Hello! Some of my friends living in the capital, always get in trouble when traveling out of town.
Either the car breaks down halfway, the mosquitoes bite, or the snakes they come across everywhere. And the previous trip ended for them even more “fun”.
Two family members were bitten by ticks. They did everything right and avoided the unpleasant consequences of such a meeting. Now I want to tell you, friends, something: where to go if you have bitten a tick. Of course, let them not bite you better at all, but everyone should know the order of actions.
The content of the article:
What to do and where to go if a tick has bitten
If the tick suction does occur, an initial consultation can always be obtained by calling 103.
It should be borne in mind that the likelihood of contracting tick-borne encephalitis, tick-borne borreliosis and other tick-borne infections depends on the amount of virus that penetrates the tick’s “bite” (that is, the time that the tick was in a sucked state) - the earlier you remove the gnawing the parasite is better.
It is convenient to remove ticks with curved tweezers or a surgical clamp, in principle, any other tweezers will do. In this case, the tick needs to be captured as close to the proboscis as possible, then it is gently pulled, while rotating around its axis in a convenient direction. Usually after 1-3 turns, the tick is removed as a whole with the proboscis. If you try to pull out the tick, then the probability of its rupture is high.
There are special devices for removing ticks. These devices have an advantage over clamps or tweezers, since the body of the tick does not squeeze, squeezing the contents of the tick into the wound is excluded, this reduces the risk of infection with tick-borne infections.
If at hand there are no tweezers or special devices for removing ticks, then the tick can be removed with a thread. A strong thread is tied into a knot, as close as possible to the proboscis of the tick, then the tick is removed by pulling it up. Sudden movements are unacceptable.
Removing a tick must be done with caution, without squeezing its body, since it is possible to squeeze the contents of the tick along with pathogens into the wound.
It is important not to break the tick when removed - the part remaining in the skin can cause inflammation and suppuration. It should be borne in mind that with the separation of the tick head, the infection process can continue, since there is a significant concentration of tick-borne encephalitis virus in the salivary glands and ducts.
There are no grounds for some far-fetched advice that for better removal, ointment dressings should be applied to the sucking tick or oil solutions should be used.
The oil can clog the respiratory holes of the tick and the tick will die, remaining in the skin. After removing the tick, the skin in the place of its suction is treated with tincture of iodine or alcohol. Bandages are generally not required.
What threatens a tick bite?
Even if the tick bite was short-term, the risk of contracting tick-borne infections is not excluded.
A tick can be a source of a fairly large number of diseases, therefore, removing a tick, save it for testing for tick-borne infections (tick-borne encephalitis, tick-borne borreliosis, if other infections are possible), usually this can be done in the infectious diseases hospital, on our website for a number of cities have lab addresses.
The tick should be placed in a small glass bottle with a piece of cotton wool slightly moistened with water. Be sure to close the bottle with a tight lid and store it in the refrigerator.
For microscopic diagnosis, the tick must be delivered to the laboratory alive. Even individual fragments of the tick are suitable for PCR diagnostics. However, the latter method is not widespread even in large cities.
However, one must understand that the presence of an infection in a tick does not mean that a person will become ill. A tick analysis is needed for calm in case of a negative result and vigilance in the case of a positive.
Two weeks after a tick bite on antibodies (IgM) to tick-borne encephalitis virus. For antibodies (IgM) to Borrelia (tick-borne borreliosis) - after three weeks.
Tick-borne encephalitis is the most dangerous of tick-borne infections (consequences - even death). Emergency prevention of tick-borne encephalitis should be carried out as early as possible, better on the first day.
Emergency prophylaxis of tick-borne encephalitis is carried out using antiviral drugs or immunoglobulin.
Antiviral drugs
In the Russian Federation it is:
- Iodantipyrine for adults and children over 14 years of age.
- Anaferon for children under 14 years old.
If you could not find the indicated drugs, theoretically they can be replaced by other antiviral agents (cycloferon, arbidol, remantadine ...).
Immunoglobulin - appropriate only for the first three days. In European countries, the release is discontinued. The disadvantages include high cost, frequent allergic reactions.
Tick-borne borreliosis - is in second place in terms of danger and the most common disease transmitted by ticks in the Russian Federation. Emergency prophylaxis of tick-borne borreliosis, as a rule, is not carried out if it is possible to donate blood for antibodies to tick-borne borreliosis (IgM).
An analysis is best done 3 weeks after a tick bite. If the result is positive, you need to contact the infectious disease specialist.
Congo-Crimean hemorrhagic fever - in the Russian Federation, the disease occurs in the southern regions. For emergency prevention, you can use antiviral drugs (iodantipyrine, cycloferon, arbidol, remantadine, anaferon children).
Step-by-step instruction
Perhaps someone from the “experienced”, having read the headline, will say: “Why bother with something ?! He pulled out a tick, rubbed the bite area with alcohol - and that’s all. ” I did it myself. True, she didn’t pull out the bloodsucker herself - she asked the nurse-neighbor. But this does not change the essence.
Once upon a time there was an ordinary family - quite young people, our peers. They worked, and on weekends, like many, went to the cottage. And on one of these trips a woman was bitten by a tick. Well, they pulled him out, processed the place of the bite, and did not turn anywhere.
And a few days later she felt unwell, then the temperature rose, she felt worse. They called an ambulance ... But the doctor just shrugged his hands: it was too late to do anything ... The finale at the usual trip to the country house turned out to be tragic ...
In general, everyone makes their choice - to risk their lives or be safe again. Personally, this story at once discouraged frivolity, but because today I will talk about how it is still worth acting with a tick bite if you want to live long and, preferably, in good health.
Step 1: we go to the nearest medical institution
Remember: you only have 72 hours to prevent potential problems. Subtract from them the day, which, most likely, will be lost in a laboratory study of the tick, and you will understand that this is not much.
In principle, if there is an extra 5-6 thousand rubles for the purchase of immunoglobulin (1 ampoule per 10 kg of weight with an average price of 700-800 rubles per ampoule), then you can take your time: buy medicine, make an injection within the same 72 hours after the bite and count on a successful outcome. If not ...
Why do not I advise you to start by extracting a tick? If you do not have the skill, it is not a fact that you will do it right. You can accidentally crush an insect - and in a dead form it is no longer suitable for research, and you will have to return to the option of buying immunoglobulin.
You can pull it out unsuccessfully, leaving your head in the wound, and the remains of such a dissected bloodsucker will not be easy to extract even to a doctor.
In the end, often for a bite, a tick selects very uncomfortable places, from where it can not be pulled out by itself. In short, if you are not a pro or do not have good practice of independently getting rid of a tick, it is better not to experiment.
Where to go? Insured - to those medical facilities that are indicated in the appendix to the contract (for more details, see article 7 of the important nuances of tick bite insurance).
If you find a tick at inopportune time, go to the ambulance station or to the emergency room of the nearest hospital (for example, I drove my daughter to an ambulance, because the first time I discovered a sucking tick we found in the late evening, and the second in the early morning )
In the afternoon - to the clinic at the place of residence. Although, in fact, upon presentation of a medical policy you should be assisted in any medical institution. And by the way, without waiting in line.
Step 2: send the extracted tick to the laboratory
If you do not have mite bite insurance, research will be paid. Let me remind you: the average cost of analysis for one virus (in our region, as of the date of writing of the article) is 250-350 rubles, for 4 - about 800 rubles. Insurance worth 150-300 rubles allows you to get this service (to the extent provided for by the contract) for free.
But even if you did not have time to insure yourself, you should not save on research.In any case, be sure to check for tick-borne encephalitis, for borreliosis (Lyme disease) - highly desirable. I think, after all that has already been said, the questions “why?” And “why?” Do not arise ...
The result of the study can be obtained on hand, as a rule, the next day (sometimes on the same day, if you brought the tick in the morning, and the laboratory's capabilities allow you to perform the analysis quickly). If the result is negative, you can breathe a sigh of relief. If positive, go to the next step.
Step 3: carry out preventive vaccination
There are 2 different approaches to this issue (I happened to encounter in practice). Some medical workers (in any case, when it comes to children) consider it necessary to make a preventive injection of immunoglobulin, regardless of the results of laboratory tests, and the sooner the better.
This position is also supported by insurance companies (in a tick bite insurance contract, as a rule, it is written that an injection is given to the insured with a positive result of a laboratory test or if it is impossible to conduct such a test).
There is no disagreement only in the deadline: no later than within 72 hours from the time of the bite. But keep in mind: sometimes the “reference point” can be set very roughly - you don’t know how much time has passed from the moment of the actual bite until you find the sucked bloodsucker. Therefore, never pull to the last.
After a tick bite, it is recommended to monitor the well-being of the victim for 2-3 weeks and, if any ailments occur, consult a doctor as soon as possible. Especially if laboratory tests showed a positive result.
It is about health, and possibly life, so do not be afraid to play it safe. In such cases, precaution does not happen.
Well, and so that you never need all these tips when going for walks in nature, do not lose vigilance - observe safety measures that will not allow the tick to get to you and bite.
Real stories of victims
Hope: I want to share my experience after sucking a vile tick that found me right in the yard of my own house in Khabarovsk !!! First, panic, fear, then comes the mind and the question arises what to do? I took off the tick myself, he just started to stick in my side. So, Saturday, evening and my actions.
- Put in a glass jar.
- On Sunday, he was taken for analysis at Khabarovsk, st. Shevchenko, 2. tel.: 46-18-59, 8-914-203-81-49. In the wax. taken from 8-13. The result was reported on Monday after 8 p.m. In my case, it turned out to be positive, i.e. encephalitis antigen was found in the tick!
- In the same minutes I went urgently to look for an anti-tick-borne immunoglobulin medicine. You can buy it around the clock in a pharmacy on Komsomolskaya Square tel .: 32-64-84. The cost of 690 rubles. for 1 ampoule. The calculation is 1 ampoule per 10 kg of human weight. Or until 21-00 a pharmacy on the street. Batuevskaya branch tel .: 31-10-09. The cost of 610 p. for 1 ampoule. In my case, 3050 rubles were spent.
- Further in the emergency room (round-the-clock) put an injection, at 106 Volochaevskaya, tel .: 22-31-18. By the way, you can without honey. policy. True, there may be a turn of an hour for 1.5-2! Put it for free!
- A week after the bite, she necessarily donated blood to the street. Shevchenko, 2. Cost 280r. Five days later, the result will be reported from 14 to 15.
- In my case, everything worked out and the encephalitis virus was not detected !!! Thank God!
- Insured by a tick bite. The cost of insurance is from 200r. up to 270 p. for 1 year. It covers all expenses associated with this business.
- I will wait for an annual vaccination against a tick bite.
Thanks.I hope my information will be useful to at least one person in the whole world))).
Alexander, Minsk: last year, I “noticed” a tick, thought and thought, but still went to the clinic (though I apologized to the doctors), I was afraid that I was worrying in vain. It turns out not in vain and did the right thing.
Galina, Kirov region Tick-borne encephalitis is a very serious disease. My husband, after being bitten by a tick (he pulled it out himself in the field and burned it at the stake), went to the clinic, as he was vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis, he was prescribed a drug against Lyme disease.
He drank it, as the doctor prescribed, donated blood for analysis, found tick-borne encephalitis, was treated in the hospital, there are no consequences, the attending physician said that vaccination helped, transferred in a mild form, was lucky. By the way, vaccination provides protection by 95%. He was insured, all expenses were reimbursed by the insurance company.
His brother was less fortunate, in May this year he went to his homeland, pulled out a tick, but since there were May holidays - while he arrived home, he could not immediately find an institution that administers immunoglabulin by insurance, he was hospitalized with a clinical picture I do not wish to experience what he experienced and what his relatives experienced.
Tatyana Zvaroya, Tyumen region and Khanty-Mansiysk I believe that it is not necessary to leave a tick in the body - the vaccine works only for encephalitis, and not for Lyme disease, and the longer the tick sits in the body, the more saliva it injects into the wound, the more serious the disease.
A station employee said that dead ticks are also taken for analysis. About 15 years ago I was bitten by such a bastard, I poured oil on it, but it dug too deeply and could not get out, but it died. For disinfection I put a bottle of penicillin with alcohol to him and went for a vaccination.
She, by the way, was done for free, but the nurse incorrectly tied the parasite and tore its head off. Do you know what she told me? It will fall away! And I went for another week with a tick head in my thigh - brrr. Now, by the way, I suffer from joint diseases (one of the manifestations of borreliosis), I’m thinking of taking an antibody test.
The faster you take it out of the body, the less consequences. A tick after all can be pure and encephalitic and encephalitic-borreliosis or only borreliosis and so on, it’s roulette ...
If a tick bit, it does not mean that you will get sick
Tick activity begins in April and continues through October. The maximum number of ticks is observed in the first half of summer.
A tick cannot jump. He waits for his victim, spreading his legs in different directions, sitting on a blade of grass or on a low bush not higher than 1 meter. So the tick can sit for days - until the victim passes by. Ticks are attracted by the smell of animals and people.
Most often, the tick attacks when a person sits on a grassy lawn to relax - "it is not necessary to guard the passing one - you can crawl". The best weather for the tick is dry, sunny, warm. On cold days, with frost or rain, the tick is passive, it hides in the forest litter and expects the weather.
If a tick is bitten, this does not mean that you will get sick. But you must immediately consult a doctor for a diagnosis and preventive treatment.
A person gets sick from ticks, which themselves are infected with encephalitis or borreliosis. After a tick bite must be removed. Removal of the tick should be carried out in a surgical room or in a trauma center of a medical institution.
If you delete it yourself, you should know: the tick cannot be crushed, since it is possible for the contents of the tick to get together with pathogens through micro cracks in the hands. In no case do not pull it, as you can tear the body from the head.
The part remaining in the skin can cause inflammation and suppuration. There are several ways to remove ticks. They differ only in the tool with which the tick is removed.
It is most convenient to remove the tick with curved tweezers or a surgical clamp, in principle, any other tweezers will do. In this case, the tick needs to be captured as close to the proboscis as possible, then it is gently pulled, while rotating around its axis in a convenient direction.
Usually after 1-3 turns, the tick is removed as a whole with the proboscis. If you try to pull out the tick, then the probability of its rupture is high. On sale there are special hooks for removing ticks. Such a hook looks like a curved double-toothed fork. The tick is inserted between the teeth and is also twisted.
You do not need to press the tick with your hands. After removing the tick, be sure to wash your hands. The wound must be treated at home with an antiseptic.
Removing a tick must be done with caution, without squeezing its body, since it is possible to squeeze the contents of the tick along with pathogens into the wound. It is important not to break the tick when removed - the part remaining in the skin can cause inflammation and suppuration.
It should be borne in mind that with the separation of the tick head, the infection process can continue, since there is a significant concentration of tick-borne encephalitis virus in the salivary glands and ducts.
There are no grounds for some far-fetched advice that for better removal, ointment dressings should be applied to the sucking tick or oil solutions should be used.
The oil may clog the respiratory holes of the tick, and the tick will die, remaining in the skin. Dripping oil on the tick with oil, kerosene, cauterizing the tick is pointless and dangerous. The respiratory organs of the tick become clogged, and the tick burps the contents, which will increase the risk of infection.
After removing the tick, the skin at the point of its suction is treated with tincture of iodine or alcohol, or another available antiseptic for the skin. Bandages are generally not required.
Subsequently, the wound is treated with iodine before healing. You don’t need to pour a lot of iodine, since you can burn the skin. If everything is normal, then the wound heals in a week. After removing the tick, wash your hands thoroughly.
If possible, check the health of the tick
Ticks can be the source of a fairly wide range of diseases. A removed tick can be destroyed, but it is better to leave it for a laboratory test for tick-borne infections.
Unfortunately, by the appearance of the tick it is impossible to judge whether it is encephalitis or not. The tick becomes infected by feeding on an infected animal.
The tick should be placed in a small glass jar along with a piece of cotton wool or cloth slightly moistened with water. Be sure to close the jar with a tight lid and store in the refrigerator (up to several days) if it is not possible to immediately deliver it to the laboratory. For microscopic diagnosis, the tick must be delivered to the laboratory alive.
It is advisable that a person affected by a tick bite be observed by an infectious disease specialist for a month, who, if necessary, will prescribe the necessary preventive or treatment measures.
After the tick is removed, you must:
- take pills according to the schedule prescribed by your doctor (if you have been prescribed). If during the examination of the tick the causative agents of infection were not found, prevention still continues according to the prescribed scheme.
- monitor your health and temperature.
- watch the bite site.
If redness occurs at the site of the bite, with an increase in temperature, the appearance of a headache, dizziness, vomiting, pain in the muscles of the trunk and extremities, it is necessary to consult an infectious disease doctor.
Redness can be both a symptom of a borreliosis and an allergic reaction to a bite - a slight redness around the wound in the first days after a tick bite is usually a reaction to a bite and goes away without consequences. If dirt got into the wound, then redness may be a consequence of the development of a purulent infection.
In most patients, symptoms appear in the second week after a bite, but may appear sooner or later (up to 21 days of tick-borne encephalitis, up to a month of borreliosis). If 21 days have passed since the bite, then tick-borne encephalitis will not develop. In tick-borne borreliosis, the incubation period can be up to a month.
Prevention
The best way to prevent tick-borne infections is protection from tick bites. Tick protection:
- Repellents.
- Vaccination.
- Tick control in garden areas.
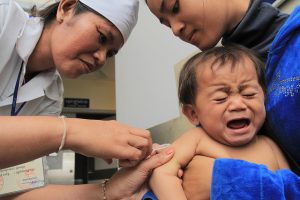
The child was bitten by a tick: what to do and where to go
Every day the street is getting warmer. In just a few days, the bare branches of the trees are covered with greenery, the first flowers bloom. Everything is drawn to the invigorating sunlight. People tend to spend more time outdoors, enjoying the precious moments of a fleeting summer.
According to Rospotrebnadzor, by May 2017, after a tick bite, about 700 people had already applied to medical institutions in Moscow. Part of the victims are children. What to do if a child is bitten by a tick? How is first aid provided, where and to whom to turn next?
What to do
A tick bite is always unexpected, unpleasant and scary, especially for children. Therefore, first try not to panic, not to fall into hysteria and calm the child. If you feel the moral strength in yourself to pull the tick yourself, then this can be done using ordinary tweezers, thread or special devices sold in pharmacies, supermarkets and online.
Otherwise, contact the nearest clinic, hospital or medical post as soon as possible, where doctors will quickly and painlessly remove the uninvited guest.
If the parasite transmitted one of the diseases to the child, then a blood test can reflect this only after 2-4 weeks. Precious time will be lost. Having passed a live tick for analysis immediately after a bite, after 1-2 days you can find out whether it was a carrier of any disease and take emergency measures.
This is especially important in the case of young children whose immature immunity is more vulnerable than that of adults. If the child is bitten by a tick, what to do for the full recovery of the baby should be decided by the attending physician based on the tests received.
Tick bit a child in the head. Contrary to popular theory, ticks do not dive at people from tree branches. They live in the grass, clinging to the clothes of people passing by, and then rise higher in search of a suitable place for a bite.
In the case of children, things are somewhat different. Led by curiosity, a child can climb bushes and wallow in the grass, completely not thinking about the consequences, while the small growth of the baby makes him an ideal victim for a pest.
If a tick has bitten a child in the head, it can be pulled out in the same way as from any other part of the body. In no case should you drip on the sucking pest with gasoline or sunflower oil according to the old grandfather's recipe. This can only aggravate the situation.
After removing the tick, making sure that the wound is clean, it is disinfected, sealed with a band-aid, and after a few hours it is lubricated with a bactericidal ointment. Even if the child does not have any alarming symptoms immediately after the bite, it is necessary to consult a pediatrician and it is very advisable to submit a live tick to the laboratory for analysis within two days.
Where to go
Any information regarding tick bites is available around the clock by emergency numbers: 103 for landlines and mobile phones and 030 for cellular networks of leading Moscow operators.
If the balance is negative, the SIM card is not active or missing, you can call the single European emergency number 112. So you can find out the address of the nearest medical center, consult first aid to the victim and find out where the nearest laboratory for receiving ticks for analysis is located.
If a child is bitten by a tick, where to go depends on your location at the moment. However, infectious disease experts recommend not postponing a trip to the doctor and go to the reception no later than 2-3 days after the bite.
By phone you can coordinate for further independent actions. The same information can be found on the Internet for requests “where to go for a child by a tick bit” or “tick-borne infection prevention centers”.
Not all ticks are carriers of dangerous diseases. If the infection was not detected, then the child is prescribed prophylactic treatment with the help of immunity-strengthening drugs. Children from 3 years old can be given preventive vaccinations against tick-borne encephalitis.
Even with a favorable outcome, the procedure for extracting a tick, going to the doctor and waiting for the results of the tests will have to spend a lot of effort, time and nerves. Now there are many ways that successfully prevent the appearance of ticks and minimize the risk of a bite.
The most popular are acaricidal, insecticidal and repellent products applied to clothing, and the disinsection of summer cottages and houses. By taking care of the problem in advance, you can avoid it in the future.
The first rule for a tick bite
If possible, seek medical attention immediately. In any medical center you will receive first aid, and a specialist will easily remove the tick from the skin.
If the nearest medical institution is far, then here are a couple of tools that can easily help get rid of the parasite.
Removal at home
When removing a tick, it is important not to squeeze the body, so as not to squeeze out the contents, and with it the infection pathogens into the wound.
After removing the tick, grease the place of suction with a solution of iodine, alcohol or cologne. If the proboscis remains in the wound, remove it with a sterile needle. Wash your hands with soap.
It is also necessary to remember that it is very difficult to distinguish an infected tick from a normal one in appearance. Therefore, it is advisable to deliver it to a specialized laboratory.
Some facts about the parasite
If the tick was on the skin (fed) for less than 24 hours - antibiotic prophylaxis is not needed. It has been proven that if an infected tick has been fed for less than 24 hours, the likelihood of developing Lyme borreliosis is zero.
If after a tick bite you feel unwell after some time, be sure to consult a doctor.
If the tick was on the skin (fed) from 24 to 72 hours - the question of the need for antibiotic prophylaxis is decided on an individual basis, for example, if the tick is analyzed and it is infected, then the need for antibiotic prophylaxis should be considered.
The time before antibiotic administration should be no more than 72 hours after tick removal. If more than 72 hours have passed, antibiotic prophylaxis is not indicated, because there is no evidence of its effectiveness.
Prevention
Before you go to the forest or other places where a tick can wait for you, do not be lazy to take some preventive measures.
- Choose clothes that completely cover the legs, elbows, abdomen, and other areas where the tick can easily reach.
- Do not forget about headgear so that the hair is covered, because the tick can crawl through the hair, and then go down to an open area of the skin.
- Before going to the forest, get anti-mite products: sprays or ointments. Pharmacies provide a wide selection of such drugs.
- In the forest, you should examine yourself every time you walk along the tall, dry grass - ticks most often set their ambush on last year's plants in shady places along forest paths.
- Arriving home, be sure to inspect yourself and your clothes. Take a shower at home, if there is a tick that has not yet sucked on the body, it will be safely washed off into the sewer.
Where to go in Moscow
Many people wonder what to do after a tick bite. Is vaccination required and can the parasite be pulled out of the wound on its own?
It should be noted right away that almost any amateur activity with tick bites is unacceptable, since it is fraught with serious problems. For example, a parasite extracted on its own can be damaged, and its body fragment (usually the head) can remain in the wound.
Often this situation ends in infection with a bitten encephalitis, borreliosis, or any other tick-borne disease. Therefore, it is important to remember that only a doctor or someone from the nursing staff (paramedic, nurse) should get the insect out of the wound.
If you managed to take out the parasite yourself, or it fell away yourself, then you should not throw it away. A tick removed from the skin should be placed in any container (a box of matches, a pack of cigarettes, a can, and so on) and delivered to a specialist for examination. In this case, a bitten person should also undergo blood tests and come for a doctor's examination of the bite site.
A tick test and a blood test of a bitten person are mandatory procedures that allow you to immediately determine whether the parasite was infected with encephalitis or other fatal infections, and if the infection was not transmitted to the patient.
If these instructions are ignored, serious complications can develop up to death (hundreds of people die from encephalitis every year, usually due to the absence or late visit to a doctor).
Where to go to get the parasite out?
If everything is intuitive with the analysis of a tick and blood of a bitten one, it is obviously necessary to take them in the laboratory, then the situation is completely different with the removal of the parasite. Many people wonder: where can I get a tick in Moscow?
In addition, even if the hospital is for adults, a child can be served there. However, children can only get primary care (removal of the parasite), while in order to administer immunoglobulin or perform tests, you need to contact a specialized children's clinic.
The addresses of private clinics where you can remove the tick (Moscow) are as follows:
- Medical center "MultiMed": Volokolamskaya metro station, Pyatnitskoye highway, 15. Phone: +7 (495) 114-63-88.
- Medical center "CELT": Perovo metro, Entuziastov highway, 62. Phone: +7 (499) 705-97-91.
- Medical center "Clinics of the Capital": Kantemirovskaya metro station, Kantemirovskaya street, 5k4. Phone: +7 (495) 111-82-96.
- Clinic "MonEstetik": metro Novogireevo, street Molostovyh, house 7a. Phones: +7 (499) 647-80-80 and +7 (495) 782-84-99.
- Health and Family Protection Center: metro Sevastopolskaya, Azovskaya street, 24k3. Phone: +7 (495) 111-82-41.
- Clinic "MedCenterService": metro Airport, Chernyakhovskogo street, 8. Phone: +7 (495) 114-60-74.
Where to take the tick for analysis?
As mentioned earlier, taking a tick for analysis is not just recommended, but necessary. If you find out in advance that the parasite was infected with deadly infections, you can prepare a bitten one in advance and put it under observation in a hospital.
After a tick bite, you need to go to a hospital or diagnostic laboratory for analysis. But where, in this case, to take the tick for analysis in Moscow? The addresses of these clinics are as follows:
- Federal State Health Institution “Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the City of Moscow”: Grafsky Lane, 4/9 (the entrance to the institution is from the yard, second floor). Phone: 952-40-98. Reception from 9:00 to 15:30 (break from 13:00 to 13:30);
- Institute of Poliomyelitis and Viral Encephalitis: Moscow Region, Vnukovo, Moscow Village. Phone: 8 (498) 540-90-96;
- Filatov Children's Clinical Hospital No.13: Sadovaya-Kudrinskaya Street, 15. Landline Telephone: (499) 254-34-30;
- Infectious Diseases Clinical Hospital No. 2: Sokolina Gora Street, 15. Landline phones: 8 (495) 365-19-28, emergency number (495) 365-01-47;
- Branch of the Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in Moscow Federal State Health Institution: 17 Krasnogvardeisky Boulevard, the first microbiological laboratory. Landline phone: 8 (499) 256-24-40. Reception is open from 9:30 to 15:00 daily.
You can also take the parasite for examination to any trauma center, where they will give you exact addresses where you need to contact to conduct its research.
Where to get blood for analysis?
In addition to passing the tick for analysis, you need to carry out an analysis of your own blood, but with one caveat: it does not make sense to carry out it earlier than two weeks after the bite. The reason is that in the first days after a bite, it is impossible to detect the presence of infection in the body by laboratory methods.
Addresses of medical institutions where you can donate blood for analysis after a tick (Moscow):
- State Research Institute of GISK named after L. A. Tarasevich, Moscow address: 41 Sivtsev Vrazhek Lane. Fixed phones: 8 (495) 241-39-22, emergency numbers 241-99-78 and 241-31-77.
- State Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology named after N. F. Gamalei RAMS, Moscow address: 18. Gamalei street, Landline phone: 8 (499) 193-30-01.
- Medical Center for Immunoprophylaxis "MEDEP": 33 Kutuzovsky Prospekt. Phone: 8 (495) 147-90-03.
- AmericanClinic Medical Center: 31 Grokholsky Lane. Phone: 8 (495) 937-5757.
- The tick should be transported for analysis in a dry container (preferably sterile).
In these clinics, immunoprophylaxis (vaccination) against tick-borne encephalitis for children and adults is also carried out.
Blood for analysis after a tick bite can also be donated in any infectious diseases hospital and hospitals with a parasitology department.
The average cost of a blood test to detect antibodies of the IgG and IgM class is 430 rubles. The average duration of the study is 2 days, in case of emergency - about 3-5 hours.
The cost of examining a tick for additional diseases (borreliosis, anaplasmosis, ehrlichiosis) is on average 430 (the price of an analysis for encephalitis) + 700 rubles.
leave a comment