
Hello! Usually I’m not afraid of the sight of blood, but last week I was a little scared. I sat in an armchair, watched TV, and then my cat came up to me and jumped to her knees.
And all her ears are in the blood. It was then that I realized that she herself had scratched them.
And not because she has such entertainment, but because of ear mites. I had to deal with the treatment and elimination of these parasites. Want to know how cats otodectosis is treated? How to carry out prophylaxis? In the article below I will write all the information in detail.
The content of the article:
Otodectosis in cats
“The cat shakes its head, combes the ears to the blood, screams and runs away when trying to clean them?” - such complaints are heard by the veterinarian from the owner of the cat, if the latter has ears such as otodectosis.
Etiology
Otodectosis is an ear scabies caused by the sarcoptoid tick Otodectos cynotis. This is one of the most common diseases of cats.
As a rule, both ears are affected. Otodectosis is easily transmitted from one animal to another, especially if they, animals, are not regularly treated with special drugs from ticks. Under favorable conditions in the external auditory canals, ticks can produce numerous offspring and, thus, cause severe damage.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptom of this disease is severe itching. The cat shakes its head strongly, scratches its ears with its paws to the blood, or rubs its ears and head on furniture. The auricles turn red, traces of combs appear on them, sometimes an inflammatory process occurs.
In the external auditory canals, an abundant dry dark secret is found, resembling dry ground coffee in appearance, it is the product of the mites' vital activity, as well as their habitat. Cleaning the ears causes severe pain in the cat, often with blood secret and pus in the ears.
Establishing diagnosis
The diagnosis of this disease is made on the basis of laboratory tests. Veterinarian takes a secret from the ears, examines it under a microscope. If ticks and their eggs are found in secret, the doctor makes a diagnosis - otodectosis.
You need to take a dark or black sheet of paper, place a small amount of dry secret on it and hold it over a lamp or other heat source. Ticks, with a large number of them, will begin to spread to the sides along the sheet and will be clearly visible to the naked eye in the form of white moving beads.
Treatment of otodectosis
If an ear tick is detected in a cat, treatment should be started as soon as possible, since this condition causes great discomfort to the animal and can cause a number of complications.
With a prolonged course of otodectosis, microbiological otitis media, inflammation of the tympanic membrane, perforation of the tympanic membrane, inflammation of the middle and inner ear can develop, in the future, the inflammatory process can also go to the meninges.
Before the introduction of the drug, you need to carefully clean all the secret from the ear canal, it is better to use special lotions (Otoklin, Ear cleaner (Globalvet), EAR-CLEAN (Beafar), Otifri, Bars, Rosinka, Cliny, Fitolar).
In any case, the ear tick in cats should be treated under the supervision of a veterinarian. Strictly follow all the recommendations and after the course of treatment, show the cat to the doctor for a control study of the contents of the auricle.
Ear tick prevention
In order for your cat not to get “ear scabies”, it is necessary to regularly treat your pet’s ears from ticks. It is better to use special drops for the withers.
The drug will help you choose a veterinarian, according to the breed and age of your cat.
Treatments should be carried out 1 time in 3 months, even if your pet does not walk and does not come in contact with other animals, since you, the owner, can bring the causative agents of otodectosis on your clothes.
The medicine for otodectosis in cats
The causative agent of otodectosis in cats is the otodectos cynotis tick, which has microscopic dimensions. The owner of the animal can see with the naked eye not the ticks themselves, but the products of their vital functions. When cleaning the ear of an animal infected with otodectosis, you will see dark brown crusts and liquid, and you will also smell.
If untreated, the sick animal develops otitis media. In advanced cases, the tympanic membrane ruptures, the infection penetrates deeper and can involve the lining of the brain in the inflammatory process, which will lead to the death of the animal.
Kittens and young cats are especially susceptible to odeodectosis, but adult animals also get sick.
Reasons for appearance and distribution
A pet can become infected with otodectosis from a sick animal through contact with it or through care items (comb, bowl, bedding). Not only cats, but also dogs, ferrets, raccoons, arctic foxes and many other predators are affected by odeodectosis.
In addition, insects can become carriers of otodectosis. For example, a flea, jumping from a sick animal to a healthy one, will transfer an ear tick to it.
Symptoms of otodectosis
At the initial stage of development of otodectosis, the cat experiences severe itching.An dirty brown discharge with an unpleasant odor accumulates inside the ear. The cat furiously scratches his ears. Due to the constant calculations in the area of the ears, long-haired animals appear warlocks.
Signs that the owner should pay attention to:
- Redness, peeling and scratching inside the ear;
- Restless pet behavior;
- Dark brown scabs and discharge from the ear;
- Bad smell from the ear;
- "Crooked head" (the cat tilts its head to one side).
The consequences of a dangerous disease
Treatment of otodectosis should begin immediately, as soon as the first symptoms of the disease appeared. Since ear parasitic mites can cause complications that pose a threat to the life of the pet. Please note that cat otodectosis in the absence of treatment can lead to serious consequences:
- Inflammation of the middle and inner ear;
- Hematomas in the auricle;
- Inflammation or perforation of the eardrum;
- Partial or total hearing loss;
- Inflammation of the meninges.
How is the clinic diagnosed?
The diagnosis of otodectosis in a cat is complex: based on a clinical examination of the animal and laboratory tests. The veterinarian takes a skin scraping from the auricle and conducts a microscopic examination. If mites are found in the samples, the diagnosis is confirmed.
Cat treatment at home
Otodectosis must be treated under the supervision of a veterinarian after an accurate diagnosis. Before injecting drugs into the ear, it is thoroughly cleaned of ear discharge and parasitic waste products. To do this, use special ear lotions and cotton buds.
The effectiveness of treatment is checked by a laboratory method. To do this, examine the scraping from the auricle. Simultaneously with the main therapy, it is recommended that the entire animal be treated with an anti-mite drug.
With the development of a secondary infection in the ear, in addition to treatment, the veterinarian prescribes antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drugs. Also do not forget about strengthening the immunity of the cat. The diet of the pet should include vitamin and mineral nutrition.
For the treatment of otodectosis in animals, veterinary specialists use the BlochNet max.
For the treatment of BlochNet otodectosis, 4-6 drops are instilled into each ear. For an even distribution of the drug, the auricle is massaged. Processing is carried out two to three times with an interval of 5-7 days. Drops from otodectosis for cats must be injected into both auricles, even in cases where only one ear is affected by an ear mite.
The use of BlochNet max drops in the treatment of otodectosis in a cat guarantees high effectiveness in treatment due to the fact that its composition includes highly effective active ingredients. FleaNet max will cure your cat of ear scabies and help protect it from reinfestation.
Preventative measures
To prevent the disease, observe the following rules:
- Protect your pet from contact with sick animals;
- Regularly inspect the ears of the cat and carry out their hygienic treatment with special lotions;
- Regularly treat your pet with insecticaricidal preparations, for example, drops on the withers of Bloch Net max. The procedure should be carried out once every two months;
- Enhance your cat’s immunity with balanced feeding and vitamins.
Ear mites in cats (otodectosis): causes, symptoms and treatment
The appearance in a cat of such a parasite as an ear tick is the beginning of a serious disease - otodectosis, which must be eradicated at the very first symptoms.The causes of its occurrence are completely different, but if you follow the basic rules of prevention, parasite infection is easily prevented.
If the cat is already sick - it can be treated with the help of simple manipulations, even at home. A.
Reasons for the appearance
In terms of biology, the tick in the ear is a small arthropod. His favorite habitat is a warm and moist surface, protected from the effects of the external environment.
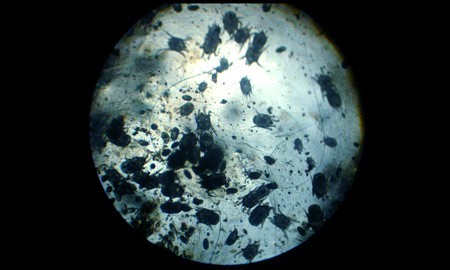
There are two types of ticks: the first live inside the shell of the ear and cause otodectosis, the second on its outer side and cause a disease called nodtohedrosis. If in the first case the tick may not make itself felt for a long time, then the second case will greatly affect the cat’s health.
The most common cause of ear tick in cats is contact with infected animals. Cats that have free access to the street are constantly suffering from this. Persons living only at home are more protected from this parasite, since they do not come into contact with wild animals and street residents.

But they can also become the habitat of the pest: the reason is contact with hygiene objects that perform the function of the carrier of this parasite.
The carrier of this parasite can also be people who bring it to the house on shoes or outerwear. Contacting street animals, they cannot become infected, but from the moment they are touched they act as a tick spread.
Symptoms of otodectosis
Among cat ear infections, the most common is ear mites. This parasite brings the pet pain, discomfort, and interferes with maintaining a normal way of life.
Symptoms of infection with otodectosis appear immediately and are the same in all cats. These include:
- restless behavior;
- itching
- the cat often shakes its head and scratches its ears;
- the auricle smells unpleasant;
- ear wax is plentifully allocated;
- the cat scratches the ears and the skin around them;
- sulfur takes the form of dense black discharge;
- in case of further spread of the tick, the cat will begin to scratch the whole body profusely.
Constant itching causes the cat to itch regularly. This can lead to baldness in some parts of the skin. Bald areas will be red and scratched, which will deepen the level of infection. Half of the cases of auricle diseases in cats are the result of ticks getting inside.
To get rid of the tick, you must necessarily consult a veterinarian. It will help the cat to get rid of such an infection quickly and painlessly.
Home treatment
Treatment for ear mites in cats can be carried out at home. It occurs in several stages.

First of all, you need to clean your ears from unpleasant black sulfur clots.
To accomplish this task, you must try hard: the cat will begin to resist, because this process will bring her pain. Therefore, it is necessary to swaddle the animal, for the least resistance, and use a pipette to drip the ears of the cat with a special lotion or hydrogen peroxide in a warm form.
Next, antiseptic drops should be placed in the ears of the cat.These funds include Amitrazin, Tactik, Amit, Akromektin, Amitraz, Otodepin. These medicines must be used for twenty days to completely get rid of the pest.
In order to properly instill the auricles, the cat must be swaddled again so that it does not prevent the owner from performing this manipulation.
Between instillations, the cat's condition can be alleviated with otonazole. This is an effective tool, drops for the ears, with the help of which it will be possible to muffle the itching and the inflammatory process.
In addition to antiseptic drops, you can buy an antifungal ointment in a veterinary pharmacy, which can be used as an additional treatment.
If the parasite has been in the animal’s ear for a long time, the appearance of the fungus is inevitable. Therefore, we must follow the process of its disappearance.
Prevention of infection
In order for the cat not to fall into the trap of the ear tick again, one should look after the state of his health and, in order to prevent it, fulfill certain mandatory conditions.
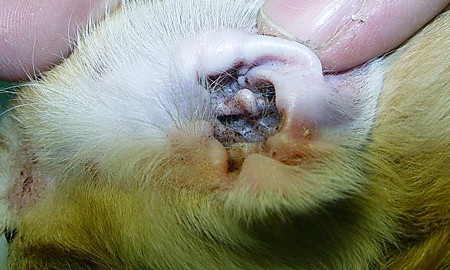
After any water procedures, it is necessary not only to wipe the cat's hair, but also to dry its ears from the inside. This will prevent the formation of a moist environment inside the ears and will make it possible to keep the ears clean.
The cat needs to clean the ear holes daily. It is contraindicated to do this with cotton buds, so as not to clog the sulfur mass even deeper. But cleansing with lotion should be an indispensable part of caring for your pet. During this manipulation, it is necessary to monitor the presence of abnormal sulfur secretions.
Twice a week, you should organize wet cleaning in the house using antiseptic agents. With its help, it will turn out to exterminate those parasites that have entered the house on the sole of shoes or outerwear.
You should have a good habit: make an appointment with a veterinary clinic once a month. During a structural examination, the doctor will pay attention to all the details in the cat’s state of health, which will prevent any diseases and maintain his health.
If, nevertheless, the pet could not be saved, then in the presence of the first symptoms of infection with ear parasites, you should immediately contact a veterinarian. If for some reason this cannot be done, then you can use the service of calling the veterinarian to your home.
How to treat an ear tick in a cat - carnivore otodectosis
Otodectosis, ear tick, ear scabies are the names of the same parasitic disease caused by microscopic sarcoptoid ticks of the genus Otodectes.
Otodectes cynotis is an ear tick that parasitizes not only in cats. The same type of otodectosis is found in dogs, fur animals, foxes and other carnivores, so a sick cat in the house can infect a dog and vice versa. As parasitizing, the tick needs blood and lymph to nourish, which it extracts by gnawing and piercing the upper layers of the skin with the parasitic focus.
These numerous injuries, richly flavored with tick products, cause severe irritation of nearby nerve receptors, stimulating severe itching, which determines the main symptoms of ear mites in cats.
As the disease progresses, which becomes chronic, putrefactive microflora accumulate in pathological foci, which further exacerbates the clinical picture of otodectosis.
However, it is worth emphasizing once again that such a phenomenon is observed in rare cases when the ear tick in cats is not subjected to any treatment.
Features of the disease
Among the total number of cats entering the veterinary clinic with a diagnosis of otitis media, 85% of them are additionally diagnosed with otodectosis, which, in fact, served as the primary cause of inflammation of the outer or middle ear in its overwhelming majority. If we talk about age, the ear tick in cats is found mainly in kittens 1-4 months of age.
Ear scabies is most common in the early spring and late fall seasons. However, in domestic cats it can be found almost year-round. In the external environment, Otodectes cynotis is not able to survive for a long time. At temperatures below minus 5 degrees, the parasite dies within a few hours.
A temperature of 0 to 5 degrees will provide a maximum two-week mite survival, and a range of 10 to 20 degrees - about 3 weeks. Such conditions ensure the transmission of the parasite from a sick animal to a healthy one through indirect means through household items, hands and clothing of the owners.
In the overwhelming majority of cases, re-infection occurs directly through direct contact of animals. Unilateral damage can be observed in rare cases, only at the first stage of the disease. In the future, the pathological process always extends to both ears.
There is ear scabies in cats everywhere throughout our country.
Brief biology
An ear mite parasitizing in cats is able to breed exclusively in the auricles and auditory canal of its owners. Like most sarcoptoid ticks, Otodectes cynotis sequentially goes through four phases of its development - an egg, a larva, a protonymph, a teleonymph and an adult, which is commonly called the imago.
This feature causes a more severe course of otodectosis in cats in the autumn-winter period of the year. The situation is further complicated by a seasonal decrease in general immunity in the animal during this period.
An interesting fact from the biology of the development of the ear tick. The penultimate stage of the life cycle, the teleonymph, has no signs of sexual demorphism. From it in the future, with the same probability, a female or male may appear.
However, adult males, ready at this moment for fertilization, are already tightly attached to the teleonymith with the help of its special devices, which are called - copulative tubercles.
In this state, the couple expects the transformation of the teleonymph into an imago. If a female happened, the male fertilizes it and falls off, and if the individual is male, the seed is not thrown, and the male disconnects in search of a new teleonymph.
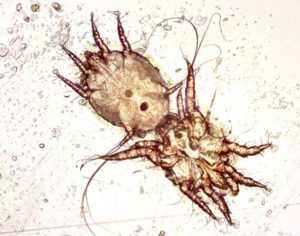
Symptoms of an ear tick
As noted above, the main symptom of otodectosis in cats is severe itching in the ears, which is manifested by the corresponding signs that any attentive owner of the animal can determine:
- The cat often shakes its head and ears.
- Rubs with auricles on any surface.
- Often trying to scratch ears with paws.
In some animals, a characteristic symptom may appear, which in veterinary medicine has been called "crooked head". The cat bends and holds its head in this state for a long time. Such a sign will tell about the severe course of the disease.
The ear tick in cats is a long-term chronic disease, with the corresponding symptoms and requiring urgent treatment, since it will never go away on its own. Given this fact, the clinical course of otodectosis is divided into three main stages.
I stage. The first 14 days of illness. The general condition of the animal, as a rule, does not attract attention, and only experienced and very attentive owners will notice that the cat somehow shakes its head very intensely and often, as if trying to shake something off its ears.
If at this moment you look at the inside of the auricle, you can see localized foci of severe redness. The first ticks have already penetrated the skin, fertilization has occurred and soon the first offspring will begin to hatch en masse. Live mites are usually not detected under a microscope.
At this moment, the animal begins to scratch more actively on the surface, loses its appetite, its coat loses its luster, shedding may increase. In scrapings under a microscope, from 1 to 3 live ticks can be found.
III stage. It occurs from 21 to 42 days of illness. The cat does not find rest, trying to constantly itch and rub his head. The animal gives its head to be touched with great caution and at the first touch it begins to actively scratch its paw.
Inflammation on the inner surface of the auricles is always well defined and plentifully covered with a brown viscous mass with alternating dry crusts. This condition can last up to three months and lead to quite serious complications. In the field of the microscope, you can see up to 10 live parasites.
The complications are the seeding of scratches and tick-borne canals of streptococcal and staphylococcal microflora, which becomes the cause of the development of purulent-putrefactive infection with the subsequent spread of the pathological process to the middle and inner ear, then to the membranes of the brain.
Similar complications of an ear tick in cats are extremely rare, as a rule, exhausted by hunger and insufficient maintenance of sick animals.
Most often, otodectosis becomes a permanent chronic form, exhausting the animal, which is increasingly losing weight, and in the end - dies from general impotence.
But in the family of canine otodectoses, it is able to go into the fourth - more severe and last form. After 2-3 months of illness, fetid pus begins to flow from the ears, deeper in the ear canal you can see a cork from a dense black-brown mass.
At the end of the pathological process, the dog dies from the penetration of purulent-putrefactive process into the membranes of the brain. Shortly before the death of the animal, he has pronounced convulsions and convulsions.
How to clarify the diagnosis?
The diagnosis of ear mite in cats is one of the simplest and is determined by the definition of symptoms and the results of laboratory tests.
Of great importance is the clarification of epizootological information regarding otodectosis - the owner always checks whether the animal has previously had ear scabies, whether this disease has occurred in other animals in the household or neighbors.
Other clinically similar scabies and fungal diseases, for example, notodedrosis, sarcoptosis or trichophytosis develop mainly in other parts of the animal’s body.
Ear scabies mites are classified as microscopic - the body size of adults is not more than 0.5 mm, so it is extremely difficult to make out with their naked eyes.
If it is not possible to go to a veterinary clinic for an accurate diagnosis, you can try to conduct a preliminary diagnosis of the ear tick in cats at home.
If possible, a few drops of 10% sodium hydroxide solution are applied to the scraping to dissolve most of the ballast mass, then the material is kept at room temperature for about 45 minutes. If caustic alkali is not possible to purchase and use, you can immediately start self-diagnosis.
To increase the likelihood of detecting parasites, 2-3 drops of black mascara can be placed on the scraping, which will color everything except the ticks themselves, which can be better seen on a black background due to the contrast. The presence of several light grains on a cotton swab may indicate the presence of parasites.
It is worth noting that such a diagnosis at home is relevant only for the second and third stages of otodectosis in cats. Moreover, the absence of ticks on the scraping does not exclude ear scabies in the presence of the rest of the symptoms.
Only professional receipt and examination of scrapings in a veterinary clinic can guarantee the diagnosis or diagnosis of otodectosis.
For this reason, whether white grains were found or not, acaricidal treatment is still recommended.
Medicine
Treatment of an ear tick in cats can be external when liniments, ointments and drops are used, applying them directly to the lesion and, in the form of subcutaneous injections of acaricidal preparations. The second option will become more effective, because ticks absorb their toxin as they feed on blood and lymph.
In professional veterinary medicine, both approaches are often used simultaneously for the treatment of otodectosis in cats of the second and third stages, which provides a much better effect.
When working with cats, you need to remember that this type of animal is hypersensitive to organophosphorus acarides, therefore, agents containing diazinon, chlorpyrifos, fosalon, karbofos and similar compounds are not used in this species.
The classic and time-tested therapeutic effect of such classic drugs in the treatment of ear ticks in cats, as:
- 0.05% aversectin ointment. The tool abundantly processes the entire inner surface of the auricle and the external auditory meatus twice with an interval of a week.
- Tanacetic or polysulfide liniment. Twice, the interval is 7 days.
- 3% creolin, externally, according to a scheme similar to the above drugs.
- Stomazan, butox, ectomine, baytikol. Outwardly, twice with an interval of 10 days.
- Ivomek, aversect-2 or cidectin, subcutaneously, twice with an interval of two weeks. Dosage at the rate of 0.1 ml of the finished solution for every 5 kg of patient’s live weight.
In addition, you can use a self-made ointment, if possible, stock up on ingredients. In 20 g of unsalted pork lard, add 8 g of potassium carbonate and 15 g of colloidal sulfur, mix thoroughly and apply externally with a frequency of once every 2-3 days until the symptoms disappear completely.
Recently, the domestic combined external agent Amidel gel NEO has been in high demand for the harm of veterinarians.
The composition of this drug, in addition to the modern acaricidal (tick-killing) means of cyfluthrin, includes the antibiotic chloramphenicol, which is quite effective against a secondary bacterial infection, often developing with otodectosis. Amidel also contains lidocaine, which almost immediately after application completely eliminates the symptoms of itching in the animal.
Before using the gel, the auricle is cleaned routinely, then its inner surface and ear canal are thoroughly wiped with a swab dipped in Amidel. After squeezing in the ear lumen of a cat or dog, 0.5-1.0 g of gel.
With appropriate treatment for otodectosis in cats, the prognosis is favorable in the vast majority of cases. After 2-3 weeks, depending on the stage of the disease and the complexity of the consequences, as a rule, it is possible to completely get rid of all the symptoms of the disease.
Otodectosis (ear tick)
Otodectosis is an infectious disease. The disease is caused by ticks Otodectes cynotis of the Psoroptidae family, is characterized by damage to the external auditory canal, eardrum and is accompanied by itching, the development of dermatitis, otitis media.
Pathogen
A skin-mite tick has a flat oval body, 0.6-0.7 mm in size. Proboscis is a gnawing type. The legs are short, the fourth pair is underdeveloped. In humid rooms, it can remain viable for up to 2 months, and quickly dies in the cold.
Development cycle
Ticks go through the full development cycle (egg, larva, protonymph, teleonymph, imago) on the animal in 10-14 days. They are permanent ectoparasites of carnivores.
Epizootological data
The source of invasion is sick animals. Healthy cats and dogs become infected by contact with the sick. Cases of transfer of the pathogen by rodents, insects, as well as maintenance personnel on shoes and clothes are possible.
The disease is recorded throughout the year, but more often in cool weather. Meat eaters are seriously ill from 1.5 to 4 months of age. Puppies and kittens become infected from female mothers. Dogs with long ears get sick more often. Most cats are tick carriers.
The disease among cats is highly contagious. Known cases of tick infection of fur animals and humans.
Pathogenesis
Ticks injure the skin of the inner surface of the auricle and cause itching. Combing the ears, sick animals pollute them, as a result of which purulent otitis media develops.
After inflammation of the eardrum and its perforation, the pathological process goes to the middle and inner ear, and eventually to the shell of the brain. Animals die as a result of purulent meningitis.
Clinical signs
The incubation period lasts 7-10 days. At the beginning of the disease, mild itching is observed. Over time, anxiety becomes more noticeable: animals rub their ears with their paws, shake their heads, run around a room or cage, squeak, bark.
Later complications develop. It is also possible inflammation of the membranes of the brain, which is manifested by convulsions, paralysis and ends with the death of the animal.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease otodectosis begins with the primary clinical signs described above (the animal is itchy, shakes its head, etc.), the next stage is prescribed otoscopy (examination of the outer and middle ear using a special device - an otoscope).
This will make it possible to assess the condition of the auricle, ear canal, eardrum, etc. But the most important thing is to see the presence of crusts characteristic of the activity of the ear tick. Then the ear is cleaned, and a sample of the contents is transferred to the laboratory for examination.
In the veterinary clinic, these crusts are transferred for examination to the veterinary laboratory (to make a scraping), where using microscopy they can determine the presence or absence of a parasite (ear tick) in the subject of the study.
Treatment
Classical textbooks recommend the use of Bars aerosol, Otovedin, Anandin-plus drops, and a medical-feed mixture based on brovermectin-granulate is also recommended. However, the active substances have toxic properties, so we do not recommend treating otodectosis on our own.
In addition, now there are more modern and effective treatment regimens for ear Otodectosis, which should be prescribed by a veterinarian, taking into account all the features of your pet. Therefore, a visit to a veterinary clinic is the best and most reliable way to cure otodectosis.
The veterinarian should examine the animal for clinical signs, make an abdominal scrape, prescribe a laboratory test to confirm the diagnosis, and prescribe treatment taking into account each specific situation and the condition of the animal as a whole.
In most cases, medications aimed at maintaining internal organs are additionally prescribed.
Treatment of otodectosis in cats
Otodectosis is quite difficult to recognize, it’s even more impossible, so do not postpone a visit to the doctor!
Otodectosis, or ear scabies is a contagious disease of the carnivores. Not only cats are affected, but also dogs and foxes. Its causative agent is a parasite - an ear tick (Latin name Otodectes cynotis).
As a rule, ticks are localized on the skin of the auricle, in the external auditory canal and on the eardrum. A cat can become infected with otodectosis by contact with other animals that are mite carriers, including when kept together, through hygiene items and grooming accessories.
Symptoms
If you notice that the skin in the auricle reddened, began to peel off, the animal scratches the affected ear all the time, shakes its head and is anxious, then these manifestations indicate the onset of the disease.
Subsequently, the skin at the site of localization of the tick becomes inflamed, excreta of serous exudate appear, which subsequently become purulent. Purulent discharge fills the auditory canal, is very plentiful and has an unpleasant smell of rot.
If otodectosis is not treated, then a bacterial infection may be added to the underlying disease, then there is a danger of death. In addition, advanced otodectosis can turn into a chronic disease.
In order to notice the development of signs of the disease in time, you must regularly examine the cat’s auricle, check for excess earwax in the ear canal area, and if there are any crusts or foci of inflammation on the skin. It is also necessary to periodically clean the ears from discharge.
If squeezing is heard when pressing at the base of the auricle, this is an alarming sign. It is also required to monitor the general condition of the cat.If it is depressed, the temperature is elevated, if you noticed that the cat keeps his head on his side all the time, then the situation requires the intervention of a veterinarian.
Self-medication is deadly for a pet. The diagnosis of otodectosis is made on the basis of the clinical picture and the results of a microscopic examination of scraping of the inner skin of the auricle.
Treatment
Medicines effective in the treatment of otodectosis exist in various forms. These are usually ear drops, for example, amitraz, amit, acromectin, amitrazine, tactics.
Also used in the form of ointments, aerosols, powders. In cases where the disease is particularly difficult to treat, intramuscular injections of antiparasitic drugs, such as, for example, otodectin, may be required.
Before starting treatment, it is required to clean the inner surface of the auricle from pus and crusts. To do this, you can use cotton swabs dipped in camphor alcohol, you can also use hydrogen peroxide (2% solution).
Then, in both ears, the drug is instilled in an amount in accordance with the instructions. For the most effective distribution of the drug, it is recommended to massage the auricle slightly. Processing is carried out with a frequency of once every 7-10 days.
The progress of treatment is preferably periodically monitored by laboratory examination of scrapings from the skin of the inner surface of the auricle. When mites are no longer detected by microscopic examination, treatment can be discontinued.
It is also necessary to treat the entire skin surface of the animal with insecticaricidal agents. In addition to the main processing of the auricles, the Otonazole preparation can be instilled into a cat’s ears. It relieves inflammation and helps relieve itching.
You can use ointments containing sulfur, for example, sulfur ointment, Vishnevsky ointment, colloidal sulfur. In the event of a complication of the underlying disease with a secondary bacterial infection, the attending physician may prescribe the use of antibiotics.
For the treatment of otodectosis, it is very important to pay attention to maintaining immunity. Therefore, the nutrition of the cat must have a high content of proteins and vitamins. It positively affects the course of treatment and the ability to be in the fresh air.
Prevention of otodectosis
Proper care of the pet will prevent infection with ear scabies. It is important to avoid contact with sick animals, pay attention to the cleanliness of cat grooming items, wash periodically and, if possible, disinfect bowls, trays, bedding, and carrying.
Re-infection of the recovered cat will prevent regular cleaning of the premises using an insecticide and acaricide. This will get rid of ticks. that could get on the floor and furniture.
leave a comment