progresses in food chains. So, the fat of freshwater fish contained five orders of magnitude more than the water in which they were caught.
The saddest event associated with the use of this insecticide was the death of entire bird populations. The content of DDT in their tissues exceeded background values by tens of thousands of times. For acute poisoning, such a concentration was still not enough, but a side effect was manifested - the eggshell was thinned.
That is why in the nesting of brown pelicans in Southern California (the volumes of DDT used at that time were maximum), only five chicks hatched in 550 pairs, the remaining embryos were crushed by the females during incubation.
Its author, Rachel Carson, spoke so convincingly about the sad consequences that the use of chemical means of protection in general and DDT brings to nature in the first place, that the US Congress and President Kennedy created a parliamentary and government commission to hear the “pesticide case”.
But the four million tons produced and sprayed over the fields, forests, swamps, pen stroke cannot be destroyed.
Due to the “resistance of the drug in the environment,” the dust that fell into the atmosphere remained there for centuries, partially settling in ocean waters, soil, and organisms of living things. The period of circulation of its particles around the globe was three to four weeks.
The naive Swedes, who decided to determine the content of DDT in their soils, focused on six hundred tons used in the country. They made a mistake five times, and in a big way.
It was soon proved that in the body of people suffering from hypertension and other diseases of the cardiovascular system, the concentration of the pesticide is slightly higher than in the tissues of a healthy person.
When it was found out that mothers with DDT in their milk found that premature babies were born in two, and the dead were born 1.5 times more often, the doctors demanded to immediately ban the drug.
Already in the mid-60s, most developed countries in one way or another limited the use of this pesticide on their territory. By 1970, the entire civilized world, including the USSR, declared DDT “illegal”.
They immediately doubted the justice of this, and not only chemists. The American N. Borlaug, who received the Nobel Prize for the creation of high-yielding grain varieties specifically for tropical countries, called his speech at the UN Food and Health Committee: “DDT or hunger?”
After listing the merits of the drug to ungrateful humanity, he mentioned a more than curious fact - the remains of DDT were found in soil samples preserved in 1911.
There were other amazing facts. Although the winds from abroad brought more than two thousand tons of pesticide to Sweden, how can we explain the fact that the fatty tissue of citizens contains more DDT than rural people?
The most incomprehensible news came from Los Angeles. The shells of the crabs, who chose to dump the city's sewage system into the sea, contained 45 times more dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane than the chitinous shells of their neighbors living in the irrigation systems of rice fields, where the pesticide was used.
The waters of the California coast are heavily polluted by these same PCBs, and the shell-like marine inhabitants just accumulate significant amounts of polychlorobiphenyls (spiny lobster, for example, up to 68 weight parts per million).
“The complete identity of the behavior of PCBs and organochlorine pesticides (which includes DDT) with any analysis methods are the last causes of a false conclusion about environmental pollution,” read the Temporary Methodological Guidelines for the Control of Soil Pollution, published in 1983.
Nevertheless, the decision made in 1970 is correct. The fact is that with the then synthesis method of the drug, the desired 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis- (4-chlorophenyl) ethane was only 70%.
One had only to change the synthesis technology in time or to invent the perfect methods of DDT purification, and there would be no planetary prohibitions.
By the way, already in the 70s there were some ways of separating technical DDT and even special additives that accelerate its decay under the influence of soil moisture. Alas, public opinion did not heed the voice of reason, and DDT was supposed to disappear.
Organophosphate insecticides that came to replace him more than once caused severe and even fatal poisonings of those who worked with them, but they quickly decomposed in the environment - so quickly that sprayings had to be repeated many times.
Recall that the most advanced combat agents of nerve agent are the closest relatives of karbofos, chlorophos and other organophosphorus pesticides.
leave a comment