Glad to welcome my readers! Sometimes I remember how in my childhood I was afraid of one film solely because of a scene in which a large number of insects crawl under a person’s skin ...
The film took place in Egypt and, I think, you can understand what I mean! When I first found out what subcutaneous mites are, and what really can happen, it got worse for me ...
But! To begin with, I propose to substantively talk about these arthropods and find out when they really can threaten you. Do not wind yourself up once again; Remember, you need to know the enemy by sight, because the familiar enemy is not such a terrible enemy. All the details in my material below!
The content of the article:
- 1 Subcutaneous tick - symptoms of infection and treatment of demodicosis
- 2 What does a tick look like under a human skin: symptoms and treatment
- 3 Subcutaneous tick in humans
- 3.1 Demodecosis: definition
- 3.2 Types of subcutaneous ticks in humans and their features
- 3.3 Infection pathways
- 3.4 Reasons for development
- 3.5 Diagnosis of the disease
- 3.6 Illness confirmation
- 3.7 Subcutaneous tick treatment in humans
- 3.8 The best drugs against demodicosis
- 3.9 Folk remedies for subcutaneous tick
- 4 The main signs and symptoms of a subcutaneous tick in humans: how to recognize the presence of parasites, how to deal with them
Subcutaneous tick - symptoms of infection and treatment of demodicosis
Subcutaneous tick (acne zheleznitsa) is a parasite that lives in the sebaceous glands or hair follicles in humans and has sizes up to 0.4 mm.
It has an elongated and translucent body. He actively moves, mainly at night, as he seeks to avoid sunlight. Demodecosis causes a disease that does not pose a threat to human life and health.
Small red spots appear on the face or back of a person, including several pimples. A person experiences itching, peeling of the skin appears. Most often, women suffer from demodicosis.
The body of the parasite consists of dense scales, which are a kind of shell. He does not allow medicines to penetrate into it. Therefore, if a tick gets under the skin, even the most modern drugs do not always cope with it.
Causes and ways of infection
A subcutaneous tick can live in the human body for years and does not declare itself in any way. Therefore, it is very important to know under what conditions he will begin active life, bringing a lot of trouble to his carrier.
A subcutaneous tick on the face becomes active in the presence of the following factors:
Weakening of the immune system, which is provoked by such moments:
- Long-term use of antibiotics and hormonal drugs;
- chronic diseases;
- severe stress.
Gastrointestinal tract diseases:
- The abuse of carbohydrate and fatty foods;
- Frequent use of alcohol and a large amount of coffee;
- The use of hot seasonings.
Hormonal changes and malfunctions in the endocrine system.
Violation of the rules of personal hygiene:
- Use of other people's personal hygiene items;
- Excessive hobby for a sunbed and a bath;
- Long exposure to the sun.
Increased production of sebum and sweat. This is facilitated by such factors:
- Stress
- Insomnia or lack of sleep;
- Low level of physical activity;
- Nervous breakdowns.
Continuous use of low-quality cosmetics.
All these causes excite the sexual instincts of ticks. Females strive to lay eggs in the deeper layers of the skin in order to protect their offspring as much as possible. Three days later, the larvae turn into adults.
The subcutaneous tick, inhabiting the subcutaneous layers, feeds, multiplies and dies. At the same time, decomposing, releases a huge amount of toxic substances into the skin.
It is very simple to get infected with demodicosis: the disease is transmitted from person to person. A subcutaneous tick living in the skin comes out with sweat and sebum.
The use of the same towel, common dishes, even a kiss or a handshake will result in the parasite moving to a new host. Sometimes infection may not occur, but a person will become a tick carrier.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The subcutaneous tick settles in the sebaceous glands, and then continues on its way. Therefore, the symptoms of the parasite can be found on almost any part of the body. However, the face, eyes and back of a person suffer most from him. A pimpled red rash appears on the skin, which is then converted to whiteheads.
You will need to see a doctor if the following symptoms are found:
- areas of the skin turn red and rashes appear on them, red pimples become purulent over time and turn into papules;
- the skin in the affected area turns red, the normal color does not return for a long time (photo at the beginning);
- the skin becomes very dry or, conversely, oily, constantly itching, and itching intensifies in the evening and at night;
- a distinctly visible vascular red net appears on the skin, which occurs due to vasodilation.
- intense hair loss, which is accompanied by the appearance of dandruff near the roots;
- the skin on the face shrinks and becomes like a mask, thickenings similar to tubercles appear;
- if the tick populated in the nose, the skin on it becomes very inflamed, the nose becomes like a huge potato;
- complexion becomes earthy, grayish, pores expand. This is due to the fact that the waste products of the tick are secrets and toxins that the parasite actively secretes into the skin. Moreover, every evening ticks go outside, and when they return, they bring with them countless other pathogenic bacteria;
- the occurrence of a feeling of subcutaneous movement;
- in the most advanced cases, the appearance of a serous or blood-pustular crust can be observed.
If a subcutaneous tick reaches the eye area, the symptoms will be more characteristic:
- intense eyelash loss begins;
- fog is increasingly appearing in front of my eyes, objects are not clearly visible (persistent visual impairment);
- conjunctivitis and tearing appear;
- dandruff occurs on the eyelashes;
- the eyelids turn red and harden;
- there is a feeling of severe itching, especially at night;
- hair loss from the eyebrow area is observed;
- mucus is released from the eyes.
The use of decorative cosmetics is also erroneous, with the help of which many women try to hide the manifestation of the disease on the face.
A dermatologist, having performed a visual examination, will refer the patient to a laboratory analysis. To carry it out, it is necessary to take a scraping from the affected areas of the skin (scales, crusts, droplets of purulent discharge). To diagnose the disease, not only particles of the skin, but also eyelashes are taken for analysis.
The disease is confirmed if the number of viable ticks exceeds five per one centimeter of skin.
It is important to recognize the disease on time. Indeed, in advanced cases, the disease flows into a chronic form. Small spots with pimples turn into abscesses, ulcers, are covered with scars and pigmentation. The face becomes swollen and covered with serous crusts.
The more neglected the disease, the more difficult it is to treat!
How to treat a subcutaneous tick
The fight against the parasite will be long and difficult. The treatment regimen is selected individually by a dermatologist and depends on the degree of skin lesion and the presence of other diseases that, quite possibly, provoked the occurrence of demodecosis.
The main therapy should be aimed at eliminating the causes that led to inflammation under the skin. Treatment of the disease must be carried out comprehensively. It is necessary to use antiparasitic drugs with a wide spectrum of action inside, and also treat damaged areas of the skin from the outside.
Most often, a treatment complex is used, which includes the following components:
- medication treatment;
- physiotherapy;
- special medical diet;
- hygiene procedures;
- a complete rejection of makeup.
Drug treatment is prescribed to cleanse the blood vessels, normalize the gastrointestinal tract, and increase immunity. The most commonly used therapy is the following drugs:
- Antiparasitic drugs that have a wide spectrum of action.
- Antibiotics.
- Preparations for the restoration of intestinal microflora.
- Drugs designed to strengthen blood vessels. They must be used, since parasites in the process of their life make the vessels that surround them very fragile.
- Immunity enhancers.
- If the body cannot cope with the disease itself, hormonal drugs can be prescribed.
It is important to remember that the use of all drugs should be agreed with the attending physician. You need to use them according to the instructions or those prescriptions that the dermatologist suggested.
In addition to the drugs used inside, it is necessary to alleviate the manifestations of the disease on the skin. The use of Demodex Complex series drugs will be quite effective. They include Chinese and Malaysian medicinal plants. Manting soap and milk are also popular.
After that, it will be effective to apply steroid preparations to the skin, such as Flucinar or Elokom. Ointments containing metronidazole and benzyl benzoate will have an antimicrobial effect.
To normalize the microflora of the skin and relieve inflammation, drugs that contain azelaic acid are used. If demodicosis is in an advanced stage, dermatologists will recommend the use of tar ointments. These products have a pungent odor, but are very effective.
Despite the use of sufficiently effective medications and adjuvants, the cure for the disease will not come if you do not adhere to a special diet. It is necessary to exclude sweets and flour, alcohol, honey and chocolate. Minimize the intake of fatty and carbohydrate foods.
The diet must include as many fresh vegetables and fruits as possible. You need to eat low-calorie dishes, boiled meat.Drinking 2 liters of water per day is another necessary condition for a therapeutic diet.
One of the important directions in the treatment of the disease is strict adherence to the rules of personal hygiene. Every day you need to rinse your face with infusions of medicinal herbs and wipe with alcohol tinctures. If possible, use only tar soap.
Mandatory is the use of personal hygiene products only! Bed linen needs to be changed every day. During treatment, do not use decorative cosmetics. It is also advisable not to visit the baths, solariums and steam rooms.
If treatment is started on time, at the initial stage of the disease, when the females of the subcutaneous tick have not yet acquired offspring, the condition will improve by 7-8 days. However, unfortunately, few can recognize the disease so early. In the chronic stage, demodicosis is treated for a very long and difficult time.
Complete the treatment by re-diagnosis.
Folk remedies
Our distant ancestors did not have modern medicines to combat subcutaneous ticks. However, they successfully treated this disease with the help of drugs that were in every home.
- Yellow clay:
When the first signs of the disease appear, you can use yellow clay. It must be mixed with warm water until thick sour cream and applied to the skin in those places where there are lesions with a tick. It is advisable to keep the mask on your face all night. Yellow clay has an antimicrobial effect, provides good nutrition and whitening the skin. - White clay mask:
For oily skin and enlarged pores, you can use a mixture of white clay, streptocide and crushed alum. All ingredients must be mixed and diluted with water. Before applying the mask, you need to wash your face with tar soap. - Laundry soap:
The subcutaneous tick is very afraid of ordinary laundry soap. You need to grate it, and then foam well. Foam is applied to the face and left there until completely dry. The procedure must be repeated several times. - Mask of solidol:
A very effective mask made with your own hands from solid oil, olive oil and birch tar. All components are mixed and applied to the face.
Prevention
The subcutaneous tick in humans is highly contagious. These parasites cannot be seen without special devices, but they are at any moment ready to move from one carrier to another. To prevent the disease, do not break simple, but very important rules:
- bed linen must be changed as often as possible;
- feather-based blankets and pillows should be heat treated as often as possible;
- use only your towels, bedding, etc .;
- after playing sports, as soon as possible, change clothes wet from sweat to dry;
- be sure to take a shower after exercise;
- you can’t always use decorative cosmetics, since powder and some greasy creams provoke the spread of the parasite (under no circumstances should anyone use other people's cosmetics);
- if there is a disease of the gastrointestinal tract, do not postpone their treatment;
- proper nutrition is the key to a healthy body, watch your diet, and this will help prevent many problems;
- maintain immunity with fresh vegetables and fruits, drink herbal teas;
- if any rashes are found on the skin, consult a dermatologist immediately;
- never try to cure a subcutaneous tick by yourself, as you will lose precious time and the disease will go into a chronic stage.
By following these simple recommendations, you eliminate the likelihood of infection with a subcutaneous tick to a minimum.
What does a tick look like under a human skin: symptoms and treatment
Human skin is a favorable place where various bacteria, fungi and parasites can settle, one of which is a subcutaneous tick. In small quantities, these pathogenic microorganisms are present in everyone, performing the functions of normalizing the level of acidity in the epidermis.
However, with a violation of the immune system in humans, a sharp multiplication of parasites occurs, which affects the negative state of the skin.
What is a subcutaneous tick
Demodex is a conditionally pathogenic parasite that constantly lives in the inner layers of the epidermis, in the sebaceous glands, inside the base of hair follicles. The main diet of a subcutaneous tick in humans: particles of dead skin and fats.
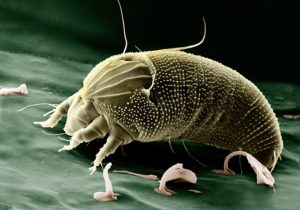
Due to the small size of 0.1-0.4 mm, this parasite is not visible to the naked eye. To understand what a tick looks like under a person’s skin, you should look at his photo taken under a microscope.
Outwardly, it looks like a creature, the front of which resembles an ordinary tick, and the back is like a worm. That is why its name "Demodex" is translated from Latin as "worm". Such parasites can come to the surface of the skin and move along it at a speed of 8-16 cm / h, which they usually do at night due to photophobia.
Specialists determine 2 types of subcutaneous mites, depending on the size and habitat:
- Short (Demodex brevis), eating sebum. It settles on the face, neck and shoulders, in rare cases, the appearance of a subcutaneous tick on the back and other parts of the human body.
- Long or Demodex folliculorum (Demodex folliculorum) - localized on the hair follicles: eyelashes, hair and eyebrows.
Both species can move on the surface of the skin in search of nutrition, preferring oily areas, they do not settle on dry ones. They are not able to penetrate into the internal organs of a person. A disease in which epidermis is damaged by subcutaneous ticks is called demodicosis.
Important! Demodex can quite easily be transmitted from one person to another, infection occurs through the contacts of the skin or hair.
Where does the subcutaneous tick come from?
Since this parasite is conditionally pathogenic, a small amount of it is present in the upper layers of the epidermis and hair follicles of people constantly.
Painful manifestations are usually fixed against the background of failures in the patient’s body, due to which he actively reproduces. Negative symptoms in the presence of a subcutaneous tick in a person usually appear under the influence of the following reasons:
- a failure in the endocrine system, which affects the increase in the production of sebum, pore enlargement, which acts favorably for the reproduction of ticks;
- changes in the hormonal background, which leads to a violation of the pH and activation of the sebaceous glands - is usually observed in women during periods associated with menstruation, pregnancy or menopause;
- decreased human immunity due to stress, depression, emotional shock, which leads to increased production of hormones responsible for overall well-being;
- improper nutrition, includinga large amount of fatty, floury foods, coffee, spices leads to changes in the skin, especially on the face;
- frequent visits to the solarium lead to trauma to the epidermis, through the damage of which microorganisms penetrate;
- the use of low-quality cosmetic preparations can lead to clogging of pores, which creates favorable conditions for the reproduction of a tick in the skin of the face and body;
- other factors: poor ecology, prolonged colds, temperature changes, etc.
Most often, children in adolescence suffer from demodex, in which hormonal changes in the body occur during this period. Also, the disease can occur in women during pregnancy and in the elderly.
Symptoms of a subcutaneous tick
The main signs of demodicosis in humans:
- the appearance of a rash on the face, which begins with redness, and then turns into acne, papules and ulcers, as seen in the photo of a tick on a person;
- redness and shine on the skin, which do not pass for a long time, a manifestation of tuberosity;
- with demodicosis of the eyelids, irritation around the eyes begins, the skin itches, lacrimation and small seals appear, scales, eyelashes stick together and even fall out;
- on the affected areas, there is a feeling of dryness and itching, which intensify in the evening, when the parasites are activated;
- the appearance of a vascular network, the removal of which will require additional treatment after the removal of the subcutaneous tick;
- when the nose is affected, its size increases, a red-cyanotic shade appears;
- in the advanced stage of the disease, the skin changes color to tan or gray, the face looks like a mask, seals and purulent bloody crusts appear.
A prolonged course of the disease causes visual impairment due to damage to the cornea. All unpleasant symptoms not only worsen the appearance of a sick person, but also make him a threat to transmission of infection to other family members. Therefore, personal hygiene should be followed using all household items individually.
Stages of the disease and diagnosis
Demodecosis in humans, according to the severity and development of the disease, proceeds in 4 stages: erimatous, pustular, papular, combined form of the disease.
In the presence of negative symptoms and a suspicion of such a disease, in order to know for sure that a tick under the skin is the cause of inflammatory or pustular processes, you should seek help from specialists.
To clarify the diagnosis, the attending dermatologist examines the patient and some tests for demodicosis:
- the study of the secret from the sebaceous glands, scrapings from skin tissues;
- analysis of the contents of acne;
- examination of the fluid that is released from the eyes when the eyelids are affected;
- analysis of eyelashes and hair follicles on the head, where mass accumulation of parasites is possible;
- general examination and questioning of the patient for chronic and hormonal diseases, which are the root cause of increased activity of parasites.
When sending for tests several days before the procedure, it is strictly forbidden to use any cosmetic products, ointments, tonics and creams, because they will affect the clinical indicators. In accordance with the studies, the specialist makes a diagnosis and selects the necessary course of therapy.
Demodecosis Treatment
For the treatment of subcutaneous mites, the use of complex methods is necessary: get rid of the reason for their active reproduction:
- to restore hormonal levels, support the immune system, cope with high emotionality and stress;
- eliminate the external symptoms of the disease.
The complex therapy of demodicosis includes the following activities:
- Improving the diet: the rejection of spicy, salty, smoked and fried foods, coffee, alcoholic beverages;
- dieting: the use of dairy products, vegetables and fruits, low-fat varieties of meat and fish;
- maintaining clean skin, including facial hygiene, the absence of cosmetics that clog pores, washing with a cold soapy solution several times a day;
- medicines: antihistamines;
- the use of ointments.
Antiparasitic therapy is carried out in stages, usually it is delayed due to the impossibility of penetration of drugs through the outer cover into the tick and the parallel treatment of concomitant diseases. After the 1st course, repeated tests are done, and then the 2nd course is prescribed according to another scheme.
Ointments for the treatment of demodicosis
The attending physician recommends the use of special ointments made up of active ingredients that help to destroy the subcutaneous tick, reduce fat production and close pores. Medical facilities: Metronidazole or its analogues (Ornidazole, Trichopolum, etc.) is an antiparasitic and antimicrobial drug. Therapeutic ointments:
- Ichthyol - contains petroleum jelly and ichthyol resin, is an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drug, draws out pus and heals damage.
- Permethrin - its active component penetrates the chitinous shell of ticks and paralyzes them.
- Sulfuric - is the most popular for getting rid of subcutaneous parasites, has drying, antimicrobial properties, causes the death of parasites, restores and heals injuries and wounds. Its main advantage is the permission to use in children, starting from 2 months of age.
- Yam is a therapeutic ointment containing birch tar, salicylic and carbolic acids, lanolin and petrolatum. Effectively destroys the subcutaneous tick, accelerates the healing of ulcers and ulcers. According to patients and doctors, this remedy is effective in demodicosis.
- Benzyl benzoate - contains stearic, citric and benzoic acids, which penetrate the shell of parasites and kill them, is available in the form of an emulsion and ointment.
- Delex Acne Gel - Acne Sulfur Remedy
- Demalan is a special cream for the eyelids and face that contains 17 active ingredients: metronidazole, glycans, chamomile extract, etc. It relieves inflammation, reduces allergy, affects metabolic and reparative processes in skin tissues, reduces itching and swelling. Before applying Demalan, it is recommended to clean the skin from crusts twice with tincture of calendula or eucalyptus twice (interval 15 minutes).
On a note! When diagnosing demodicosis in a child, the doctor prescribes more sparing drugs. Ointments with tar or sulfur, Mayfule cream, Demodex stop spray, etc. are recommended.
Folk methods
In addition to the use of pharmaceuticals, it is recommended 2 times a day to use a medicine for a subcutaneous tick in the form of a talker, which is prepared at home. Recipes of a therapeutic talker:
- Main ingredients: 100 ml of salicylic alcohol, 4 tablets of Levomycetin and 4 - Trichopolum, which must be crushed to a powder state. Pour the prepared mixture into a glass bottle and use as a tonic for application to the affected areas in the morning and evening. After treatment, a nourishing cream is applied to the chatterbox to avoid overdrying the skin.
- Shredded 2 tablets of Trichopolum mixed with 1 tbsp. l of castor oil. It is recommended to apply in the evening on the affected areas, do not rinse and leave until the morning.
Herbal remedies for the treatment of demodicosis in humans:
- The infusion of celandine is made from 250 g of crushed fresh roots and 200 ml of vegetable oil, which are set for infusion in a sunny or warm place for 2 weeks. Then strain and pour into glass containers sealed with dark paper so that light does not penetrate, it is better to store in the refrigerator. Before processing, a little infusion should be mixed with sour cream and applied to the affected area, you can bury it in the nose, ears, eyes, etc.
- A 6% solution of apple cider vinegar is also used to treat demodicosis, however, when applied to the eyes, one should be careful not to get into the visual organs.
- To cleanse the affected areas and rinse hair, you can use folk remedies - decoctions of calendula and chamomile, where grated tar soap is added in a proportion of 15 g per 1 liter of liquid.
Although treatment can take a long time, you should not despair. Timely contacting a specialist and conducting complex treatment will help to successfully defeat subcutaneous ticks and cure demodecosis in humans.
Subcutaneous tick in humans
In the case of a red acne or acne on a person’s face, attention should be paid to the fact that demodecosis can be affected, especially if the usual means do not allow them to get rid of.
The presence of subcutaneous ticks in humans causes this ailment. This article describes why and how subcutaneous ticks appear, as well as how to effectively get rid of them, both by pharmacy and folk methods.
Demodecosis: definition
This term refers to a chronic ailment associated with the skin of a person that is caused by a subcutaneous tick. Acne is the second name for this disease.
The World Health Organization indicates that about 90% of the total population can be affected by this parasite. The manifestation of demodicosis in humans is associated with the skin of the face, forehead, eyelids, nasolabial folds, and external auditory canals. In addition, the subcutaneous tick settles in the hair on the head, on the chest and on the back.
Types of subcutaneous ticks in humans and their features
As a rule, 2 types of ticks take root in a person, depending on the part of the body where they parasitize. For example:
- Demodex folliculorum, which prefers to live in the hair, on the eyebrows and on the eyelashes. This type of tick reaches a size of 0.2 to 0.4 mm.
- Demodex Brevis. This type of tick parasitizes in the human sebaceous glands. The size of the parasite is from 0.15 to 0.48 mm.
It is interesting to know where such a disease can come from in a person?
Infection pathways
This serious disease can occur in any person, regardless of gender and other signs. As far as is known, there are two ways of infection with demodicosis. Namely:
- As a result of direct human-to-human contact. This can be an ordinary handshake, touching the skin of a person, as well as a kiss, maybe even the most harmless, friendly.
- As a result of indirect contact, through everyday items. Such items can be: bedding, personal hygiene products, a wrap on a chair or sofa, interior items, etc.
The subcutaneous tick feels great in conditions when the person’s immunity is weakened and is unable to cope with the vital activity of such parasites. These arthropods, from the class of arachnids, begin to actively breed under certain conditions, which will be discussed further.
Reasons for development
A subcutaneous tick is a parasite that is able to stay in the human body for a long time and wait for optimal conditions in order to appear “in all its glory”, delivering maximum discomfort to a person.
The appearance of such an ailment is associated with some factors that, one way or another, affect the development of the disease. For example:
- Weak functioning of the immune system.
- Violations of the normal functioning of the endocrine system.
- Leading an unhealthy lifestyle.
- Problems with the normal operation of the digestive tract.
- Neuropsychic imbalance.
- Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
- Imbalance of hormonal balance in the body.
- Violation of metabolic processes.
- Period of pregnancy.
- Problems with the environment.
- Passion for cosmetics, solarium and bath.
Such a disease is treated if a person approaches the treatment problems with all seriousness. In order to correctly determine the treatment, it is necessary to study the symptoms of this disease well.
Diagnosis of the disease
Like any other disease, demodicosis is characterized by the appearance of external signs that can be associated with the appearance of a subcutaneous tick in humans:
- In a person affected by a subcutaneous tick, the skin becomes oily, increased moisture appears on the body, as evidenced by the appearance of shine.
- As a result of the skin losing its ability to breathe, a rash, acne or minor ulcers appear on it.
- As a result of the vital activity of subcutaneous ticks, a person begins to feel, as if the presence of a foreign body in the eyes.
- In the region of the eyelids, intolerable itching and swelling are manifested, and the appearance of the eyelids indicates signs of an ongoing inflammatory process.
- Mucus begins to stand out from the eyes.
- Eyelashes begin to fall out on a person, against the background of the appearance of white scales on them.
- In places of a strong inflammatory process, purulent crusts are visible.
- As a result of this, the patient feels severe discomfort, especially at night, when the subcutaneous tick shows maximum activity.
- In a sick person, the nose increases in size, moreover, it is very noticeable, which surprises others.
- In places where hair grows, severe itching is felt, and hair loss is also noted.
- An unbearable itching is also felt in the ears.
All of the above symptoms indicate the appearance of a subcutaneous tick. This is a signal to begin treatment immediately.
Illness confirmation
In the event of the first signs of demodicosis, you should immediately consult a doctor to confirm the fears. To determine the treatment regimen, it is necessary to pass tests. This is the only way to count on a quick recovery. In no case should you self-medicate, because getting rid of this parasite is not so simple.
To do the analysis, scrapings are taken from the affected areas, after which the material is examined under a microscope. If the concentration of these arthropods exceeds more than 5 individuals per 1 cm square of skin, then the diagnosis of demodicosis is confirmed. Confirmation of the diagnosis is the basis for starting a full course of treatment to get rid of parasites.
Subcutaneous tick treatment in humans
It is not so easy to cope with a subcutaneous tick, especially if the disease is started. As a rule, they try to treat demodicosis on their own, which only leads to a worsening of the situation.
This is especially true if the eyelids and eyelashes are affected. In this case, you will have to visit an ophthalmologist to prescribe additional treatment. But first you need to visit a dermatologist who prescribes a comprehensive treatment. Treatment of demodicosis is a long process that requires maximum patience.
In addition to the course of the use of medications, it is very important to know how to properly care for face skin, which creams are best used for this and how to eat.
The best drugs against demodicosis
Treatment of a disease such as demodicosis requires an integrated approach, otherwise it is unlikely to be able to get rid of a subcutaneous tick once and for all. To get rid of this disease, doctors prescribe various medications that differ in mode of action. This allows you to use all drugs as efficiently as possible. For example:
- Preparations of the antiparasitic group, based on metronidazole or tinidazole. Such components penetrate the skin, acting on ticks, which causes their death.
- Antimicrobial agents designed to reduce the number of parasites and normalize the metabolic processes of the skin.
- Antihistamine drugs that relieve intolerable itching of the skin and relieve swelling.
- Antibacterial agents, including in the form of drops, for the treatment of demodicosis affecting the eyelids and eyelashes.
- Preparations of the vaso-strengthening group.
- Drugs to stimulate the immune system, which allows you to enable the protective functions of the body.
In combination with medications, doctors prescribe a number of physiotherapeutic procedures, such as:
- Physiotherapy sessions.
- TCA peeling, to cleanse the skin of epidermal cells where ticks are located.
- Ozone therapy, as a means of increasing the body's resistance to pathogens.
- Cold treatment (cryotherapy), which helps get rid of burning and itching.
If you prescribe the correct treatment, and then strictly adhere to all procedures, then you can get rid of the subcutaneous tick once and for all.
Folk remedies for subcutaneous tick
Many people resort to the treatment of demodicosis with various ointments, infusions and decoctions, prepared on the basis of natural components. They have antibacterial, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. Often, birch tar, laundry soap, kerosene, etc. are used to treat this disease.
It is possible to actually get rid of a subcutaneous tick using folk remedies prepared on the basis of various recipes. For example:
- Aloe juice is mixed with boiled water in equal proportions. In this solution, a piece of clean tissue or a piece of gauze is wetted, squeezed out a little and applied to the problem area for 20 minutes. You need to make 25 such lotions, every other day.
- The use of a decoction of linden flowers. To prepare a decoction of linden inflorescences, you need to take 2 tbsp. tablespoons of the source material and pour it with 200 ml of purified water. Then all this is put in a water bath, somewhere for 10 minutes. After this, the solution is filtered. When it cools down, then affected areas of the body are wiped with this solution in the morning and evening, every day.
- A decoction of dried chamomile inflorescences. The cooking method is the same as with linden inflorescences. The broth is filtered, after which compresses are made on its basis several times a day. In this case, you need to alternate cold and hot compresses.
- Based on herbal harvest. To prepare the current remedy, you will need herbs such as wormwood, mint, plantain, nettle, tansy and others. The solution is prepared on the basis of the same volume of all components (1 tablespoon each). Here is added 2 tbsp. tablespoons of the string, after which the starting material is poured into 0.5 liters. boiling water, covered with a lid and infused for about half an hour. After this, the solution is filtered and taken orally 100 ml half an hour before meals for 1 month.
The main signs and symptoms of a subcutaneous tick in humans: how to recognize the presence of parasites, how to deal with them
Human skin is a vital organ. Its functions are to protect internal organs from the effects of the external environment, thermoregulation and solving many other problems.
It often turns out to be a convenient haven for beneficial and pathogenic bacteria. 90% of the people living on the planet are carriers of the subcutaneous tick. Within the acceptable number, it has a positive effect on the pH of the skin layer, absorbing dying elements and eating skin fat.
Expanding its presence, the subcutaneous tick is spread in small glands on the skin of a person. They become clogged and inflamed, which is fraught with acne. How to recognize a subcutaneous tick and how to deal with a parasite? This problem and many others will be disclosed in this publication.
Species of parasites
Subcutaneous tick - a parasitic organism that settles under the skin of a person. The parasite is not detected visually, it can be seen only using an optical device. People come to a dermatologist with a request to help get rid of the rash, but do not know the reason for their ailment.
Dermatologists involved in the study of subcutaneous tick species distinguish them by size and area of habitat. The first type, eating sebum, is localized on the skin of the face, shoulders, neck.
Remember! Many factors can lead to the rapid spread of subcutaneous mites. Having seen the first signs of the disease, you need to immediately contact a dermatologist, delay can result in intensive reproduction of the parasite, which will entail many problems with well-being.
Causes of the disease and breeding conditions
The parasite is activated for various reasons, sometimes leading to catastrophic consequences:
- with functional pathologies of the human thyroid gland, as a result of which the sebum secretion increases, the pores expand, thereby creating fertile soil conditions for the prosperity of the subcutaneous tick and similar parasitic microorganisms;
- failures in the hormonal system lead to an imbalance in the chemical composition of the skin. Enhanced production of sebum begins - an excellent nourishment for the parasite. Especially susceptible to such phenomena are women in whom the hormonal set is constantly changing in connection with the menstrual cycles, pregnancy and the onset of menopause;
- a weakened immune system is one of the main causes of the spread of destructive arthropod skin. During prolonged depression or nervous shock, the body's resistance decreases, which contributes to the emergence and development of a subcutaneous tick that attacks the protective membrane of a person;
- the use of sweets, oily, spicy foods, abuse of alcohol, strong coffee does not reflect well on the skin, spoils the complexion, its structure. Normalize the sebaceous glands, get rid of parasites will help the right approach to nutrition.
- excessive makeup, the use of aggressive agents during washing, exposure to ultraviolet rays leads to an imbalance of chemical processes occurring on the skin, providing excellent conditions for aggression of the subcutaneous tick on the face and body. The skin is affected by a tanning bed, which leads to a violation of their protective functions, which, under the influence of artificial radiation, open the way for harmful organisms.
- other factors contributing to the development of the disease include respiratory infections, hypothermia, adverse ecology. The subcutaneous tick is easy to navigate, finds weak spots in the human body and attacks them, causing physical and mental suffering.
The demodex tick often attacks adolescents who do not value health, do not pay proper attention to hygiene, and do not follow the skin well enough.At this age, perestroika processes occur in the body.
Often there is the appearance of the disease in those preparing to become mothers and the elderly. It is useless and sometimes dangerous to treat a rash that has independently appeared on the face or other areas of the body. It is necessary to consult a doctor so that he, after making an in-depth analysis of all aspects, makes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of infection
It is possible to independently determine the presence of a subcutaneous tick on your face, back, and hairline. The clinical picture characterizing the patient’s condition in connection with the presence of the parasite will give a signal about the need to start treatment:
- the first sign of the presence of a tick is enlarged pores that secrete a large amount of sebum. The second stage is the appearance of subtle pimples, mild itching, worse at night, due to the activation of the vital activity of the microorganism. The tick begins to move, which causes discomfort;
- the appearance on the skin of the face of irritation, crimson spots, oily sheen is characteristic of disorders of the epidermis. Irregularities are visible on the skin, the surface loses its smoothness, tubercles appear;
- the nose and cheeks turn red and swell slightly;
- eyelashes suffer from a tick no less. They are covered with small fragments of scaly formations, under the influence of the released moisture stick together and fall out;
- constantly haunted by the feeling that under the skin there is a creeping movement;
- the stage of the running process is expressed by pustular formations and bloody crusts on the skin.
The subcutaneous tick slowly but surely expands the boundaries of its influence, capturing the hairline on the head, making it flaky and greasy. Hair begins to fall out intensively, which significantly affects the appearance and mood.
Diagnostics
A visual examination to establish a diagnosis is not enough, the symptoms occur differently in representatives of the opposite sex and age. Medical workers will suggest a series of tests to thoroughly study the picture of the disease.
In a laboratory study, analyze the allocation of sebaceous glands, acne, eye mucosa. To make the picture clear, take eyelashes, hair follicles attacked by parasites for analysis.
Remember! In order for the test results to be objective and reliable, do not use cosmetics, pharmacy ointments, creams before sampling the test material. Then the picture will be clear.
Treatment methods
It is not easy to overcome a subcutaneous tick, it is necessary to apply treatment in a complex. The first thing to do is find the causes and phase out them.
First, they treat diseases of a chronic nature, normalize the hormonal background, strengthen the immune system, and take them out of a depressed state. After getting rid of all diseases, measures are being taken to eliminate signs of epidermal damage by a microscopic parasite.
Pharmaceuticals
For medical treatment, ointments are suitable, which include components that destroy the tick and help regulate the metabolic processes of sebum. Such means normalize the state of the epidermis.
The drugs are especially effective:
- Ichthyol ointment is a strong antiseptic, a sulfur-containing compound of ichthammol and medical vaseline.The first component is the basis of an ointment with a therapeutic effect, the second nourishes the skin. In tandem, they successfully cope with a subcutaneous tick, dry and eliminate the damage that has appeared on the skin, and relieve inflammation. Price - 90 rubles;
- Permethrin ointment is endowed with an insecticidal property. It paralyzes the tick, falling into its nerve cells. You can buy the drug for 200 rubles;
- Sulfuric ointment. From time immemorial, a well-known drug used in official and traditional medicine. It has a detrimental effect on the tick, paralyzing it. The action of the drug is not limited to the destruction of parasites, it relieves inflammation and promotes wound healing. The average price of sulfuric ointment is 45 rubles.
- benzyl benzoate. Antiparasitic ointment, extremely effective in controlling parasites, toxicly affecting them and disrupting their vital functions. Medicines in the form of ointments can be purchased for 20 rubles, a suspension will cost more.
- Yam ointment is a bactericidal preparation with a concentrated creolin odor. The product successfully fights the tick, softens, heals the pustular foci and restores the structure of the skin. The cost of the drug is not more than 80 rubles, and the effect is significant.
How to use funds:
- wash with tar soap, wipe dry with a sterile cloth, now proceed to apply the ointment to the face;
- put the drug in a thin layer on the problem area, carefully distribute it over the entire surface of the inflamed area, capturing a couple of centimeters around the infection area;
- leave the applied layer until absorbed. Repeat the procedure daily in the morning and evening until the final recovery.
The medicinal components need to be crushed into powder, combined with alcohol, placed in a convenient jar. Daily treat the affected part of the face with a swab soaked in the solution. After the procedure, apply a moisturizer so as not to dry the skin.
Treatment with nutrition and folk remedies
Nutrition should be rational and balanced. On your table should be present products, including proteins, fats and carbohydrates in reasonable proportions.
Refuse sweets, smoked meats, pickles, hot spices, consume less fat, exclude hard drinks. They negatively affect the work of the intestines, body functions, skin. They are dangerous in that they create favorable conditions for the activity of a subcutaneous tick.
Products containing fiber, vitamins, useful microelements will help to overcome the ailment. The leading place on the podium of your diet should be occupied by fruits and fish, milk and cottage cheese, cereal and white meat products.
It is impossible to conduct experiments with the skin, you need to treat the face, body and hair with gentle means: decoctions of herbs, light tinctures. A good effect is given by a mixture of one liter of herbal decoction with 15 grams of tar soap.
Prevention
You can avoid the disease by taking preventive measures. It is necessary to strengthen immunity, avoid stressful situations, follow hygienic requirements, treat colds in a timely manner, be examined regularly, and prevent malfunctioning of the body's vital systems.
If a subcutaneous tick has attacked you, a dermatologist will help get rid of the parasite, provided that you immediately contact it. After a comprehensive examination, he will prescribe complex therapy. Fulfilling all his instructions, you will gain former attractiveness and self-confidence.
leave a comment