
Hello! When I first saw how my dog began to itch regularly, and then also lose tufts of hair, I was seriously excited.
At that time, I did not have much experience in caring for animals, so the moment was stressful.
Fortunately, my grandfather once worked as a veterinarian. He helped me diagnose the threat to my pet and get rid of it. Want to know all the details about scabies mites and effective treatments? Now I will describe the most effective ways.
The content of the article:
- 1 Sarcoptosis and Noothedrosis - Itch Mite in Dogs
- 2 Sarcoptosis, demodicosis and otodectosis in dogs: methods of treatment
- 3 Symptoms and treatment of scabies in dogs (risk of human infection!)
- 4 Scabies in dogs is one of the most acute diseases
- 5 Scabies in dogs: how to quickly rid a pet of a scabies tick and prevent complications
Sarcoptosis and Noothedrosis - Itch Mite in Dogs
Scabies in dogs - sarcoptosis and notothedrosis. According to the symptoms and photos, the owners will learn to distinguish between the disease and treat scabies in dogs at home.
Scabies in dogs, in the classical sense of this condition, is caused by two pathogens - microscopic mites Sarcoptes cams and Notoedres cati.
These pathogens parasitize not only in dogs - they cause similar manifestations of itchy scabies in all carnivores, including cats. For this reason, infection between different species is possible. A person does not become infected with this disease.
The size of adult ticks is not more than 0.5 mm, and given the peculiarities of parasitization inside the skin layers, it is not possible to distinguish them with the naked eye. For this reason, accurate diagnosis of sarcoptosis or notoedrosis is possible only in a veterinary laboratory under a microscope.
Infection with scabies in dogs occurs mainly by contact. An indirect transmission path of the tick through household items is also possible. This phenomenon is especially observed when the concentration of parasites in a sick dog is extremely high, then live ticks and their eggs can be found on its litter.
Fertilization occurs on the surface of a dog’s skin. After - the female bites into the thickness of the skin and lays eggs in an amount of 20 to 50. At the end of the egg laying, she again comes to the surface, gnawing new passages for air to access her eggs.
The cycle of development of scabies mites consists of four stages - eggs, protonymph, teleonymph and adult. Only the last form is sexually mature.
Unlike ear scabies, sarcoptosis and notothedrosis do not develop on the skin of the inner surface of the animal’s auricles and auditory canal. As well as otodectosis, at least in its first stages, it is impossible to meet anywhere in the body, except for the area of the ears.
This state of affairs is the main condition that allows even without a detailed laboratory diagnosis to distinguish between the ear and itchy (classic) scabies in dogs.
Why is scabies dangerous?
Scabies mites are aggressive external parasites that will not leave their host independently. The immune systems of the dog's body provide invaluable support in the fight against scabies, but sooner or later the disease still takes up.
For this reason, treatment should be started as soon as possible, until the animal is completely rid of parasites.
Severe itching is the main symptom of scabies in dogs, which manifests itself after the appearance of the first adult individuals from eggs laid by the female. As we recall, this period requires an average of about 15 days - it is this time that determines the time of the onset of the first symptoms after the initial infection.
We describe the main pathological conditions that affect the dog’s body most during the development of scabies.
Itching in itself is not dangerous, but it has a rather strong pathological effect on the behavior of the animal. The dog constantly itches, her appetite decreases, exhaustion occurs, which in turn is extremely detrimental to the general state of immunity.
As the parasite population grows, the number of toxic products of their vital activity increases, which enter the bloodstream directly, causing general toxic reactions.
Painful inflammations of the skin develop in scabies foci - dermatitis, which over time becomes covered with a dense, dry crust.
The presence of a crust complicates the access of air to the pathological focus, thereby provoking a more active reproduction of purulent-putrefactive microflora. As a result, on the skin of dogs in the subsequent stages of scabies, you can find the foul-smelling foci of purulent infection that affect the deeper layers of the skin.
As the disease progresses, the number of ticks on the animal increases, and additional pathological processes aggravate the condition so that generalization of the disease develops.
The animal loses much weight, hardly eats, there are serious metabolic disorders, an increase in the number of eosinophils, a decrease in red blood cells and hemoglobin.
This picture is reflected in a violation of the normal functioning of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, and in severe, advanced forms of the disease, scabies in dogs results in death.
Symptoms
The first symptoms of sarcoptosis and noterosis in dogs are different. Most of all it concerns the localization of scabies. Sarcoptosis develops mainly in the head, thoracic region, at the root of the tail, as well as on the abdominal part of the body, where there is less hair.
A distinctive symptom of sarcoptosis in males is the appearance of foci on the foreskin.
The main characteristic symptom of sarcoptosis and notothedrosis is, of course, itching.Almost with the first visible signs of the disease, the dog begins to itch actively, which attracts the attention of its owner.
It is worth noting that the symptoms of scabies in dogs, regardless of the type of pathogen, develop gradually and step by step, and the treatment will be almost the same at any stage.
Conditional stages of the development of the disease
The appearance of foci of redness on the skin. As a rule, at this stage, the owners rarely independently determine such a sign, since not all of us examine the skin of the dog under the hair, immediately after the dog scratched his face. Although this is one of the basic principles of early anticipation of scabies.
Small pustules form - red dots on the skin filled with liquid contents, the scabies depletes the coat. When combing, the dog damages the thin shell of the pustules, their contents moisturize the skin.
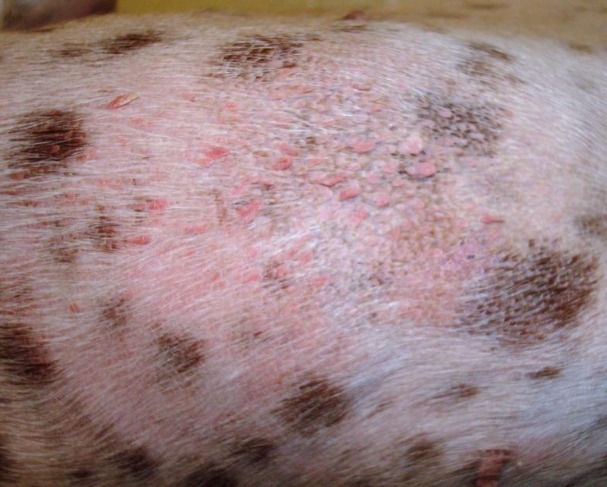
The skin in the pathological foci coarsens, the coat falls out more and more intensely. Torn epidermal particles are formed on large amounts of hair and skin in large quantities, and a phenomenon resembling large dandruff can be observed.
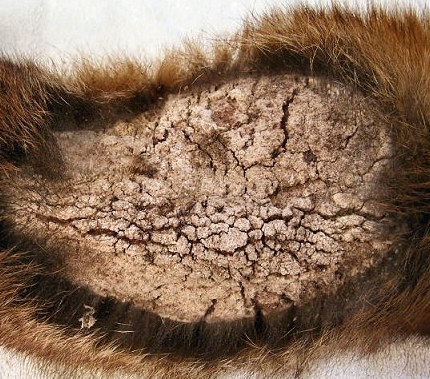
In process of more and more combing up to blood, hard crusts are added to dogs to the above mentioned symptoms of scabies, the skin is very rough, crackes to blood, loses elasticity, the effect of elephantiasis is observed. The remnants of the coat, where the coat was long and thick, fall off with the products of skin inflammation, forming a kind of felt.
Scabies foci begin to spread throughout the body of the animal. The dog is losing weight, losing appetite, constantly itching. In addition to the lesions, the coat becomes dull, the hair falls out in shreds all over the body. The death of an animal occurs mainly due to severe exhaustion.
Very often, the development of parallel current infectious diseases is observed. In the presence of helminthic infestations in the dog, mortality is one and a half times higher.
It is worth noting that these symptoms of scabies in dogs can also occur not specifically - some of the clinical signs may fall out of the picture. For this reason, only accurate laboratory diagnostics, as already noted, can confirm or refute sarcoptosis or notoedrosis.
How to distinguish scabies from other diseases
Dogs, however, like other carnivores, have a relatively small number of diseases that have symptoms similar to scabies. This situation greatly simplifies the process of differential diagnosis, including at home.
Dog scabies should be distinguished from the following diseases:
- Otodectosis of carnivores. As already mentioned, the causative agents of ear scabies parasitize mainly on the inner surface of the auricles and auditory canal. However, in dogs, at the last stage of this disease, transition of otodectheses to the muzzle is possible, but in any case, lesions in the ears will be present. With classic scabies, this is not.
- Demodecosis of dogs. Demodexes parasitize in the hair follicles, where there are no nerve receptors, so itching is rare in this disease. In addition, the coat falls first. More on demodicosis in dogs.
- Skin allergic eczema. Allergy in dogs is an extremely complicated pathological condition, the symptoms of which are most difficult to distinguish from scabies, at least outwardly, to an unprepared person.
But it is worth noting that allergic foci grow bald much faster, and spread through the body more slowly. In addition, in this case, no epidermal scabs form on the skin of the dog.
In order for the owner to be able to independently distinguish eczema from itchy scabies, it is first of all necessary to look for the cause of the development of allergies in the history of keeping the dog, or conduct a therapeutic diagnosis. In this case, the animal is treated against scabies and, if the effect is not observed, then it is worthwhile to find another reason for the appearance of pathological foci on the skin.
Despite the complexity of the symptoms and the active progression of scabies in dogs, the treatment, if it is correct, allows a quick cure. In many ways, this effect is observed due to the direct effect of drugs on the bodies of parasites and the almost complete absence of the pathological effect of drugs on the animal's body.
The most effective treatment regimens
In large kennels, bathing dogs in a solution of activated creolin, hexalin, hexatalp or colloidal sulfur is considered the best anti-scratch treatment. Massive bathing of animals can almost simultaneously get rid of the disease. However, at home, such treatment can become overly complex.
The following treatment can be used at home: the affected lesions on the dog’s body are thoroughly wiped with a 50-60% hyposulfite solution (sodium thiosulfate, antichlor), preventing the animal from licking the treated areas.
If there are difficulties with obtaining the above drugs, you can go an even simpler way by injecting the dog subcutaneously Ivomec (ivermectin) at a dosage of 250-300 mcg per kilogram of dog weight. The drug can be purchased at any veterinary pharmacy.
For injection, a conventional medical disposable syringe is used. If there is no experience in setting injections, you can learn more about the injection procedure from this article.
For antiparasitic treatment of scabies in dogs, both sarcoptosis and notothedrosis, with the help of injections, you can use any drugs based on ivermectin - baimek, ivomek, tsememek, newmek, ivermek, ecomectin and others, at the dosages indicated in the annotations for the corresponding medicine.
Sulfur ointment is some exception, but the number of treatments should be frequent, pathological foci need to be protected from licking the dog, and the smell of the ointment is quite unpleasant. For these reasons, the treatment of scabies with sulfuric ointment in dogs and other pets is less and less used.
For those of our readers who would still prefer a topical treatment of scabies with their pet, we recommend the following drug.
Amidel gel NEO - the easiest and most effective way to treat scabies in dogs
In veterinary practice, a domestic drug is widely used - Amidel gel NEO (API-SAN LLC, Moscow). This tool is quite effective against sarcoptosis and notothedrosis in dogs, which is recommended for use at home.
This approach is certainly convenient for owners who do not have the opportunity to visit a veterinary clinic during the course of treatment for their pet, and also have not overcome the fear of injecting.
Amidel gel is a combined preparation for external use, which includes the following components.
Tsiflutrin is a synthetic pyrethroid that has a detrimental contact effect on ticks. This tool is safe for the dog itself, because it does not have the ability to be absorbed into the blood, working only in the upper layers of the epidermis, where most parasites are concentrated.
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic that significantly reduces the itchy effect just a few minutes after the gel is applied, by directly acting on the animal's nerve receptors. Thus, the quality of itching in a dog is significantly reduced, which positively affects its behavior and resumes appetite.
Chloramphenicol is a remedy for a number of broad-spectrum antibiotics. The drug destroys bacteria that cause scabies complications that occur at the site of scratching, thereby excluding the development of purulent-putrefactive inflammation in the pathological focus.
Glycerin, dimethyl sulfoxide, polyethylene glycol-400 are auxiliary agents that soften hard crusts and upper layers of the skin, which improves the penetration of drugs into the deeper layers of the epidermis, thereby improving the therapeutic effect.
As a result, Amidel NEO gel is considered one of the best domestic external treatments for the initial stages of scabies in dogs. In especially advanced cases of the disease, we recommend using this tool in combination with ivermectin injections.
Amidel treatment is carried out until the symptoms of sarcoptosis and notothedrosis disappear. As a rule, from 2 to 5 treatments with an interval of a week are sufficient.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that the price of Amidel gel NEO is quite low and at the time of writing this article is from 170 to 190 rubles for a 10-gram syringe dispenser. This amount is quite enough for the full course of treatment of the dog. However, with a complex neglected course of the disease, it is recommended to stock up on a large amount of the drug.
Sarcoptosis, demodicosis and otodectosis in dogs: methods of treatment
Scabies is a contagious dog disease caused by Sarcoptesscabeivarcanis ticks. Transmission usually occurs through direct contact with affected animals, less often animals become infected by contact with the environment. Animals can also be carriers without clinical signs.
The tick cannot exist outside the host for a long time. Its life cycle is from 10 to 21 days. Clinically, scabies is manifested by severe itching.
In 90% of cases in dogs affected by scabies, an “ear-foot reflex” is observed - the dog makes an attempt to scratch when irritating the edge of the auricle, but it is also observed with allergic itching. To confirm the diagnosis, microscopy of superficial skin scrapings is performed, which give a positive result in 30-50% of dogs with scabies.
With a negative result of microscopy of scrapings, a trial treatment is performed. In Europe, specific antibodies are secreted in dogs with sarcoptosis for more than 6 weeks. With proper conduct, the specificity and sensitivity of this study is above 90%.
Scabies can be treated with various antiparasitic drugs. Selamectin is part of an external agent that is registered in many countries for the treatment of scabies.I appoint him three times, every 2 weeks.
Perhaps treatment with systemic drugs containing ivermectin or milbemycin oxime. For the treatment of sarcoptosis in dogs, I prescribe milbemycin oxime orally at a dose of 2 mg / kg 2 times a week for 3-4 weeks.
Ivermectin should not be given to dogs of collie breeds, since these breeds have serious side effects. In dogs of other breeds, side effects are also possible, such as ataxia, bradycardia, dilated pupils, respiratory arrest, increased salivation, loss of consciousness, trembling.
At the first application, dogs are prescribed 50-100 μg / kg of verimectin orally or subcutaneously once a day and the dose is gradually increased to 150-300 μg / kg, then I recommend to continue using the same dose once a week for three weeks.
Owners should carefully monitor the condition of the animal throughout the course. If side effects occur, discontinue use of ivermectin immediately.
Fourteen dogs with scabies were treated by a lawyer twice with an interval of a month, in laboratory conditions. Ticks were not found a month after the first treatment, alopecia decreased by 80%.
The test was based on the principle of no less efficacy, that is, its purpose was to show that the imidacloprid / moxidectin combination is no less effective than selamectin in this application. Similar results were obtained in another study.
In case of itching, at the beginning of treatment, glucocorticoids are prescribed at a dose of 1 mg / kg daily for 3-4 days. In most patients, remission occurs after 4 weeks, but in some cases it is necessary to continue treatment until 8 weeks. Animals in contact with the patient also need to be treated.
Demodecosis
Demodecosis occurs in dogs with pathological propagation of Demodexcanis ticks. Localized demodecosis is not a serious disease and usually goes away after 6-8 weeks, but this process can take several months.
A generalized form of demodicosis is a more serious threat to the animal. It is characterized by alopecia, scabs, follicular papules and pustules, mainly arising on the muzzle and limbs, and then spreading throughout the body.
Clinical signs such as acne, erythema, scaly and oily skin are also possible. Itching is usually not severe, but if a secondary bacterial infection occurs, it may intensify. In severe cases, fever and lymphadenopathy are possible.
The diagnosis is confirmed by microscopy of deep skin scrapings. Properly performed hair microscopy is also useful in confirming the diagnosis, especially in the case of skin lesions in the muzzle and feet. In rare cases, the diagnosis is made on the basis of a skin biopsy.
The most common tick killing agents contain amitraz or macrocyclic lactones. To prevent deterioration and the resumption of clinical signs of unsterilized females with a generalized form of demodicosis, ovariogysterectomy is recommended.
Systemic disorders such as neoplasia, hypothyroidism, or hyperadrenocorticism can cause generalized demodecosis and poor response to treatment. Some dogs can recover without the use of parasicides if the primary disease is eliminated.
Amitraz is a foramide acaricide. Before using it, it is necessary to remove scabs (it is preferable to use a shampoo with an antibacterial effect). The dog should dry completely before treatment with amitraz.
Processing is carried out in a well-ventilated area, wearing rubber gloves. People with asthma are encouraged to ask someone else to do the treatment. The dog should stand in a container with amitrase solution during processing.
Amitraz may have a temporary sedative effect for 12-24 hours. With severe ulceration of the skin, it is necessary to first improve its condition with antibacterial shampoos and antibiotics.
The concentration of the solution and the frequency of treatment affect the effectiveness of the treatment. I prescribe a 0.06% solution once a week. Dogs should not be bathed or wetted during treatment. The effectiveness of treatment with amitraz, according to the results of various studies, is 70-100%.
Some studies show the effectiveness of ivermectin orally at a dose of 0.3 mg / kg per day. Possible side effects and the method of increasing the dose are indicated above (see Scabies).
Milbemycin oxime can be used to treat demodecosis orally once a day at a dose of 2 mg / kg. Its advantages in relation to amitrase are a more convenient dosage regimen and less chance of side effects.
However, for large dogs, treatment can be very expensive. Efficiency is comparable to amitraz. Milbemycin continues to be used for 4 weeks after the second negative microscopy result of deep skin scraping.
In three studies, moxidectin solution at a dose of 0.2-0.4 mg / kg orally once a day was used to treat generalized demodecosis. In total, 52 dogs participated in three studies, 41 of them were puppies.
Moxidectin 2.5% together with imidacloprid 10% is part of the remedy Lawyer in the form of a spot-on, registered against many ecto- and endoparasites.
In laboratory studies on 18 dogs with a generalized form of demodicosis, Advocate led to an impressive improvement in the condition of dogs and a decrease in the tick population by more than 95% after 5 monthly treatments.
Another study in Europe involved 72 dogs, divided into 2 random groups, which were used Lawyer (moxidectin 2.5% / imidacloprid 10%) or milbemycin oxime (as a control).
Usually, dogs with a generalized form of demodicosis should be examined every 2-4 weeks by microscopy of skin scrapings to assess the effectiveness of treatment. Scraping should be done at the same points. In the absence of improvements, it is necessary to change the treatment.
Almost always, demodicosis is accompanied by secondary pyoderma, caused mainly by Staphylococcusintermedius.Of the gram-negative bacteria, the most common are Proteusmirabilis and Pseudomonasaeruginosa.
Therefore, it will be appropriate to prescribe antimicrobials for 3-8 weeks. In addition to systemic antibiotics, antibacterial shampoos are often used to remove scabs and surface effects on bacteria.
Ear mites
Ear mites (Otodectescynotis) - freely moving ticks that develop from the egg stage to an adult in 3 weeks, passing the larval stage and 2 nymph stages. After laying the egg is fixed on the surface.
After 4 days of the incubation period, a larva hatches from the egg, which actively eats for 3-10 days, rests for one day and turns into a protonympha, and after molting it passes to the deutrophy stage. An adult male impregnates a female deutrophy, and she, in turn, lays eggs.
Ticks can live in the environment for 8-12 weeks. Infection occurs in a direct or indirect way. Ticks and eggs can attach to fleas that can transfer them to another animal.
Ticks feed on epithelial debris and tissue fluids on the skin surface. They cause severe irritation and the formation of large red-brown scabs in the ears.
Ticks are also found on other parts of the body, especially on the neck, in the sacral region and on the tail. Parasites are easily transferred from one individual to another and are especially common in puppies.
For the treatment of otodectosis, external agents are applied that are applied to the skin or directly to the ears, as well as systemic drugs.
Ivermectin, permethrin, selamectin and fipronil were found to be effective according to the results of various studies. The effectiveness of the drug Advokat (imidacloprid 10% / moxidectin 2.5%) against ear mites in dogs is more than 98%. In most cases, one treatment is enough.
Symptoms and treatment of scabies in dogs (risk of human infection!)
Scabies in dogs is transmitted by contact from infected individuals. The disease caused by several types of ticks gives a lot of trouble to animals and their owners.
Depending on the parasitic tick found on the body of the pet, scabies is divided into the following types. The type of scabies depends on the tick detected.
Sarcoptosis
The disease is non-seasonal and very contagious. It is caused by Sarcoptes canis - a tick that penetrates deep into the skin, making moves and laying eggs. Read more about it in this material.
The favorite habitat of the tick of this species is the place covered with short hairs. Most often, a tick is found on the head (nose, eyebrows, ears) and limbs (in the places of joint bends).
Sarcoptosis often occurs on the nose of a dog.
Symptoms. With sarcoptosis, the dog constantly itches. The main signs that are difficult not to notice:
- Animal Concern. The dog cannot find a place for itself, constantly fussing, spinning, itching;
- Severe itching and constant scratching of problem areas;
- Scrubs with bloody discharge, crusts around the wound;
- Profuse dandruff in the affected area;
- When the owner tries to touch the auricles, a twitching of the hind limbs is noticeable. The scratching reflex occurs precisely when Sarcoptes canis is infected.
To identify the causative agent of the disease, you will have to visit a veterinarian. He will take a deep scraping and only after that he will make an accurate diagnosis.
Ear scabies - otodectosis and its symptoms
The tick populates the dog’s ear and causes itching. Ear scabies is most often diagnosed in canine breeds with hanging ears. Saggy ears are an excellent habitat for Otodectes cynotis ticks.
Infection occurs by contact with an infected pet, then the tick is populated in the auricle or ear canal of the dog. The movement of ticks, their livelihoods and constant bites cause itching in the dog.
Symptoms. With ear scabies, the dog often tilts its head toward the affected ear. Shakes his head and rubs against any objects not only at home, but also on the street. Due to constant friction and scratching, bleeding wounds arise, which often suppurate and cause pain to the animal.
As the mite's waste products accumulate in the auricle, a dark mass similar to pieces of earth can be seen there. Adhesive with an unpleasant odor.
Features. The disease leads to deafness of the animal, since the tick affects not only the external auditory canal, but also reaches the middle and inner ear, reaching the meninges.
Therefore, at the first signs of an ear tick, it is necessary to proceed to treating the dog. To make the correct diagnosis, the veterinarian will definitely prescribe a laboratory analysis of the biomaterial.
Heyletiosis
Heyletiosis often occurs on the back of the dog. Pityripe stray scabies is one of the most infectious scabies in dogs. Very rarely observed in humans, so do not be afraid of infection from a pet.
The itchy tick Cheyletiella yasguri lives on the surface of the skin, its main food is dead epidermal cells and tissue fluid. Favorite places of parasitism are the back along the ridge, neck, ears.
Symptoms. In order to recognize the disease in time, it is necessary to know its main symptoms:
- Partial hair loss. Wool falls out in shreds, hanging ugly in places;
- The appearance of areas with large dandruff. If you look closer at this dandruff, you can see its movement - this is the movement of ticks over the body of the dog.
- combing the affected areas due to itching;
- inflammation and suppuration at the lesion sites, the appearance of scab crusts.
Knothedrosis
Noothedrosis spreads rapidly and is considered contagious. When Notoedres cati is infected, the dog is diagnosed with nothedrosis.
Symptoms of infection:
- vesicles or nodules on the skin (most often on the head, eyebrows, nose, ears);
- the progression of the disease is accompanied by hair loss in the affected areas and the appearance of folds on the skin.
Demodecosis
Demodecosis is diagnosed against the background of a decrease in immunity in a dog. The Demodex canis tick is present on the skin of healthy animals; its abnormal reproduction is caused either by a hereditary predisposition or a weakened immune system against the background of any serious diseases.
Puppies older than six months are subject to multiple lesions (generalized), with more than 5 spots.
Signs and Symptoms. With demodicosis, dandruff is observed in the dog. The signs of demodicosis include:
- redness of the affected skin;
- scaly, dandruff;
- focal baldness;
- itching can be subtle with a localized form of the disease, or severe with progression;
- the appearance of bleeding ulcers and hard crusts around the lesion sites.
It is impossible to identify the type of tick without laboratory tests, which means that for proper treatment it will be necessary to undergo a diagnosis by a veterinarian.
Treatment
For the treatment of scabies mites, not only external agents are needed. It will also require internal treatment. Therapy will depend on the degree of damage, the type of parasitic tick and the condition of the dog.
When processing a pet, disposable hygiene gloves should be used; after all procedures, hands are thoroughly washed with soap.
It is necessary to act in several directions at once: to strengthen the dog’s immunity, to engage in the treatment of skin integuments and to normalize hormonal levels.
For subcutaneous administration, the drug Ivomek is recommended, which helps to eliminate ticks. The active active substance that kills ticks is Ivermectin.
Massive use of the drug has led to a marked decrease in its effectiveness, and immunity has developed in parasites. Intravenously, 1% trepan blue solution can be used. Ointments, drops, sprays, shampoos are prescribed externally.
Against ticks of this type, Bravecto tablets can be used. In inflammatory processes caused by a bacterial infection, a course of antibiotic treatment is carried out.
To improve the condition of the skin at the stage of recovery, oil mixtures are used. You can use sea buckthorn oil, which well restores the skin.
Dog scabies treatment
To treat otodectosis, there are a lot of ear drops.
Drops of Bars need to be used once a week. You can buy drops of Bars, the active substance of which is diazinon. To kill ticks, it is necessary to instill a solution of 3-6 drops in each ear (depending on the weight of the animal). The instillation procedure is repeated after a week.
Drops on the stronghold withers in the composition have an active substance - selamectin of various concentrations (6 and 12%). In the treatment of ear mites, the drug is applied to the area between the shoulder blades once, after a month the treatment is repeated. Can not be used to handle puppies for up to one and a half months.
Preventative measures
In the room where the sick animal is located, it is necessary to regularly carry out wet cleaning with disinfectants. It is recommended to change the litter daily, wash it with bleach or bleach, iron it or dry it in the sun.
The child’s access to the sick dog should be limited.
Walking the dog around the apartment should be limited to one room, then it will be easier to carry out disinfection. If there are children and other animals in the house, their communication with a sick dog is temporarily stopped. But the animal should not feel abandoned. Adult family members should play with him, take them out for walks, and not just treat and feed them.
Ticks that fell from a dog to a person are not able to exist for a long time. Human scabies can only be infected by monkeys.
It is in them that the same type of scabies mites parasitizes as in humans.But precautions when communicating and handling sick dogs should still be followed.
Scabies in dogs is one of the most acute diseases
Small dogs Sarcoptes canis cause itchy scabies in dogs, which veterinarians call "sarcoptosis." These parasites have a body length of 0.2-0.4 mm, they live and multiply in the thickness of the skin. Female scabies itching lays 40-60 eggs for her life.
Infection of a dog with sarcoptosis occurs after contact with a sick animal or through care items and litter. This disease poses the greatest danger to young dogs with thin skin. Animals are especially difficult to tolerate itchy scabies in the cold season.
Scabies in dogs are transmitted to humans. The risk of infection is high enough
After detecting sarcoptosis in a dog, it should be protected not only from other animals, but also from people. The skin of an infected person begins to itch, blisters and bloody crusts appear on it.
The disease, as a rule, disappears on its own after communication with a sick animal ceases.
Symptoms and signs
After itching gets on the skin of the pet, the first symptoms of the disease begin to appear after 1-2 weeks. The disease has the following symptoms:
- At the first stage of the disease, redness is observed in the affected tick area of the skin. Most often, the head and neck of the dog are primarily affected;
- Further, point rashes of small bubbles filled with liquid are noticeable. During combing, the bubbles burst. Such areas of the skin are very flaky and seem to be sprinkled with bran;
- In the last stage of itchy scabies, in the absence of treatment, the dog's body becomes exhausted.
The main signs of scabies in dogs, which the owner can notice with the naked eye, are:
- Itching, worse at night, which constantly bothers the animal;
- The coat fades, looks disheveled, falls out in shreds;
- Peeling and peeling are observed on bald areas of the skin.
How is the treatment
Only a veterinarian in a clinic can diagnose and prescribe sarcoptosis treatment for your pet. When making a diagnosis, the specialist takes into account the clinical symptoms of scabies in a dog and the results of a study of deep skin scrapings under a microscope.
After the itchy scabies in dogs has been established, the animal is prescribed medication for the underlying disease and related symptoms, feeding is adjusted.
Scabies in dogs: how to quickly rid a pet of a scabies tick and prevent complications
A dog gets infected with a tick by contact with a sick animal or bypass - through the ground, grass, human clothing on which the parasite can live for two weeks. Even a pet dog can become infected with scabies if the owner brings a tick to the house on shoes or clothes.
The causative agent of scabies is the scabies mite, which the dog can catch in direct contact with a sick animal.
The causative agent of scabies is a tick of the genus Sarcoptes canis - a microscopic parasite, 0.5 mm in size, which is almost impossible to discern with the naked eye. Once on the dog’s coat, the tick penetrates the epidermis and begins to feed on tissue fluids.
Single specimens that have fallen on the coat and have invaded the skin of the dog begin to make moves and spread throughout the body. In passages reaching 3 mm per day, parasites lay eggs, new specimens hatch from them. The female’s life cycle lasts 15 days, during which time she is able to produce up to 50 eggs.
The peak of infection of animals with scabies mites occurs in autumn and winter, less often it can be infected in summer. Dogs have neither a pedigree nor an age-related predisposition to infection, so any dog can suffer from scabies.
Sarcoptosis (or scabies) is dangerous for inflammation of the skin and the depletion of the dog’s body that develops against them. The skin reacts to tick products by the formation of infiltrates and hyperkeratosis.
It is the infection introduced into the inflamed skin that poses a danger to the dog. If the parasite is not destroyed in time and treatment of the skin is not started, the dog will die.
Symptoms and hallmarks of scabies
Compliance with the rules of caring for the dog and keeping it clean is not a protection against infection with scabies, so you should carefully monitor the changes that occur on the skin of the pet and start treatment on time.
The disease begins with redness of the skin on the head, face, neck, the dog is actively itching. After some time, small nodules appear at the site of redness, gradually turning into bubbles filled with liquid.
The liquid flowing out from the bubbles sticks to the hair, and crusts grow on the skin. When combing, the skin is injured, non-healing wounds appear on it. Scabies are characterized by increased itching while warm, especially near a battery or heater.
The next stage of the disease is the onset of dog baldness. The worst hair loss is observed on the head. In places without hair, dense crusts form. The dog emits an unpleasant odor with sour tones.
The dog becomes lethargic, her appetite disappears. If the disease is not treated, an increase in lymph nodes begins, general intoxication of the body. The dog begins to rapidly lose weight, refuses food.
The skin is completely covered with scabs, the hair resembles a felted felt, gradually the dog balds completely. This condition of the animal leads to imminent death.
Is it possible to protect a dog from scabies mite
Prevention of infection of a dog with scabies consists in a regular examination of the animal to identify the first signs. It is impossible to completely protect the dog from getting a parasite on its coat.
Reasonably possible measures must be taken:
- Do not walk your pet in the habitats of stray animals.
- Change of place of walks if an animal with scabies is noticed on the site.
- Regularly treat the dog's skin with antiparasitic drugs. Well-proven protective product BlochNet, which is dripped on the withers of the dog with the frequency recommended by the instruction. The same tool can be used to treat the litter of a pet.
- Periodically carry out antiparasitic treatment of places of keeping a pet: aviary, booths, stove benches.
With strict observance of the recommendations of specialists, scabies in a dog can be cured quickly and completely. After treatment, the dog needs an enhanced diet and a course of fortification to maintain immunity.
leave a comment