
The Pest Blog Welcomes You Again! A neighbor, Anastasia Petrovna walks upset.
She had a thriving chicken coop for many years, which provided the eggs of all her relatives and friends. But recently, hens began to grow more slowly, and most of the young began to die.
She turned to the vet. He diagnosed “chicken mite” and prescribed a course of delcide to the laying hens. Deltsid for hens how to apply, I will tell you. First-hand information!
The content of the article:
Delcid for chickens, dogs, pigs and other animals - instructions for use
Application: The drug for the fight against ectoparasites of animals, pest control and decontamination of livestock buildings. Release form: Ampoule of 2 ml. Outer packaging - cardboard box for 5 ampoules. 1 l bottle
Benefits:
- It is used for insect-acaricidal treatment of both an animal and its habitats.
- Convenient and economical (available as a concentrate).
- High degree of efficiency when spraying rooms.
- Universal - acts on both insects and ticks.
Composition and pharmacological properties
The medicinal product for external use as an active substance contains synthetic pyrethroid deltamethrin - 4.0%. Deltamethrin has a pronounced insectoacaricidal intestinal and contact effect.
The mechanism of action of deltamethrin is based on the blocking of neuromuscular transmission of nerve impulses at the level of ganglions of peripheral nerves, which leads to paralysis and death of parasites.
"Delcid" in the recommended doses do not have a local irritant, resorptive-toxic and sensitizing effect. Contact with mucous membranes causes slight irritation. Toxic to fish and bees.
Indications for use
For the treatment of sheep, cattle, pigs, rabbits and dogs with arachno-entomoses, as well as for the disinfestation and deacacification of livestock buildings and other objects of veterinary supervision.
Contraindications: Do not use "Delcida" for the treatment of weakened and depleted animals, as well as females later than 2 weeks before birth.
Application procedure
Animals are treated by spraying or bathing in swimming baths.
The required volume of "Delcide" is thoroughly mixed with 2-3 volumes of water, and then poured into a floating bath with water or the tank of the spraying device, adding water to the required volume with stirring.
Before use, "Delcid" is diluted to the required concentration with cool tap water.
Spraying. Preparation of the emulsion: dilute the measured amount of "Delcide" in several liters of water, pour the resulting solution into the tank of the spraying device, add the required amount of water, mix thoroughly.
Spraying is carried out using a horizontal spray universal boom (SHGR) installed in the gates of summer pens or other spraying devices that provide small-droplet spraying.
The processing time is determined depending on the dominant components of the vulture and meteorological conditions: with a high number of horseflies and midges, animals are treated after morning milking, and with a high number of mosquitoes and midges, after evening milking once a day
With a moderate abundance of midges, treatment is carried out every 2-3 days, and with an attack of only pasture flies - every 7-10 days. In rainy and cold weather animals are not processed. Milking cows in the regimes recommended for protection against midges and pasture flies are allowed to be treated with Delcid no later than 7 hours before the next milking.
Bathing animals. Before treating animals, 2 hours before treatment, it is necessary to water. After shearing, sheep are bathed no earlier than 3 days later.
Lambs under the age of 1 month are bathed separately from adult animals. It is not recommended to treat animals in the heat. Before processing the animals, the bath is cleaned. The required amount of "Delcide" is mixed with 2 corresponding volumes of water and poured into the bath, the volume of water in the bath is adjusted to the calculated one.
20 animals are passed through the bath; these animals are re-processed. Then the entire stock is processed. After the animals take out 10% of the working emulsion from the bath, the bath is refilled at the rate of 1.2 L of “Delcide” for each ton of added water. After processing 2.5-3 thousand sheep, the liquid from the bath is poured into the sump wells, the bath is cleaned and washed for the next treatment.

Room Handling. "Deltsid" is used for processing rooms, nightmares, corrals. Processing in the presence of animals and birds is allowed. It is used to treat surfaces against all flying and creeping arthropods, including against red chicken ticks, downy eaters, argus and nightmare ticks, bedbugs, cockroaches, flies and other insects.
The treatment is carried out by an aerosol method or by small drop spraying with 0.125% aqueous emulsion.
1 hour after treatment, the room is ventilated for at least 1 hour, the dead ectoparasites are swept away and disposed of, the feeders and drinkers are thoroughly washed and after that the bird is placed in the room.
It is allowed to process the premises in the presence of a bird, without violating the technological regime. In this case, no more than 2/3 of the total area of the premises is sprayed.Processing is carried out with running ventilation or open doors, poultry and equipment are not processed.
Supply ventilation for the treatment period (30–40 min) is turned off. Attendants are allowed into the room no earlier than 30 minutes after processing.
Poultry facilities are treated twice, taking into account the development cycle of parasites, at an air temperature in the house of 15–20 ° С - with an interval of 10–20 days, at a temperature above 20 ° С - with an interval of 5–8 days.
Against bestial flies, disinfestation of livestock buildings, fodder kitchens, artificial insemination points and other objects of veterinary surveillance apply 0.125% Delcida water emulsion by selective spraying of insect landing sites (windows, walls, doors, support beams, etc.) with a consumption rate of 80 –100 ml / m2 of the treated surface.
Before mass treatment, each batch of the drug is preliminarily tested on a small group of animals (7–10 animals) of various fatnesses. In the absence of complications in animals within 48 hours, they begin processing the entire livestock.
special instructions
Sick and exhausted animals, as well as females no later than 2 weeks before birth, are not allowed to process. The combined use of Delcide and organophosphorus insecticides is not recommended, due to increased toxicity of the drug.
After processing, workers should wash their face and hands with soap and water. In case of accidental contact with the drug on the skin or mucous membranes of a person, immediately rinse it off with a stream of water. If the drug gets inside, give the victim several glasses of warm water and 8-10 tablets of activated charcoal.
Milk of dairy cows treated against sarcoptoid ticks and lice is allowed to be used for food purposes no earlier than 3 days after treatment with Delcid, milk from animals treated against horseflies, pasture flies and midges is allowed to be used without restrictions.
Side effects
When used in accordance with the instructions, side effects and complications are not observed. With increased individual sensitivity of animals to deltamethrin, refusal of food, vomiting, edema, impaired coordination of movements is possible. In this case, further use of the drug is stopped and desensitizing therapy is carried out.
Storage
Store in the manufacturer’s sealed packaging, in a dry place protected from direct sunlight, separately from food and feed products, at a temperature of minus 10 ° С to 30 ° С. Keep out of the reach of children. The shelf life of the drug subject to storage conditions is 2 years from the date of manufacture. Delcid should not be applied after the expiration date.
Delcid (Agro-protection)
Delcid (Delcid) is an insecticide and acaricidal drug in the form of an emulsion concentrate for external use, designed to combat ectoparasites of animals, disinsect and deacarize livestock buildings.
As an active ingredient it contains synthetic pyrethroid deltamethrin - 4.0% and auxiliary components.
Deltamethrin, which is part of the drug, belongs to the group of synthetic pyrethroids and has a pronounced insecticaricidal intestinal and contact effect.It is active against sarcoptoid, ixodid and chicken ticks, bed bugs, downy eating, lice, fleas, flies, horseflies, mosquitoes and other ectoparasites of animals.
The mechanism of action of deltamethrin is based on blocking the neuromuscular transmission of nerve impulses at the level of ganglions of peripheral nerves, which leads to paralysis and death of parasites.
Indications for use
Deltsid is used for the treatment of sheep, cattle, pigs, rabbits and dogs with arachno-entomoses, as well as for the disinsection and deacarization of livestock buildings and other objects of veterinary supervision.
Assign:
- with sheep psoroptosis
- for the treatment of cattle against bloodsucking dipterans insects (gnats) and pasture flies
- with sifunculosis and cattle bovikolosis
- with pig sarcoptosis
- with rabbit psoroptosis
- with entomosis and sarcoptosis of dogs
Contraindications: Do not use Delcid for the treatment of weakened and exhausted animals, as well as females later than 2 weeks before birth.
Side effects
When using Delcide in accordance with this instruction, side effects and complications, as a rule, are not observed.
With increased individual sensitivity of animals to deltamethrin and the occurrence of side effects (refusal of food, vomiting, edema, impaired coordination of movements), the use of the drug is stopped and desensitizing therapy is carried out.
Doses and method of application
Animals are treated by spraying or bathing in swimming baths. After processing, allow the surface to dry, be sure to ventilate the room. The sequence of spraying the animal: the auricles, head, body, tail, the area around the anus, limbs.
At the end of the treatment, wash your hands thoroughly with warm water and soap. Delcid is prescribed in the following doses (g per animal weight):
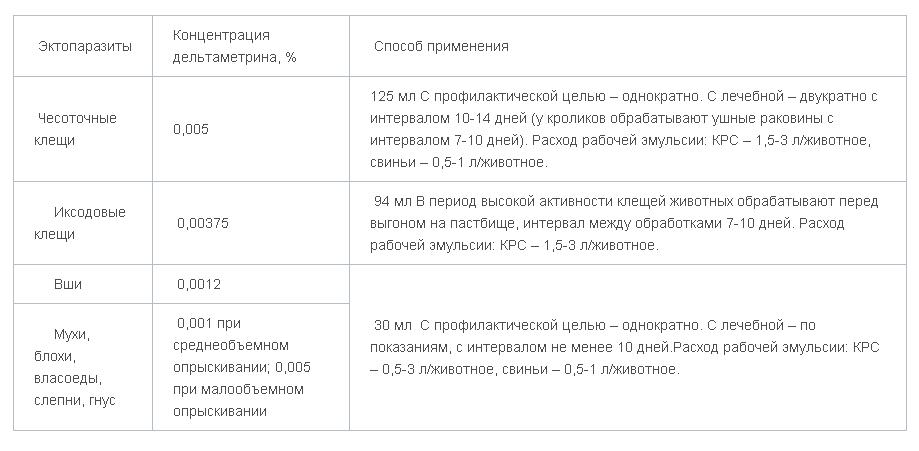
With scabies mites. 1 dose per 1.6 liters of water for prophylactic purposes - once. With treatment - twice with an interval of 10-14 days (auricles are treated in rabbits with an interval of 7-10 days). The flow rate of the working solution: cattle - 1.5-3 l / animal, pigs - 0.5-1 l / animal.
With ixodid ticks. 1 dose per 2.2 liters of water. In the period of high tick activity, the interval between treatments is 7-10 days. The flow rate of the working solution: cattle - 1.5-3 l / animal.
With lice, fleas, hairs, flies, horseflies, nests. 1 dose per 6.4 liters of water for prophylactic purposes - once. With treatment - with an interval of 7-10 days. Cattle - 0.5-3 l / animal. Pigs - 0.5-1 l / animal.
special instructions
Before mass treatment, each series of Delcid is preliminarily tested on a small group of animals (7-10 animals) of different fatness. In the absence of complications in animals within 48 hours, they begin processing the entire livestock.
Milk of dairy cows treated in regimes against sarcoptoid ticks and lice is allowed to be used for food purposes no earlier than 3 days after treatment with Delcid. Milk obtained before the expiration of the specified period can be used after heat treatment to feed fur animals.
Milk of dairy cows treated with Delcid in the regimes against nests and pastoral flies is allowed to be used for food purposes without restrictions.
Storage
Store in the manufacturer’s closed packaging, in a dry place protected from direct sunlight, inaccessible to children and animals, separately from food and feed, at a temperature of 0 to 30 ° C.
Release form. In ampoules - 5 ampoules of 1 dose (2 ml), in metal canisters with a capacity of 1 liter.
"Delcid": reviews, instructions for use
Parasites cause many inconveniences to both animals and their owners. Often, in order to rid fleas of your pet and completely free them from the room, you have to make a lot of effort. Significantly helps to facilitate this process using high-quality insecticide.
It is important to carefully read these recommendations. In what cases is Delcid effective? How should a working solution be prepared? How to properly handle the room? How to use the product for animals? How long does the finished emulsion retain its beneficial properties?
Composition
The main active substance of the drug "Delcid" in ampoules is a special insecticide deltamethrin (namely, its four percent solution). In order to enhance the effectiveness of the main component, a number of auxiliary components are used. The solution is a brown liquid with an oily consistency.
“Delcid” is packaged in ampoules of one and a half and two milliliters, as well as in durable bottles made of metal, three, five and twenty milliliters each, respectively.
The drug remains effective for two years from the date of its release. The useful properties of the prepared working solution are stored for no more than forty-eight hours. It is recommended to use the finished emulsion immediately after preparation. After two days, the insecticide becomes useless.
Act
How does Delcid work against fleas? It effectively blocks nerve impulses in the body of the parasite. This provokes his paralysis and, as a consequence, death. Specialists attribute this insecticide to the third hazard class in terms of toxicity.
The instruction recommends using Delcid for cats and dogs in order to get rid of fleas twice a month. As a preventative measure, it is enough to do this once every thirty days.
Indications for use
There are several situations in which the tool "Delcid" is used. Reviews confirm its unconditional effectiveness in all these cases.
So, among the indications for use, there are: the need to treat dogs or cats in the presence of arachnoentomiasis (this diagnosis includes demodex, lice, fleas, flies and horseflies, gnats, scabies and ixodid ticks, as well as hairs); the need to treat the rooms in which animals live from a number of insects (namely cockroaches, fleas, ticks, ants, flies and bugs).
Preparation of working solution
The main question that arises when using the drug "Delcid": "How to dilute the emulsion?" To do this, use water at room temperature. For each square meter of floor space you will need from twenty-five to fifty milliliters of finished working solution.
It is important to open the ampoule immediately before starting the cooking process, dilute its contents in water and mix thoroughly for twenty minutes. After this, the finished solution can be poured into a spray bottle.
Processing Rules
Many people use Delcidum in ampoules to process an apartment. Reviews confirm the effectiveness of this method.
It is important to carry out pest control in a clean room. Therefore, it is initially necessary to do the cleaning (vacuum and thoroughly wash the floor). All furniture that adheres to the walls should be pushed back so that areas can be processed on it. Only then can we proceed to the process of pest control.
Since the agent in question is toxic, attention should be paid to personal protective equipment. It is important to carry out the procedure in a respirator, gloves and a specialized suit that would protect the skin from the effects of an insecticide.
After disinsection, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and go out into the fresh air, having previously locked all the windows and doors in the room. It should remain closed for an hour.
After its expiration, it is necessary to ventilate the room for about two hours. Subject to all recommendations "Delcid" in ampoules for processing an apartment, reviews are called one of the most effective insecticides.
Animal processing
You can use "Delcid" as a method of spraying the animal, and his bathing. The concentration of the solution (0.125%) must be strictly observed. The most convenient option is to use a ready-made working solution in ampoules. In this case, it will take five to ten milliliters of funds per kilogram of body weight of the animal.
Spray your pet against the coat. It is important to treat the entire body, carefully avoiding the eye, nose and mouth. The next two hours, the pet should not be stroked and kept away from children or other animals. You can bathe a pet only two days after processing.
Effect on animals. When the drug "Delcid" is used, this may affect their behavior. Changes can be manifested by the appearance of apathy, trembling, increased salivation and a temporary loss of appetite. All these symptoms, as a rule, disappear within three days after treatment with an insecticide.
What can an animal owner do? Give him more clean drinking water and ensure comfort and peace. If symptoms persist or allergies occur, show your pet to an experienced veterinarian.
Drug effectiveness. About the tool "Delcid" reviews report that it successfully copes with adult fleas during the first treatment of the premises with an insecticide. As soon as the parasites come into contact with the surface treated with the substance, paralysis occurs.
But the eggs of the parasites can survive, because they are protected by a special shell. Therefore, it is recommended to re-process after two weeks to destroy those fleas that appear from the eggs during this time.
Reviews
Most of the reviews on the drug "Delcid" leave positive. Customers focus on its exceptional performance and usability.
Despite the fact that the product is toxic, in compliance with all the recommendations that are prescribed for the use of the drug "Delcid" instructions, it is safe for both humans and animals. It is important to carefully follow all the rules for using the drug.
Disposal
In no case should you pour the rest of the Delcid solution into the toilet. Reviews recommend processing the container in which the working solution was located, using soda and a soap solution. The remaining product must be completely neutralized with slaked lime and carefully buried in the ground to a depth of at least one meter.
Buyers speak of him as an incredibly effective insecticide that helped them completely get rid of the insects that bothered them. It is important to remember that the maximum effect can be achieved only if you strictly adhere to all recommendations regarding the preparation of a working emulsion, as well as the processing of an animal or a room.
Exactly following the instructions contained in the instructions will help to avoid the occurrence of any adverse reactions on the part of the body to the exposure to the substance in question.
It is necessary to carry out the processing of the room as carefully as possible, without missing any surfaces and crevices. It would also be wise to spray the hard frame of upholstered furniture with a tool.
Therefore, experts recommend that after ten to fourteen days an additional pest control procedure be carried out, which will destroy the newly born parasites. In this case, the victory over the fleas will be final.
Recommendations for the prevention of ectoparasites
The successful development of animal husbandry, regardless of ownership, largely depends on the health status of animals and birds and the epizootic well-being of farms for invasive diseases. A special place in the pathology of animals is occupied by ectoparasitoses.
When examining cattle in the farms of the Leningrad Region, it was found that representatives of different classes of arthropods are the most common and significantly affecting animal health.
From the class Arachnida - arachnids - ticks of the genus Chorioptes, causing chorioptosis - skin-scabies. Ticks are localized on the skin in the area of the root of the tail, the outer surface of the hind limbs, the udder, causing itching, leading to scratching.
Ticks of the genus Demodex - cause demodecosis or iron gland. They parasitize only in the sebaceous glands and hair follicles, forming papules that open after 3 to 4 weeks, and new ones form in neighboring areas. The main lesions on the skin of the head, neck, chest, forelimbs. The number of papules can reach 5 million.
Demodecosis manifests itself in scaly, papular and generalized forms. With this invasion, animals do not have itching.
Ticks of the genera Ixodes, Dermacentor are pasture ticks that attack animals only for feeding blood. They have two activity peaks: mid-April - May and August - September. Attached to the skin of the neck, chest, groin and very rarely on the back and sides.
Nutrition lasts from 15 minutes to 30 days at an ambient temperature of at least 16 ° C. In livestock buildings and human dwellings never creep. They are carriers of blood parasitic diseases - babesiosis, pyroplasmosis.
No less common are representatives of the class Insecta - insects. Bestial flies live on livestock farms and pastures.Representatives of the Musca genus — true flies (housefly, housefly, housebird, viviparous field, Siberian field) —are widespread in the farms of the region.
In addition to these flies, they also have a certain pathogenicity - autumn lighter, small cow lighter. They can live indoors and outdoors. The brood occurs in rotting plant debris. Being blood-sucking, they suck blood for a long time, causing depletion of animals and a sharp decrease in productivity. Are carriers of anthrax, gabronematosis.
Common are blue and green (meat flies). Places of hatching - corpses of animals, meat, fish waste, slop, cesspools, rotting vegetables, fruits, silage. The larvae of these flies cause myiasis, complicating purulent inflammation, wound necrosis.
Representatives of the genus Hypoderma are often diagnosed in cattle in the farms of the region - subcutaneous gadfly (large subcutaneous or sternum and esophagus). Adult insects resemble a bumblebee; they do not feed. Gadfly years and egg laying takes place in June - July.
Common in all areas of the region are representatives of gnats - horseflies, mosquitoes, midges, biting midges. Horseflies (family Tabanidae) are aggressive bloodsuckers, mainly attacking cows in the morning 8 - 11 hours, then 15 - 17 hours. The optimum temperature for the summer is 19 - 30ºС. Years begin at the end of May.
The development of horseflies is inextricably linked with water, so they fly no further than 600 - 800 m from water bodies. They attack in large numbers, prefer phlegmatic animals with a black color. They can tolerate pathogens of anaplasmosis, filariasis, anthrax, tularemia.
Mosquitoes (family Culicidae) are annoying small insects that attack animals for feeding blood in the morning (6-12) and evening (18-21) hours. Larvae and pupae develop in water or very waterlogged soil.
Pups (family Simuliidae) - small dipterous - 2-4 mm. Active bloodsuckers, breeding places - fast-flowing rivers, streams, drainage ditches. In one season they give 1 - 3 generations. Active in the morning - 6-11 hours and in the evening 17-22 hours. They are intermediate owners of onchocerci. Always attack in large numbers (more than 1000 individuals).
Bites are painful, with a mass attack, the development of simuliotoxicosis is possible. It is manifested by severe anxiety, hypersalivation, swelling of the tongue, submandibular space, chest, enlarged lymph nodes, severe shortness of breath. in young animals this leads to death.
Bells (family Ceratopogonidae) are outwardly similar to midges, but they are much smaller. Active bloodsuckers throughout the daylight hours. The brood places are shallow rivers, lakes, swamps, waterlogged soil, tree hollows.
Stationary ectoparasites. These are representatives of the order Mallophaga - down-feather-lice-beetle. In cattle, representatives of the genus Bovicola (bovicola) are parasitic. These are wingless insects of light brown color, the head is wider than the chest. Parasitize on the skin of the neck, back, root of the tail.
The development of bovicol with incomplete metamorphosis is completed in 3-4 weeks. Numerous in winter - spring. Transmitted by contact, as well as through care items. Cause significant itching, inflammation of the skin.
Siphunculata squad - lice. The insects are dark brown in color, the head is narrower than the chest, development with incomplete transformation in 14-18 days. They are localized on the skin in the neck, chest, sides, back. Especially intensively affect calves.
There are 2 known types of cattle lice - Haematopinus eurysternus (hematopinosis pathogen) and Linognatus vituli (linogen pathogen). Eating blood, cause severe itching, a sharp decrease in productivity. They can transmit pathogens of protozoal, bacterial and viral infections.
Ticks of the genus Dermanyssus are most common in poultry houses with floor and multi-tier contents. In one gram of substrate, their number reaches 50-1000 individuals at different stages of development. Due to the massive population of poultry houses with ticks, they feed on the bird almost around the clock.
For laying eggs use any substrates, surfaces and even a chicken egg. A massive attack on a bird leads to inflammation of the skin, a sharp feather loss, pecking, and a decrease in egg production.
In addition to ticks, representatives of the Insecta class, insects, were discovered in the houses. Fleas - rat fleas are especially common. Xenopsylla. They feed on blood on the bird, causing great concern, eggs lay in any substrates. They can parasitize on people, poultry and animals.
Poohoids are a detachment of Mallophaga, insects whose head is wider than the chest develop with incomplete metamorphosis in 18-20 days. Localized on the skin in the area of the scallop, earrings, under the wings. There are 3 species on farms - Menopon gallinae, Menacanthus stramineus, Lipeurus variabilis.
Flies — domestic and blue meat, barn moths, beetles — flour flies (large and small), and predatory mites were found in production workshops, utility rooms, and practically all the examined poultry farms. The products of their metabolism change the moisture of the feed, pollution, lumpiness.
Against this background, the acidity of the feed changes, molds actively develop, which in turn significantly reduces the nutritional value of the feed.
In some farms, the number of ectoparasites of animals is so great that veterinarians are forced to spend considerable money and time on antiparasitic measures.
Special events
The organization of treatment and preventive treatments of animals and birds, as well as the processing of premises should be carried out comprehensively, taking into account accurate diagnostics, determining the degree of invasion, climatic conditions, economic opportunities and necessarily involving zootechnical and engineering services.
The proposed drugs and methods of their use have a good effect against all previously considered ectoparasites. The following preparations were rational in use.
Insecticidal checker PESHA-V, manufacturer LLC “MK“ Peri ”(St. Petersburg). The composition of the checkers includes synthetic pyrethroid - cypermethrin, auxiliary aerosol forming components.
The principle of operation is the evaporation of the active substance of the drug, followed by cooling in air and the formation of a condensation aerosol.
The method of application consists in the following algorithm:
- the maximum possible sealing of the room,
- placing checkers on a fireproof surface,
- ignition of the wick from any source of open flame,
- processing exposure of at least 0.5-2 hours,
- natural or artificial ventilation of the room.
Neocidol(synonyms: diazinon, manjin, bazudin, nucidol). The manufacturer is Siba-Geiga. Organophosphorus compound has a contact and alimentary pathway of penetration into the parasite. The drug was tested and adapted for use on the territory of the Russian Federation by Agrovetzashchita company (Moscow).
For the treatment of premises, animals and birds use aqueous solutions of 60% K.E. at a temperature not higher than 35ºС. The concentration of the working solution is 0.5-1.5%. Of the FOSs, Diakan, Blotik, Sulfidofos (Baytex, Tiguvon, Fenthion), Tsiodrin, Sebacil (Foxim, Baytion) have a good effect.
All of the above funds have been tested in different climatic zones of Russia during the processing of farm animals and poultry against ectoparasites. A high effect in their application can be achieved only with a strictly planned set of measures for each individual farm. With the obligatory observance of the proposed instructions and instructions.
When treating cattle and livestock buildings, it is rational to apply the following methodology:
In order to destroy zoophilic flies (family Muscidae, family Calliphoridae), as well as to prevent attacks on animals by gnats (horseflies, mosquitoes, midges, biting midges). PESHKA-B insecticidal checkers are placed in stockyards and in the maternity ward at the rate of 1 checker / 300-600 cubic meters of room space.
To bring the drafts into action, one or two workers working in overalls and respirators are enough. Before processing, they close doors, windows, ventilation shafts of courtyards, however, it is difficult to achieve complete sealing of the premises, taking into account the specifics of livestock buildings, especially in the hot season.
The farm workers are removed from the premises, then the checkers fuses are set on fire at the same time, the end of the burning of the igniter and the beginning of heavy smoke emission are awaited, after which the employees conducting the treatment leave the room. Moreover, if the burning of the active substance continues after the fuse has been triggered, it is recommended to extinguish the flame by covering the checker with a piece of thick cardboard.
A feature of the treatment of stockyards is that the smoke of the premises is carried out in the morning, i.e. during the activation period of flies. However, to withstand exposure for more than 1-2 hours, as a rule, is not possible, due to the strict observance by the farm workers of the daily routine. After 1-2 hours, farm workers open doors, windows and ventilation shafts for 15-30 minutes of natural ventilation.
A single use of the PESHKA-B insecticidal checkers leads to the complete destruction of bestial flies and gnats living in the yards; Due to the repellent properties of the preparation, the activity of attacking blood-sucking dipteran insects on animals both on the territory of farms and on pastures decreases.
Animals in the presence of which they are processing (cows, bulls, calves) tolerate excessive smoke in livestock yards, cases of intoxication, a sharp decrease in productivity, the occurrence or exacerbation of respiratory diseases in cattle are not observed.
When processing poultry houses, both in the presence of a bird and without it, we recommend using the following methods with a high degree of efficiency:
Processing rooms in the absence of poultry
The use of PESHKA-V checkers as an insecticaricide at the rate of 1 checker per 300 cubic meters. m. Processing with the use of checkers is carried out immediately after removal of the bird, before the dismantling of equipment and mechanical cleaning. Exposure processing for at least 1 day.
Carry out a thorough wet mechanical cleaning of the house (cages, ducts, floor, walls, manure channel) using any disinfectant. For washing, use hot water (70-90ºС).
Ventilate the room, carry out ongoing equipment repairs, and whitewash the walls. Treat the room and equipment inside with a solution of neocidol. The working solution is prepared at the rate of 1 liter of 60% ke for 2400 liters of water with a temperature of 15-30 ° C.
After mixing, the working solution is sprayed with the help of the DUK (the nozzle of the sprayer must be similar to diesel to achieve fine spraying). Particular attention is paid to the processing of the egg conveyor belt. It is carefully sprayed with a solution of neocidol from two sides before dismantling, i.e. immediately after using insecticidal checkers.
The transverse egg conveyor belts are processed twice, the first time simultaneously with the processing of longitudinal ribbons, the second time - clean.
It is advisable to treat these objects with an oil solution of neocidol. It is prepared using mineral oils and used engine oil as a solvent. For 1 liter, 10 ml of 60% ke is required. neocidol. The prepared working solution is applied to these objects with a brush or tissue swab.
Re-processing of the premises is carried out after 3-4 days. Evaluation of the quality of the treatments is carried out 7-10 days after the second spraying with neocidol. To do this, carefully examine and collect the substrate from the sites of the highest concentration of ticks (see paragraph 1.5.).
The substrate is collected in a Petri dish, then microscopic or examined using a magnifier. Set the number of ticks, their mobility. Treatments are considered satisfactory if out of 10 ticks, 7 are immobile.
Poultry is placed in prepared poultry houses, only after preliminary treatment with a solution of the drug "Delcid" 3 days before moving. To do this, prepare a working 0.002% solution. The bird is sprayed once. The temperature of the solution should be between 15 - 20 ° C.
Processing facilities in the presence of a bird
In the house, carry out the most thorough mechanical cleaning. Particular attention should be paid to the thoroughness of cleaning the litter, the quality of cleaning the egg conveyor belt, narthex cages, rubber pads, watering channels, etc. These objects are cleaned by carefully removing the accumulated substrate.
Carry out the method of fine spraying with an aqueous solution of delcide at a concentration of 0.002%. Treatments are carried out before feeding in the absence of feed in the feeders.
After processing the cell batteries, proceed to sequential processing of the floors of the aisles, walls, supporting structures, ducts. For deacarization of the latter, it is advisable to use insecticidal checkers PESHA-B. Be sure to process the table, walls, floor in the room for sorting eggs and other technical rooms.
The metal arcs above the upper tier of cells, the space under the rubber pad in the egg conveyor (if any) is lubricated with a 1% neocidol oil solution (for the preparation technique, see paragraph 1.5.), Excluding the surfaces accessible to the bird.
Repeated treatment with delcidum is carried out twice with an interval of 5 days. When working with acrycides, observe personal safety precautions.
Organizational activities
- Remove unused structural elements that create pockets for accumulation (rubber inserts from watering channels, rubber pad on the wall of the tray of the egg conveyor, etc.)
- For each house, it is necessary to provide individual equipment, it is imperative to mark the equipment in order to exclude it from other houses. After each use of the inventory, it must be processed in des. solution (formalin-acaricide 1: 1 at recommended concentrations).
- Treat poultry cages and egg transport containers before and after use with any insecticide and acaricide in an aqueous solution concentration of at least 0.1%.
- Use radical rodent control measures.
- In spring, it is advisable to plant tansy, rosemary, Caucasian or Dolmak chamomile with repellent properties in the area around the houses.
- Tighten control over compliance by workers with the rules for moving around the factory.
Delcid for the control of ectoparasites of animals, disinfestation and decontamination of premises
Delcidum contains synthetic pyrethroid deltamethrin as an active ingredient - 4.0%, and tween 80, neonol and nefras as auxiliary components.
In appearance, the drug is an oily transparent liquid from yellow to brown. When mixed with water forms a stable white emulsion. 2 ml packaged in glass ampoules are packaged in a cardboard box of 5 ampoules.
Pharmacological properties
Deltamethrin, which is part of the drug, belongs to the group of synthetic pyrethroids and has a pronounced insecticaricidal intestinal and contact effect. It is active against sarcoptoid, ixodid ticks, bed bugs, lice, fleas, flies, mosquitoes and other ectoparasites of animals.
The mechanism of action of deltamethrin is based on the blocking of neuromuscular transmission of nerve impulses at the level of ganglions of peripheral nerves, which leads to paralysis and death of parasites.
According to the degree of exposure to the body, deltsid belongs to moderately hazardous substances (hazard class 3 according to GOST 12.1.007-76), in the recommended doses it does not have a local irritant, resorptive-toxic and sensitizing effect. Contact with mucous membranes causes slight irritation. Toxic to fish and bees.
Mode of application
The emulsion for processing is prepared immediately before use. At the same time, the volume of the emulsion required for processing and the amount of Delcide required for its preparation are determined.
The required volume of Delcide is thoroughly mixed with 2-3 volumes of water, and then poured into a bath with water or the tank of the spraying device, adding water to the required volume with stirring.Shorthair animals are sprayed with a water emulsion of Delcide, longhaired - bathed in an aqueous emulsion of the drug.
The drug is dissolved in cool tap water in the following concentrations. Spraying or bathing animals:
- Honest ticks, demodex: 1 dose per 1.6 liters of water for prophylactic purposes - once. With treatment - 2-3 times with an interval of 7-10 days. The affected areas are treated with a grip along the perimeter of the focus of 1-2 cm of healthy skin. The interval of 7 days until 2 negative findings of the study of scrapings.
- Ixodid ticks: 1 dose per 2.2 liters of water. In the period of high tick activity, the interval between treatments is 7-10 days.
- Lice, fleas, hairworms, flies, horseflies, gnats: 1 dose per 6.4 liters of water for prophylactic purposes - once, with treatment - twice with an interval of 7-10 days.
The sequence of spraying the animal: the auricles, head, body, tail, the area around the anus, limbs. When processing, prevent the emulsion from entering the eyes, nose and mouth of the animal. Moisten the animal’s hair and allow it to dry. Do not flush the drug. It is not recommended to bathe the animal with shampoos 3 days before - and 3 days after treatment.
To prevent licking of the drug, animals put on a muzzle or close their jaws with a loop from the braid, which is removed 15-20 minutes after treatment. Within 10-12 hours after treatment, the dog should not be stroked and kept away from small children.
Spraying the rooms where animals are kept:
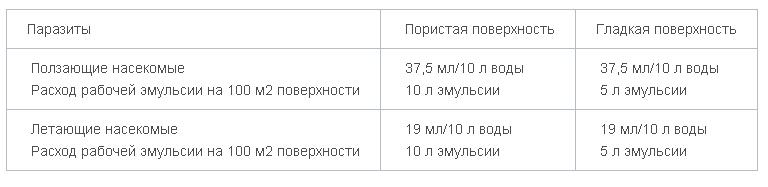
- Crawling insects - 2 doses per 1 liter of water.
- Flying insects - 1 dose per 1 liter of water.
Before disinsection, the remains of feed and water are preliminarily removed from the premises. After treatment, the room is ventilated for at least 1 hour, the dead flies are swept away and disposed of, the feeders and drinkers are thoroughly washed, and then the animals are placed in the room.
Contraindications
It is not allowed to use Delcid for the treatment of weakened and exhausted animals, as well as females later than 2 weeks before birth.
Side effects
When using Delcide in accordance with the instructions, side effects and complications, as a rule, are not observed.
With increased individual sensitivity of animals to deltamethrin and the occurrence of side effects (refusal of food, vomiting, edema, impaired coordination of movements), the use of the drug is stopped and desensitizing therapy is carried out.
Personal Prevention
When working with Delcid, the rules of personal hygiene and safety precautions provided for when working with medicines should be observed.
If Delcid entered the body through the mouth, give the victim several glasses of warm water with 8-10 tablets of activated charcoal or another adsorbent, and then a saline laxative.
If signs of poisoning appear (dizziness, general weakness, nausea), it is necessary to stop processing, wash the face of the hand and consult a medical professional.
A container contaminated with Delcid is neutralized by filling it with a 3-5% solution of soda ash for 5-6 hours, and then washed with running water. The residues of Delcid are neutralized with a 5% solution of caustic alkali or an aqueous suspension of hydrated or bleach (1: 3) and poured into slurry wells.
They are poured into slop wells or into a pit to a depth of at least 5 m, located away from sources of water supply and buried. The use of containers for domestic purposes is prohibited.
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from direct sunlight and inaccessible to children and animals, separately from food and feed at a temperature of 0 to 30 ° C. The shelf life of the drug subject to storage conditions is 2 years from the date of manufacture.
Delcid should not be applied after the expiration date.
leave a comment